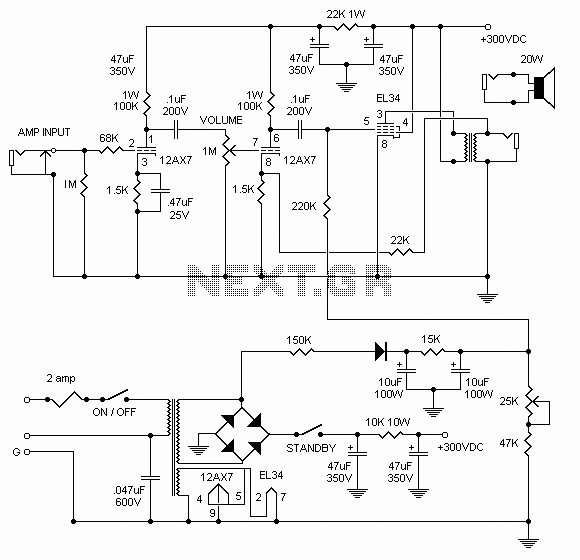
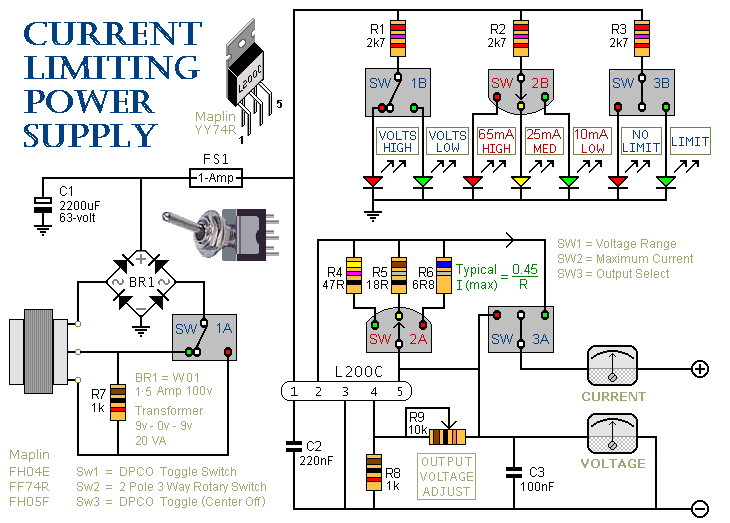
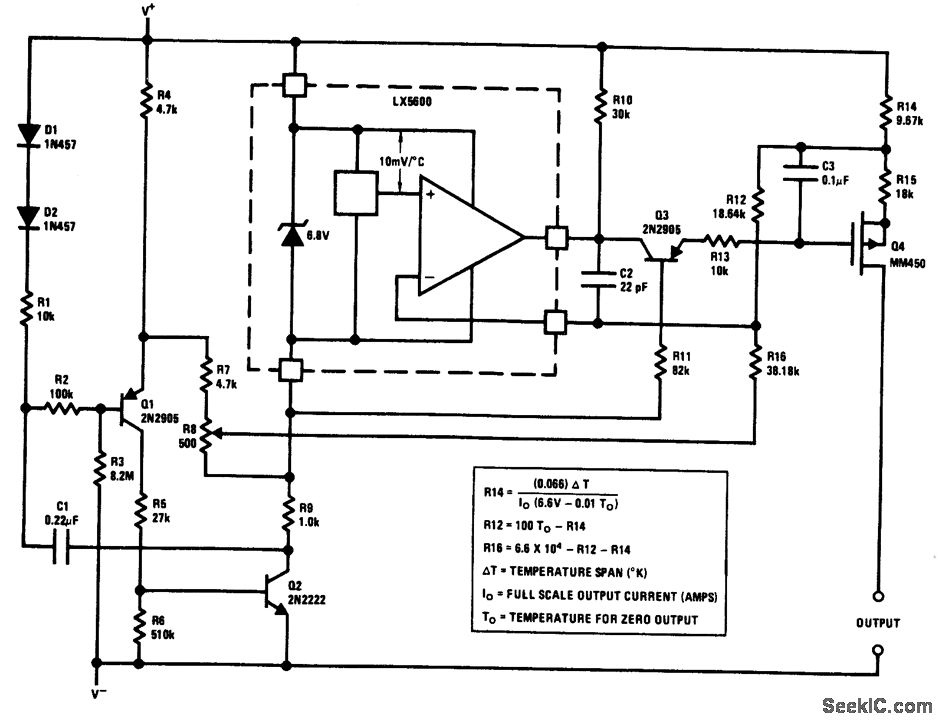
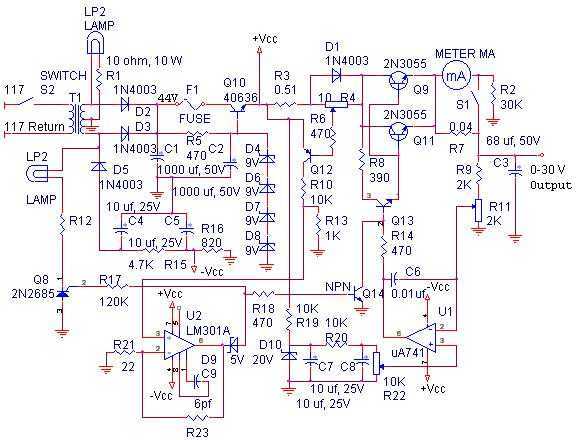
SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supply)
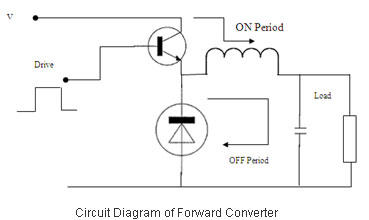
Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are categorized as DC to DC converters and DC to AC converters.
Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are essential components in modern electronic devices, providing efficient power conversion from one form to another. The primary function of an SMPS is to convert a direct current (DC) input voltage to a different DC output voltage or to convert DC to alternating current (AC).
The operation of an SMPS is based on the principle of switching regulation, where the input voltage is rapidly switched on and off at high frequencies. This switching action is typically performed by semiconductor devices such as transistors or MOSFETs. The high-frequency operation allows for the use of smaller magnetic components, resulting in a compact and lightweight design compared to traditional linear power supplies.
An SMPS typically consists of several key stages:
1. **Input Stage**: This stage includes filters and rectifiers that prepare the incoming voltage for conversion. It may also include components to protect against voltage spikes and noise.
2. **Switching Stage**: Here, the input voltage is switched on and off by the control circuitry, which regulates the output voltage. The frequency of switching can range from tens of kilohertz to several megahertz, depending on the design requirements.
3. **Transformer Stage**: In cases where isolation is needed, a transformer is used to step up or step down the voltage. The transformer also plays a critical role in energy transfer and provides electrical isolation between the input and output.
4. **Output Stage**: This stage includes rectification and filtering components that convert the high-frequency AC output from the transformer back into a stable DC voltage. This may involve diodes and capacitors to smooth out the output.
5. **Feedback Control**: A feedback mechanism is implemented to monitor the output voltage and adjust the switching duty cycle accordingly. This ensures that the output remains stable under varying load conditions.
SMPS are widely used in various applications, including computer power supplies, battery chargers, and LED drivers, due to their high efficiency, compact size, and versatility. They are particularly advantageous in portable devices where space and power efficiency are critical.What is SMPS? Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) belongs to the category of D.C. to D.C. converters and D.C. to A.C. Converters 🔗 External reference
Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) are essential components in modern electronic devices, providing efficient power conversion from one form to another. The primary function of an SMPS is to convert a direct current (DC) input voltage to a different DC output voltage or to convert DC to alternating current (AC).
The operation of an SMPS is based on the principle of switching regulation, where the input voltage is rapidly switched on and off at high frequencies. This switching action is typically performed by semiconductor devices such as transistors or MOSFETs. The high-frequency operation allows for the use of smaller magnetic components, resulting in a compact and lightweight design compared to traditional linear power supplies.
An SMPS typically consists of several key stages:
1. **Input Stage**: This stage includes filters and rectifiers that prepare the incoming voltage for conversion. It may also include components to protect against voltage spikes and noise.
2. **Switching Stage**: Here, the input voltage is switched on and off by the control circuitry, which regulates the output voltage. The frequency of switching can range from tens of kilohertz to several megahertz, depending on the design requirements.
3. **Transformer Stage**: In cases where isolation is needed, a transformer is used to step up or step down the voltage. The transformer also plays a critical role in energy transfer and provides electrical isolation between the input and output.
4. **Output Stage**: This stage includes rectification and filtering components that convert the high-frequency AC output from the transformer back into a stable DC voltage. This may involve diodes and capacitors to smooth out the output.
5. **Feedback Control**: A feedback mechanism is implemented to monitor the output voltage and adjust the switching duty cycle accordingly. This ensures that the output remains stable under varying load conditions.
SMPS are widely used in various applications, including computer power supplies, battery chargers, and LED drivers, due to their high efficiency, compact size, and versatility. They are particularly advantageous in portable devices where space and power efficiency are critical.What is SMPS? Switched Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) belongs to the category of D.C. to D.C. converters and D.C. to A.C. Converters 🔗 External reference