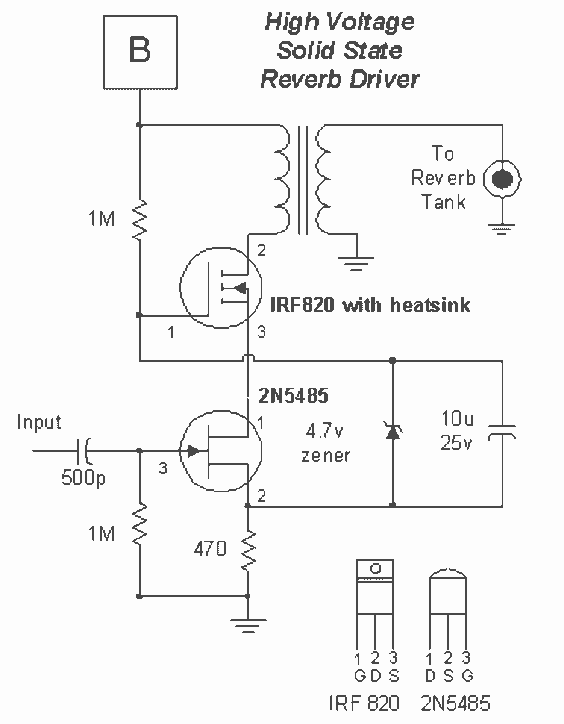
soft start circuit
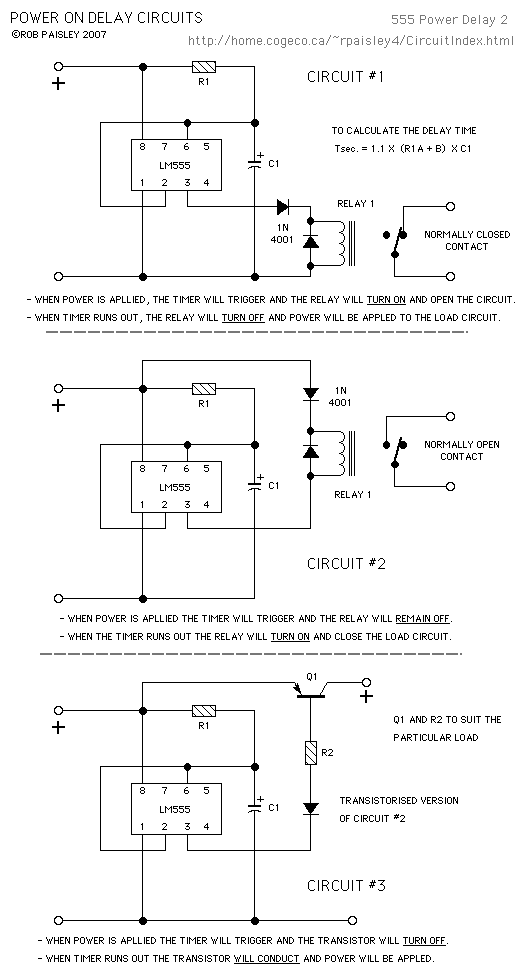
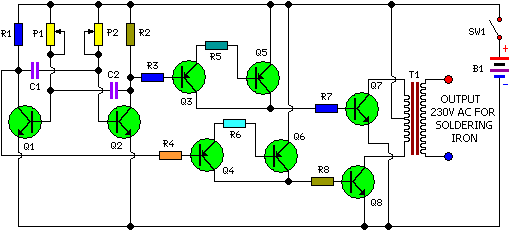
A simple soft start circuit is being developed that initially routes power through a resistor or thermistor before activating the main load.
The soft start circuit is designed to gradually increase the power supplied to a load, thereby minimizing inrush current and reducing stress on components. The circuit typically consists of a power source, a main load, a resistor or thermistor for initial current limiting, and a control mechanism, often implemented using a relay or a transistor.
In operation, when power is first applied, the current flows through the resistor or thermistor, which limits the current and allows for a gradual increase in voltage across the load. This component can be selected based on the desired time constant for the soft start process. As the temperature of the thermistor increases or as the voltage across the resistor rises, the resistance decreases, allowing more current to flow to the load.
The control mechanism is activated after a predetermined time or voltage level is reached. This can be achieved using a timer circuit or a microcontroller that monitors the voltage across the load. Once the soft start period is complete, a relay or a transistor is triggered to bypass the resistor or thermistor, allowing full power to be supplied to the load.
In summary, this soft start circuit effectively reduces inrush current and prolongs the life of the connected components, making it suitable for applications such as motors, power amplifiers, or any other devices sensitive to sudden power changes. Proper selection of the resistor or thermistor, as well as the control mechanism, is critical to achieving the desired performance and reliability of the circuit.Hi All, I have been trying to come up with a simple soft start circuit that routes power initially through a resistor or thermistor and then activates .. 🔗 External reference
The soft start circuit is designed to gradually increase the power supplied to a load, thereby minimizing inrush current and reducing stress on components. The circuit typically consists of a power source, a main load, a resistor or thermistor for initial current limiting, and a control mechanism, often implemented using a relay or a transistor.
In operation, when power is first applied, the current flows through the resistor or thermistor, which limits the current and allows for a gradual increase in voltage across the load. This component can be selected based on the desired time constant for the soft start process. As the temperature of the thermistor increases or as the voltage across the resistor rises, the resistance decreases, allowing more current to flow to the load.
The control mechanism is activated after a predetermined time or voltage level is reached. This can be achieved using a timer circuit or a microcontroller that monitors the voltage across the load. Once the soft start period is complete, a relay or a transistor is triggered to bypass the resistor or thermistor, allowing full power to be supplied to the load.
In summary, this soft start circuit effectively reduces inrush current and prolongs the life of the connected components, making it suitable for applications such as motors, power amplifiers, or any other devices sensitive to sudden power changes. Proper selection of the resistor or thermistor, as well as the control mechanism, is critical to achieving the desired performance and reliability of the circuit.Hi All, I have been trying to come up with a simple soft start circuit that routes power initially through a resistor or thermistor and then activates .. 🔗 External reference