Solar Panel to Battery Switch Circuit
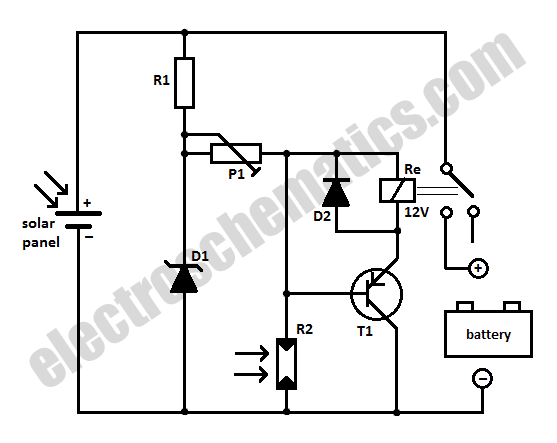
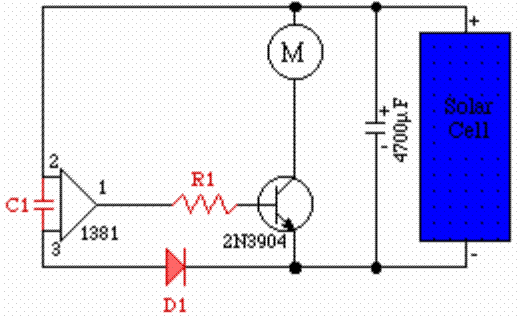
When charging a battery during the day using a solar panel, there is a risk of the battery partially discharging through the panel after sunset. This solar panel power switch circuit eliminates the need for a diode by utilizing a relay contact to connect the panel to the battery. The relay engages when the voltage is sufficiently high, and the light-dependent resistor (LDR) detects adequate light to activate transistor T1. Once activated, the relay will close, allowing the battery to charge. The relay remains engaged even when the solar panel voltage begins to decline. A charged battery cannot trigger the relay when light intensity diminishes, as resistor R2 will inhibit T1. The light level at which this occurs can be adjusted using potentiometer P1. Given that power consumption is mainly dictated by the relay, it is crucial to select a miniature relay with high coil resistance that can handle switching currents up to 10 Amps.
The described circuit operates as an efficient solar battery charger, utilizing a relay to manage the connection between the solar panel and the battery. The fundamental components include a solar panel, a relay, a light-dependent resistor (LDR), a transistor (T1), and resistors (R2 and P1).
During daylight, the solar panel generates sufficient voltage to engage the relay, which closes the circuit and allows current to flow from the solar panel to the battery, charging it. The LDR plays a critical role in detecting ambient light levels. When the light intensity is above a certain threshold, it allows T1 to conduct, thus energizing the relay coil and maintaining the relay in the 'ON' state. This design effectively prevents reverse current flow from the battery back into the solar panel during the night or in low-light conditions.
Resistor R2 is strategically placed to ensure that once the battery is charged, it cannot activate the relay when the light intensity falls below the set threshold. This feature is essential for preventing battery discharge through the solar panel during times when there is insufficient solar energy.
The adjustment of potentiometer P1 allows for fine-tuning of the light sensitivity of the circuit, enabling the user to set the precise brightness level at which the relay will disengage. This flexibility ensures optimal performance under varying environmental conditions.
The choice of a miniature relay with high coil resistance is vital for minimizing power consumption, as the relay itself is the primary load in this circuit. The relay must be capable of handling a load of up to 10 Amps, ensuring it can accommodate various battery charging scenarios without overheating or failing.
Overall, this solar panel power switch circuit presents a robust solution for efficient solar energy utilization, protecting the battery from unnecessary discharge while ensuring reliable charging during daylight hours.When loading a battery during the day from a solar panel it can be partially discharging through the panel after nightfall. This solar panel power switch circuit replaces the diode and connects the panel to battery through a relay contact.
When the voltage is high enough to engage the relay and the LDR receives enough light in order to open T1, the relay will switch and the battery will charge. The relay remains ON even when the solar panel voltage starts to decrease. A battery connected and charged can not action the relay when the light intensity decreases because R2 will block T1. The brightness at which this occurs is set by P1. Because the power consumption is determined primarily by the relay, it is important that the relay should be a miniature one, with high coil resistance but also be capable to switch up to 10 Amps.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as an efficient solar battery charger, utilizing a relay to manage the connection between the solar panel and the battery. The fundamental components include a solar panel, a relay, a light-dependent resistor (LDR), a transistor (T1), and resistors (R2 and P1).
During daylight, the solar panel generates sufficient voltage to engage the relay, which closes the circuit and allows current to flow from the solar panel to the battery, charging it. The LDR plays a critical role in detecting ambient light levels. When the light intensity is above a certain threshold, it allows T1 to conduct, thus energizing the relay coil and maintaining the relay in the 'ON' state. This design effectively prevents reverse current flow from the battery back into the solar panel during the night or in low-light conditions.
Resistor R2 is strategically placed to ensure that once the battery is charged, it cannot activate the relay when the light intensity falls below the set threshold. This feature is essential for preventing battery discharge through the solar panel during times when there is insufficient solar energy.
The adjustment of potentiometer P1 allows for fine-tuning of the light sensitivity of the circuit, enabling the user to set the precise brightness level at which the relay will disengage. This flexibility ensures optimal performance under varying environmental conditions.
The choice of a miniature relay with high coil resistance is vital for minimizing power consumption, as the relay itself is the primary load in this circuit. The relay must be capable of handling a load of up to 10 Amps, ensuring it can accommodate various battery charging scenarios without overheating or failing.
Overall, this solar panel power switch circuit presents a robust solution for efficient solar energy utilization, protecting the battery from unnecessary discharge while ensuring reliable charging during daylight hours.When loading a battery during the day from a solar panel it can be partially discharging through the panel after nightfall. This solar panel power switch circuit replaces the diode and connects the panel to battery through a relay contact.
When the voltage is high enough to engage the relay and the LDR receives enough light in order to open T1, the relay will switch and the battery will charge. The relay remains ON even when the solar panel voltage starts to decrease. A battery connected and charged can not action the relay when the light intensity decreases because R2 will block T1. The brightness at which this occurs is set by P1. Because the power consumption is determined primarily by the relay, it is important that the relay should be a miniature one, with high coil resistance but also be capable to switch up to 10 Amps.
🔗 External reference