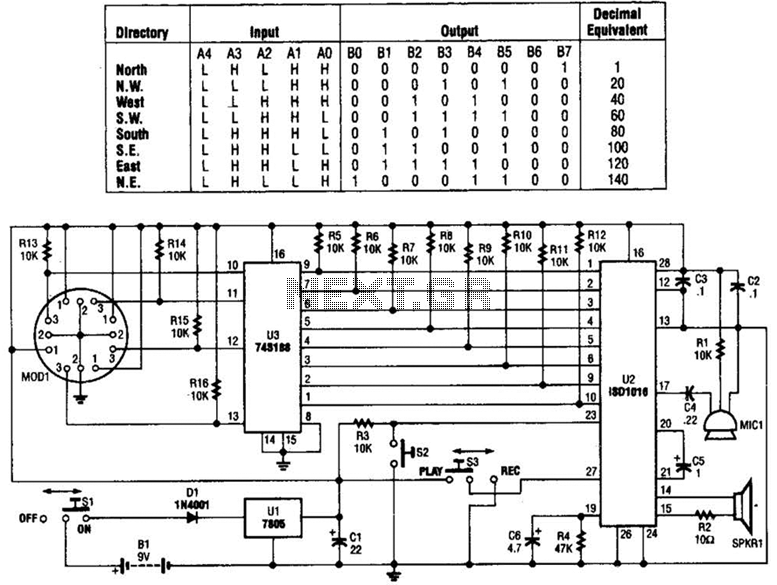
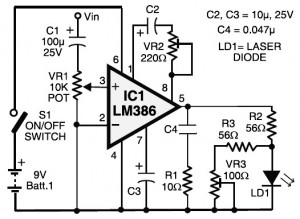
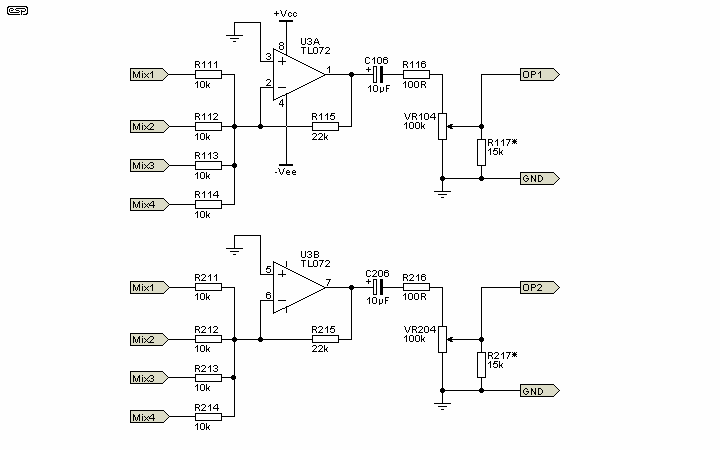
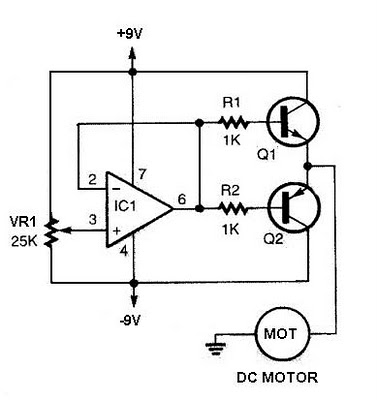
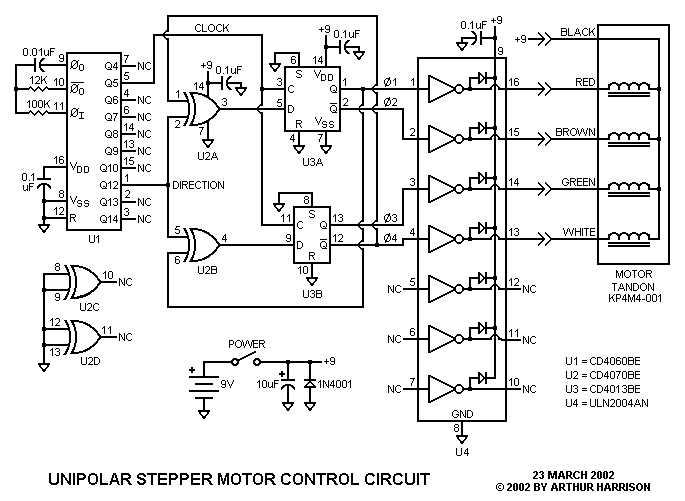
Solid laser range finder receive circuit diagram
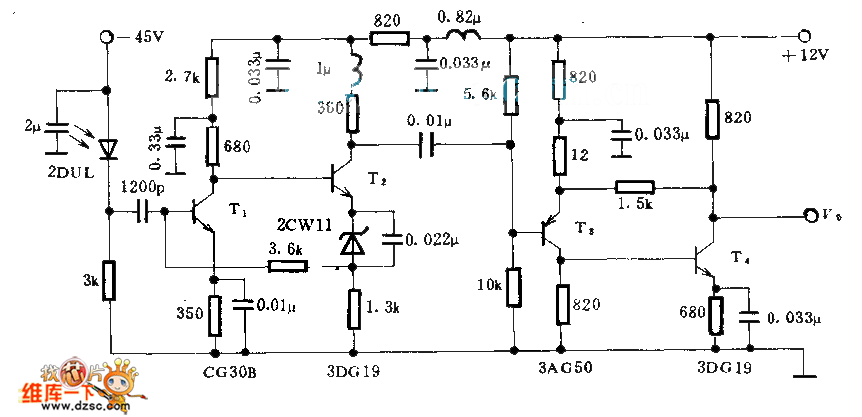
This circuitry provides a magnification of 1,200,000 times, with a bandwidth ranging from 0.5 to 14 MHz. The input impedance is 700 ohms, while the output impedance is 35 ohms when measured at 5 MHz. The output noise level ranges from 0.6 to 0.8 V. In the schematic, T1 and T2 function as directly coupled amplifiers, utilizing negative current feedback through parallel connections. The enhancement of T2's emitter leads to...
This circuit is designed to achieve high levels of magnification while maintaining a broad frequency response, making it suitable for applications requiring precise signal amplification. The input impedance of 700 ohms allows for effective interfacing with various signal sources, ensuring minimal signal loss during the amplification process. The output impedance of 35 ohms at 5 MHz is optimized for compatibility with standard measurement equipment, facilitating accurate signal analysis.
The use of transistors T1 and T2 as direct coupling amplifiers is crucial for maintaining signal integrity across the amplification stages. Direct coupling minimizes phase shifts and frequency response variations that can occur with capacitive coupling. The implementation of negative current feedback in parallel configuration enhances the linearity and stability of the amplification process, reducing distortion and improving overall performance.
The circuit's bandwidth of 0.5 to 14 MHz indicates its versatility in handling a wide range of signal frequencies, making it applicable in various electronic measurement and testing scenarios. The noise level output of 0.6 to 0.8 V is indicative of the circuit's design efficiency, ensuring that the amplified signal remains distinguishable above the noise floor.
In summary, this circuit represents a sophisticated approach to high-gain signal amplification, characterized by its high magnification factor, broad bandwidth, and carefully designed impedance matching, making it suitable for advanced electronic applications.This circuitry zooms in magnification of 1200000 times, the bandwidth is 0.5~14 Mhzs, the input impedance is 700 ?, the output impedance is 35 ?(to measure in the 5 MHZ), the output level of noise is 0.6~0.8 V. In the chart, T1 and T2 are direct coupling amplifiers, and be current negative feedback in parallel connection.
The promotion of T2`s emitter l.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to achieve high levels of magnification while maintaining a broad frequency response, making it suitable for applications requiring precise signal amplification. The input impedance of 700 ohms allows for effective interfacing with various signal sources, ensuring minimal signal loss during the amplification process. The output impedance of 35 ohms at 5 MHz is optimized for compatibility with standard measurement equipment, facilitating accurate signal analysis.
The use of transistors T1 and T2 as direct coupling amplifiers is crucial for maintaining signal integrity across the amplification stages. Direct coupling minimizes phase shifts and frequency response variations that can occur with capacitive coupling. The implementation of negative current feedback in parallel configuration enhances the linearity and stability of the amplification process, reducing distortion and improving overall performance.
The circuit's bandwidth of 0.5 to 14 MHz indicates its versatility in handling a wide range of signal frequencies, making it applicable in various electronic measurement and testing scenarios. The noise level output of 0.6 to 0.8 V is indicative of the circuit's design efficiency, ensuring that the amplified signal remains distinguishable above the noise floor.
In summary, this circuit represents a sophisticated approach to high-gain signal amplification, characterized by its high magnification factor, broad bandwidth, and carefully designed impedance matching, making it suitable for advanced electronic applications.This circuitry zooms in magnification of 1200000 times, the bandwidth is 0.5~14 Mhzs, the input impedance is 700 ?, the output impedance is 35 ?(to measure in the 5 MHZ), the output level of noise is 0.6~0.8 V. In the chart, T1 and T2 are direct coupling amplifiers, and be current negative feedback in parallel connection.
The promotion of T2`s emitter l.. 🔗 External reference