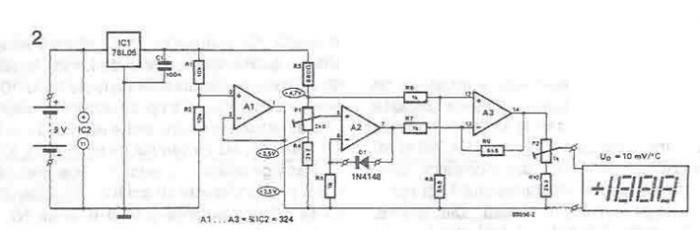
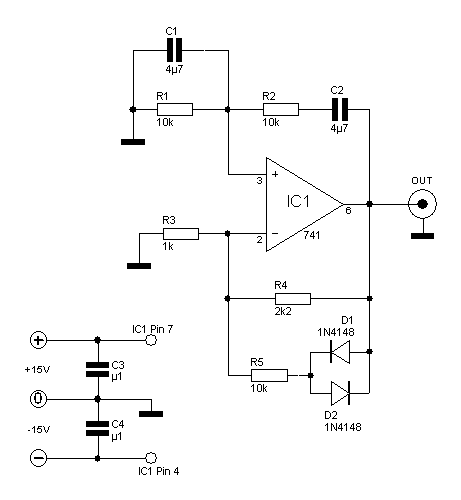
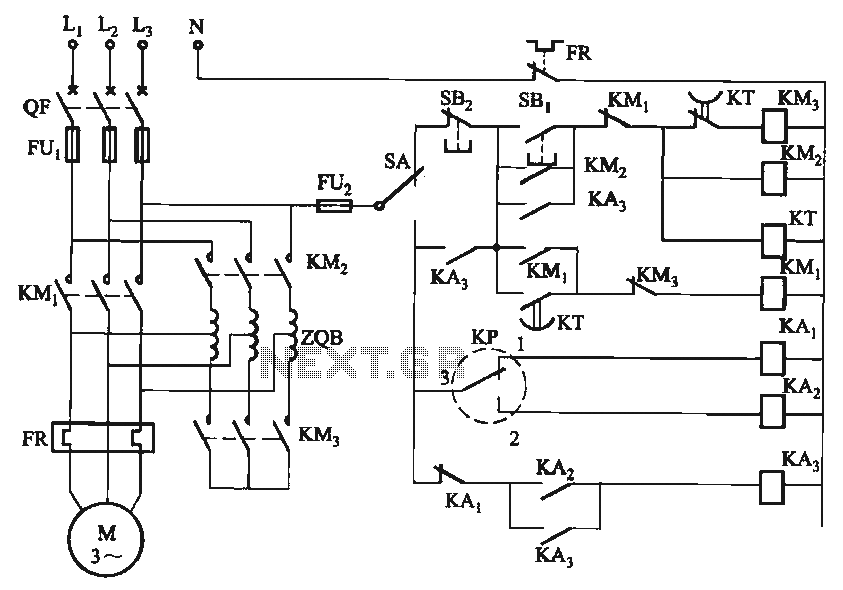
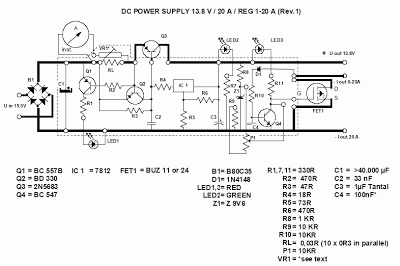
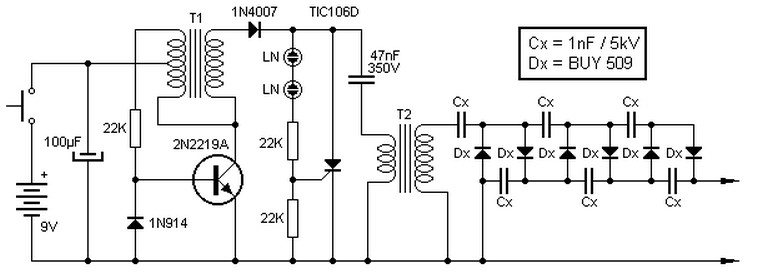
Sophia Electric EL34 Schematic
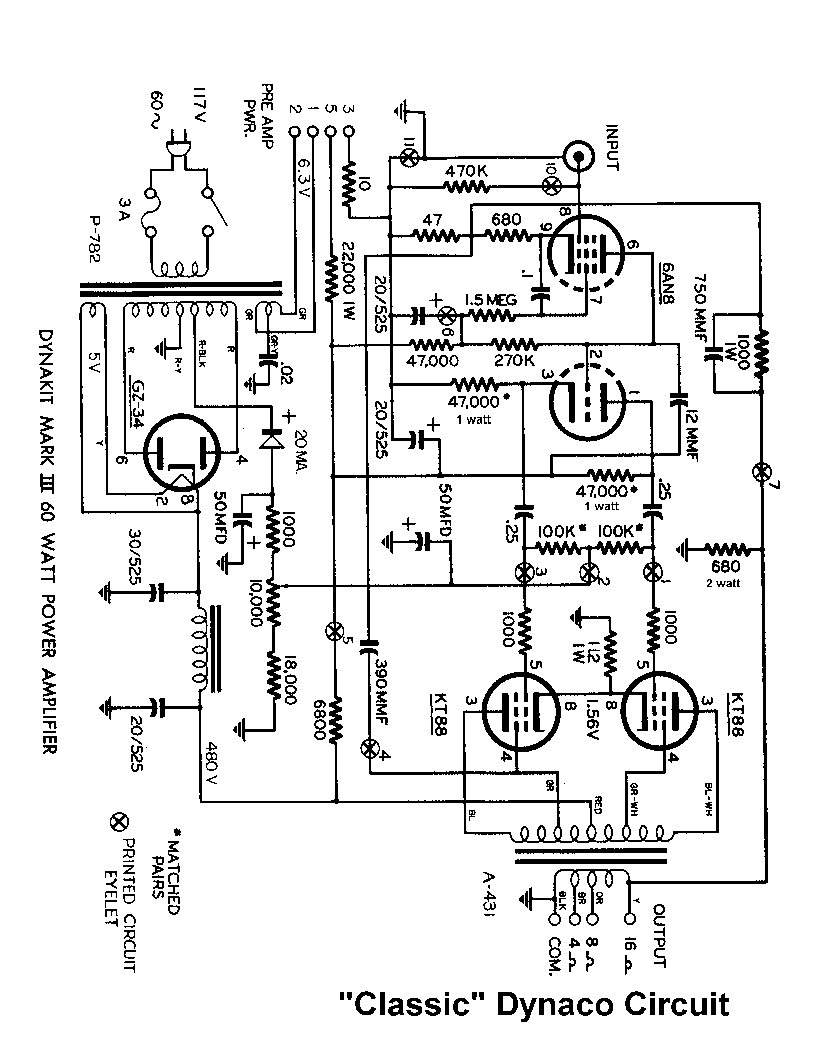
This schematic has been developed as an exercise to learn about amplifiers. There are several aspects that require clarification and further understanding.
The schematic in question likely involves a basic amplifier circuit, which may include components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and possibly operational amplifiers (op-amps). The primary function of an amplifier is to increase the amplitude of a signal, which can be an audio signal, radio frequency, or any other type of electronic signal.
In a typical amplifier circuit, the input signal is fed into the base or gate of a transistor or op-amp, which then controls the larger current flowing through the collector or drain, effectively amplifying the input signal. Resistors are commonly used for biasing the transistors, ensuring they operate within their active region, while capacitors may be employed for coupling and decoupling signals, as well as for filtering purposes.
Power supply considerations are also critical in amplifier design, as the circuit needs to be powered adequately to handle the required output levels without distortion. The output stage may include additional components to drive speakers or other loads, ensuring that the amplified signal is delivered effectively.
Understanding the role of each component in the circuit and how they interact is essential for mastering amplifier design. This knowledge can be further enhanced by experimenting with different configurations, such as inverting and non-inverting amplifier setups, to observe how changes affect performance parameters like gain, bandwidth, and linearity.I have finally worked out this schematic as an exercise to learn about amps. There are a number of things i am not so sure about and would appreciate.. 🔗 External reference
The schematic in question likely involves a basic amplifier circuit, which may include components such as resistors, capacitors, transistors, and possibly operational amplifiers (op-amps). The primary function of an amplifier is to increase the amplitude of a signal, which can be an audio signal, radio frequency, or any other type of electronic signal.
In a typical amplifier circuit, the input signal is fed into the base or gate of a transistor or op-amp, which then controls the larger current flowing through the collector or drain, effectively amplifying the input signal. Resistors are commonly used for biasing the transistors, ensuring they operate within their active region, while capacitors may be employed for coupling and decoupling signals, as well as for filtering purposes.
Power supply considerations are also critical in amplifier design, as the circuit needs to be powered adequately to handle the required output levels without distortion. The output stage may include additional components to drive speakers or other loads, ensuring that the amplified signal is delivered effectively.
Understanding the role of each component in the circuit and how they interact is essential for mastering amplifier design. This knowledge can be further enhanced by experimenting with different configurations, such as inverting and non-inverting amplifier setups, to observe how changes affect performance parameters like gain, bandwidth, and linearity.I have finally worked out this schematic as an exercise to learn about amps. There are a number of things i am not so sure about and would appreciate.. 🔗 External reference