Soundbar Design From Start To Finish: Clocks Clocks Clocks
TI's Dafydd Roche concludes his 4-part series on soundbar design with a thorough explanation of clock design for the digital section of the circuit.
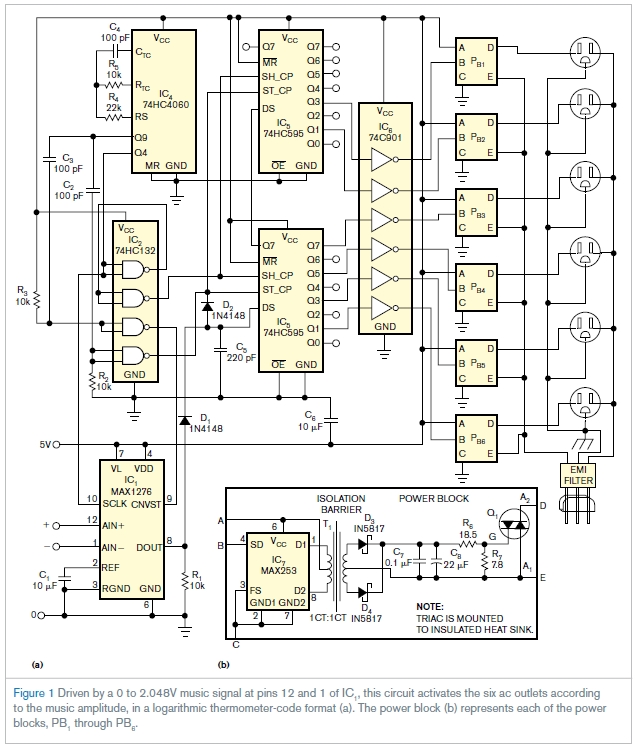
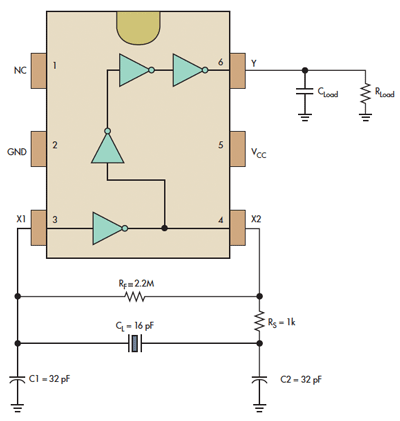
The clock design in digital circuits, particularly in soundbar applications, plays a crucial role in ensuring synchronized operation of various components. A clock signal is essential for timing control, data transfer, and overall system performance. In soundbars, which often integrate multiple digital signal processors (DSPs), audio codecs, and other digital devices, precise clocking is vital for maintaining audio quality and minimizing latency.
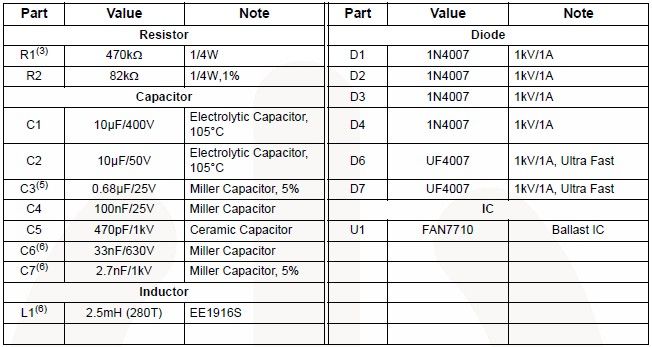
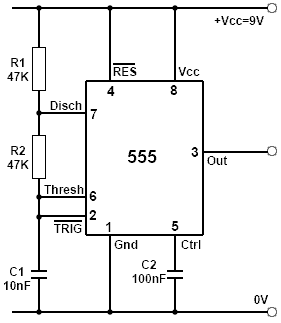
The clock circuit typically consists of a crystal oscillator, which generates a stable frequency signal, and may include dividers or phase-locked loops (PLLs) to derive additional clock frequencies required by different components. The choice of the oscillator frequency is determined by the requirements of the digital components in use, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
Furthermore, the layout of the clock circuit within the PCB design must be carefully considered to minimize noise and interference. Proper grounding techniques, short trace lengths, and adequate decoupling capacitors are essential to ensure signal integrity. Additionally, the use of differential signaling for clock lines can further enhance performance by reducing electromagnetic interference.
In summary, effective clock design in the digital section of soundbar circuits is fundamental for achieving high-quality audio reproduction and reliable operation of the system.TI`s Dafydd Roche completes his 4-part series on sound-bar design with a detailed explanation of clock design for the digital portion of the circuit 🔗 External reference
The clock design in digital circuits, particularly in soundbar applications, plays a crucial role in ensuring synchronized operation of various components. A clock signal is essential for timing control, data transfer, and overall system performance. In soundbars, which often integrate multiple digital signal processors (DSPs), audio codecs, and other digital devices, precise clocking is vital for maintaining audio quality and minimizing latency.
The clock circuit typically consists of a crystal oscillator, which generates a stable frequency signal, and may include dividers or phase-locked loops (PLLs) to derive additional clock frequencies required by different components. The choice of the oscillator frequency is determined by the requirements of the digital components in use, ensuring compatibility and optimal performance.
Furthermore, the layout of the clock circuit within the PCB design must be carefully considered to minimize noise and interference. Proper grounding techniques, short trace lengths, and adequate decoupling capacitors are essential to ensure signal integrity. Additionally, the use of differential signaling for clock lines can further enhance performance by reducing electromagnetic interference.
In summary, effective clock design in the digital section of soundbar circuits is fundamental for achieving high-quality audio reproduction and reliable operation of the system.TI`s Dafydd Roche completes his 4-part series on sound-bar design with a detailed explanation of clock design for the digital portion of the circuit 🔗 External reference