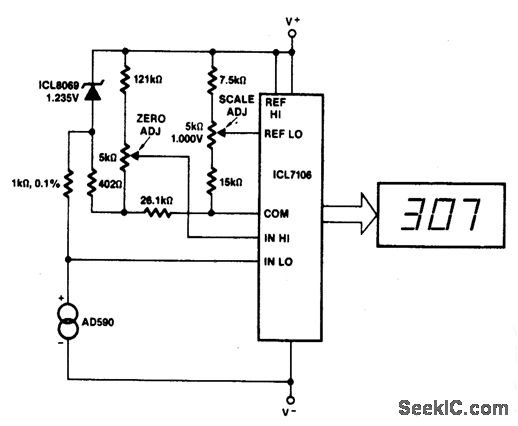
SR63 holiday lights ASIC
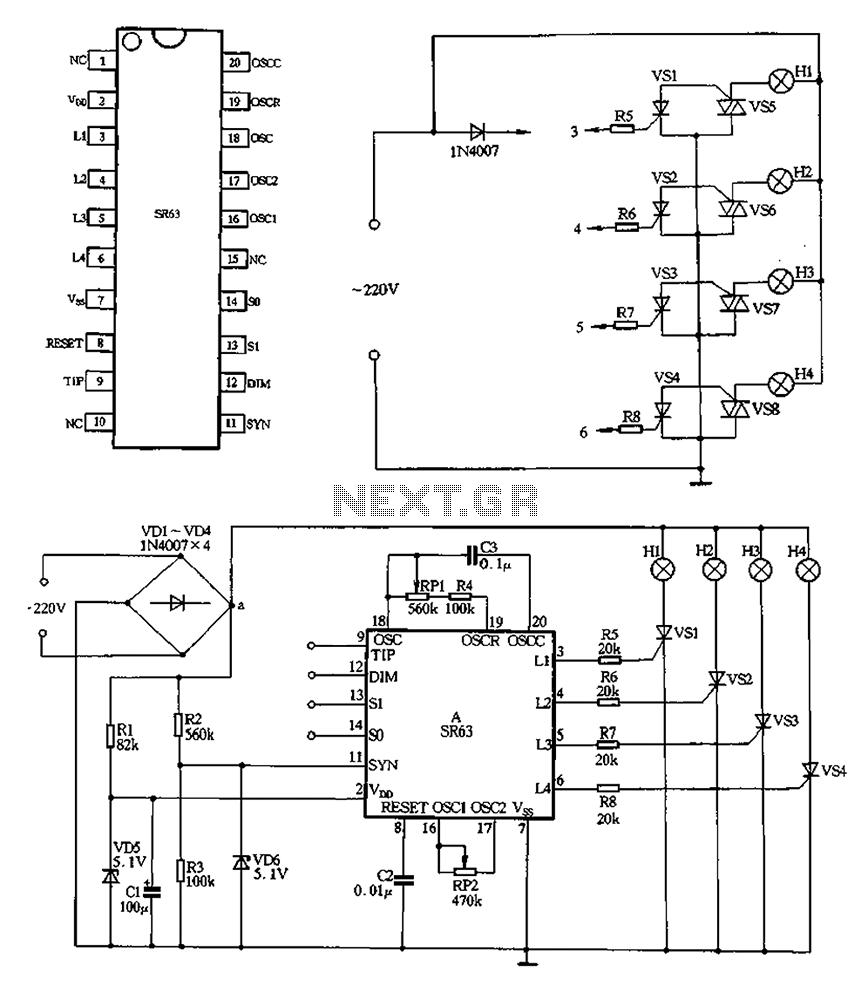
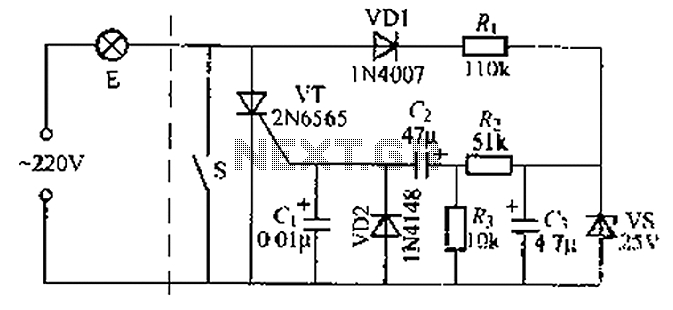
220V AC is converted to DC after passing through a VDI ~ VD4 bridge rectifier. The output from one point supplies power directly to lights H1 through H4. Another route passes through R1, a buck converter, and VD5, which regulates the output to approximately 5V DC. The voltage supply manifold A is supported by a voltage divider formed by R2 and R3, which provides a synchronization signal for manifold A. Components RP1, R4, C3, and SR63 are part of the oscillator circuit system, where adjusting the value of RP1 can change the oscillation frequency, affecting the chase speed of the four lights. RP2 is incorporated into the dimming oscillator circuit; adjusting RP2 alters the speed and brightness contrast of the lights. The circuit also includes a control terminal for four lights, which should be connected to a switch or a switching operation as needed, as referenced in table 2-41.
The circuit described operates by first converting an AC voltage of 220V to a DC voltage using a bridge rectifier formed by diodes VD1 to VD4. The output is then utilized to power four lights (H1 to H4) directly, ensuring reliable illumination. Additionally, a secondary pathway involves a buck converter (R1) and a voltage regulator (VD5) to step down the voltage to approximately 5V DC, which is essential for powering low-voltage components within the circuit.
The voltage divider composed of resistors R2 and R3 serves a dual purpose: it not only stabilizes the voltage supply to manifold A but also generates a synchronization signal that is critical for the timing functions of the circuit. The oscillator circuit, which includes RP1, R4, C3, and SR63, is designed to produce a variable frequency output. By adjusting RP1, the frequency of oscillation can be modified, which in turn influences the chase speed of the lights, allowing for dynamic visual effects.
Furthermore, RP2 is integrated into the dimming oscillator circuit, providing the capability to adjust the brightness of the lights. The adjustment of RP2 affects both the speed and the contrast of the light output, enabling a range of visual presentations from bright to dim settings.
The control terminals for the four lights can be connected to a switch or configured for a specific operation mode, as indicated in the referenced table 2-41. This flexibility allows for the customization of the lighting effects based on user requirements or specific application scenarios, making this circuit suitable for various lighting control applications.220V AC after VDI ~ VD4 bridge rectifier, the output of a point, all the way to direct electricity for lights H1 ~ H4; another way through Rl buck, VD5 regulator, about 5v DC o utput voltage, the electricity supply manifold A. R2, R3 form a voltage divider provides a synchronization signal for the manifold A. RP1, R4, C3 and SR63 within the oscillator circuit system, adjust the value of the RPI system can change the oscillation frequency rate, muscle and can be adjusted four lights chase speed. RP2 inner circuit dimming oscillator circuit, the adjustment value of RP2 can change the speed and dimming lights bright and dark contrast.
FIG DIM, Sl, so, TIP missed four control terminal t in the actual production should be connected with a switch or a switching operation according to the pattern need to refer to table 2-41.
The circuit described operates by first converting an AC voltage of 220V to a DC voltage using a bridge rectifier formed by diodes VD1 to VD4. The output is then utilized to power four lights (H1 to H4) directly, ensuring reliable illumination. Additionally, a secondary pathway involves a buck converter (R1) and a voltage regulator (VD5) to step down the voltage to approximately 5V DC, which is essential for powering low-voltage components within the circuit.
The voltage divider composed of resistors R2 and R3 serves a dual purpose: it not only stabilizes the voltage supply to manifold A but also generates a synchronization signal that is critical for the timing functions of the circuit. The oscillator circuit, which includes RP1, R4, C3, and SR63, is designed to produce a variable frequency output. By adjusting RP1, the frequency of oscillation can be modified, which in turn influences the chase speed of the lights, allowing for dynamic visual effects.
Furthermore, RP2 is integrated into the dimming oscillator circuit, providing the capability to adjust the brightness of the lights. The adjustment of RP2 affects both the speed and the contrast of the light output, enabling a range of visual presentations from bright to dim settings.
The control terminals for the four lights can be connected to a switch or configured for a specific operation mode, as indicated in the referenced table 2-41. This flexibility allows for the customization of the lighting effects based on user requirements or specific application scenarios, making this circuit suitable for various lighting control applications.220V AC after VDI ~ VD4 bridge rectifier, the output of a point, all the way to direct electricity for lights H1 ~ H4; another way through Rl buck, VD5 regulator, about 5v DC o utput voltage, the electricity supply manifold A. R2, R3 form a voltage divider provides a synchronization signal for the manifold A. RP1, R4, C3 and SR63 within the oscillator circuit system, adjust the value of the RPI system can change the oscillation frequency rate, muscle and can be adjusted four lights chase speed. RP2 inner circuit dimming oscillator circuit, the adjustment value of RP2 can change the speed and dimming lights bright and dark contrast.
FIG DIM, Sl, so, TIP missed four control terminal t in the actual production should be connected with a switch or a switching operation according to the pattern need to refer to table 2-41.