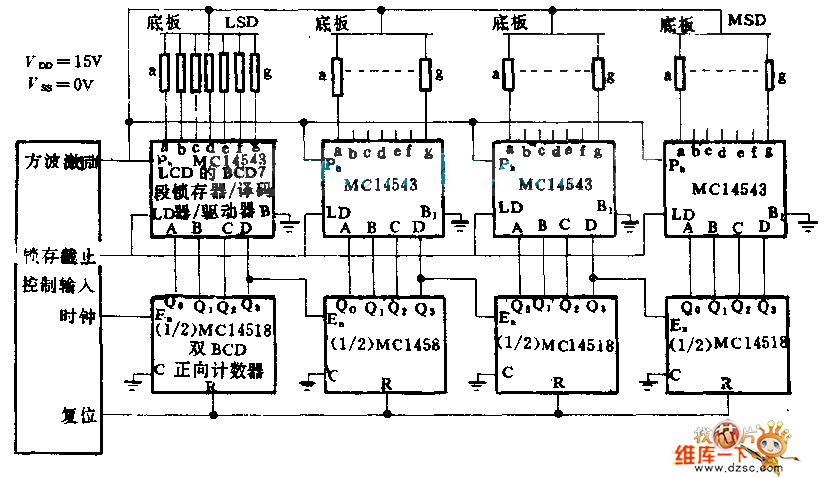
static 0 to 9 display
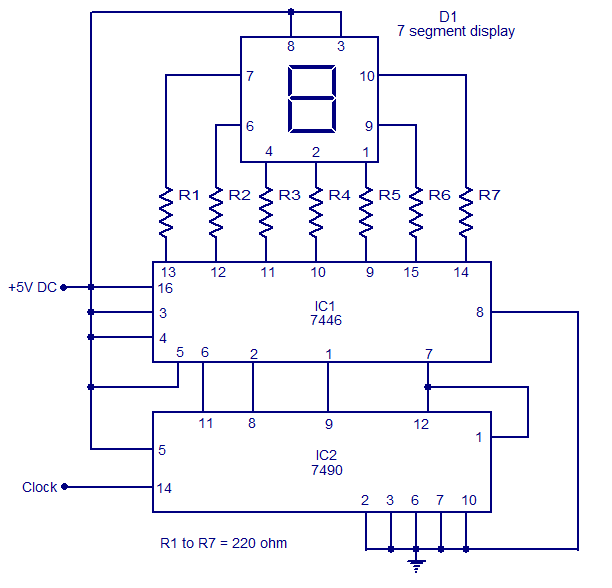
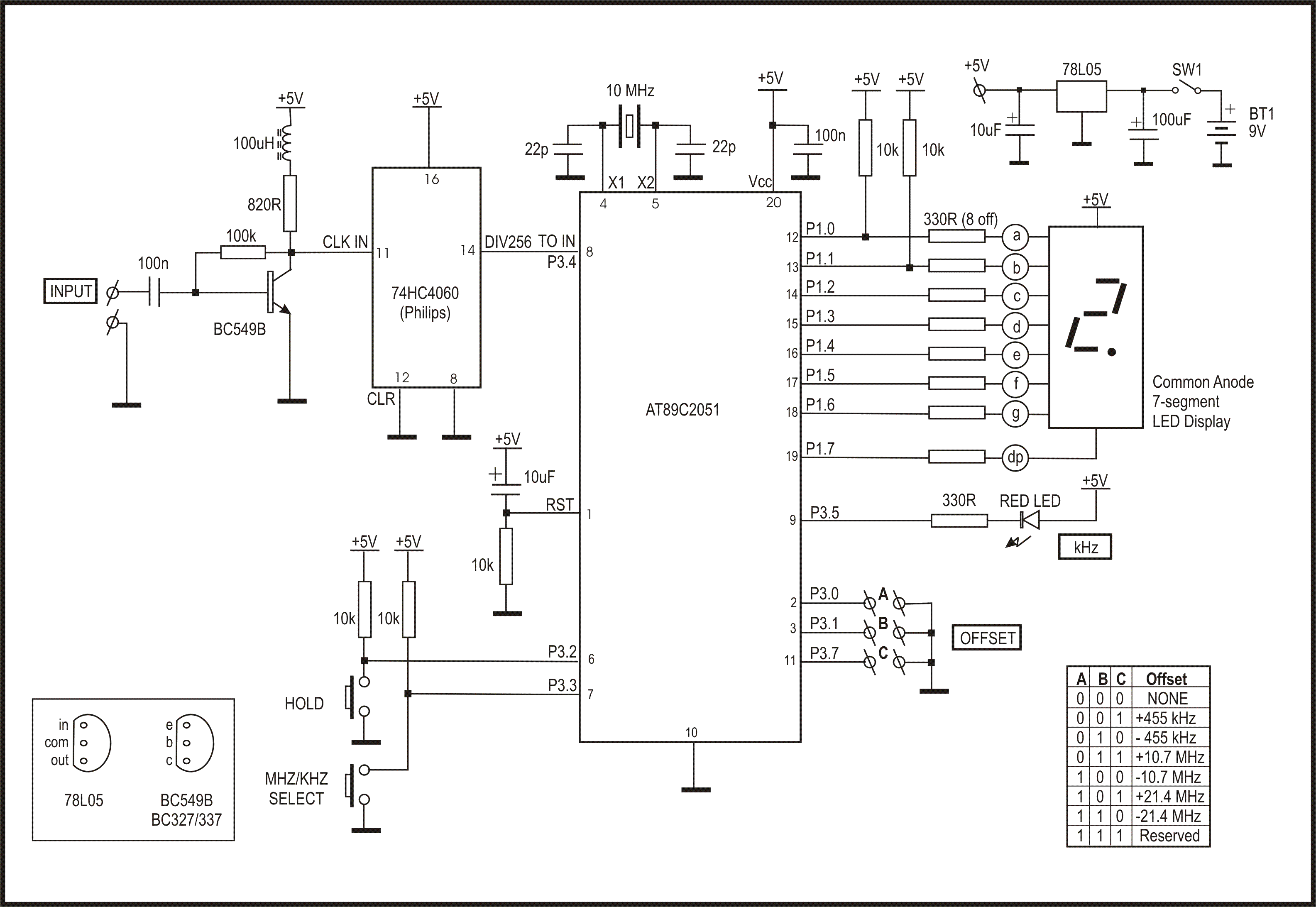
The circuit illustrated is a simple 0 to 9 display suitable for various applications. It utilizes an asynchronous decade counter (7490, IC2), a seven-segment display (D1), and a seven-segment decoder/driver IC (7446, IC1). The seven-segment display comprises seven LEDs labeled from a to g. By forward biasing different LEDs, the digits 0 through 9 can be displayed. There are two types of seven-segment displays: common cathode and common anode. In the common anode type, the anodes of all seven LEDs are connected together, while in the common cathode type, all cathodes are connected together. The display used in this circuit is a common anode type. Resistors R1 to R7 serve as current-limiting resistors. The IC 7446 functions as a decoder/driver IC that drives the seven-segment display. The operation of this circuit is straightforward; for each clock pulse, the BCD output of IC2 (7490) increments by one bit. The IC1 (7446) decodes this BCD output into the corresponding seven-segment format and drives the display to indicate the respective digit.
This circuit is designed to effectively showcase numerical values from 0 to 9 using a seven-segment display, which is a common requirement in digital electronics for applications such as timers, counters, and simple user interfaces. The asynchronous decade counter (7490) is a binary-coded decimal (BCD) counter that counts from 0 to 9 and then resets to 0 upon reaching 10, making it ideal for this application.
The seven-segment display is composed of seven individual LEDs arranged in a figure-eight pattern, allowing for the representation of decimal digits. The common anode configuration means that all anodes of the LEDs are connected to a positive voltage, while the individual cathodes are connected to ground through current-limiting resistors (R1 to R7). These resistors are critical in preventing excess current from flowing through the LEDs, thereby ensuring their longevity and proper operation.
The decoder/driver IC (7446) takes the BCD output from the 7490 counter and converts it into the appropriate signals required to illuminate the correct segments of the display. Each output from the 7446 corresponds to a specific digit, illuminating the necessary segments to form that digit visually.
Clock pulses, which can be generated by an external clock circuit or a microcontroller, provide the timing mechanism for the counter. Each pulse increments the counter, and the decoder interprets the new state of the counter to update the display accordingly. This seamless interaction between the counter, decoder, and display allows for a clear and immediate visual representation of the counted value, making it a versatile solution for various electronic projects requiring numerical output.The circuit shown here is of a simple 0 to 9 display that can be employed in a lot of applications. The circuit is based on asynchronous decade counter 7490(IC2), a 7 segment display (D1), and a seven segment decoder/driver IC 7446 (IC1). The seven segment display consists of 7 LEDs labelled a` through g`. By forward biasing different LEDs, we can display the digits 0 through 9. Seven segment displays are of two types, common cathode and common anode. In common anode type anodes of all the seven LEDs are tied together, while in common cathode type all cathodes are tied together. The seven segment display used here is a common anode type. Resistor R1 to R7 are current limiting resistors. IC 7446 is a decoder/driver IC used to drive the seven segment display. Working of this circuit is very simple. For every clock pulse the BCD output of the IC2 (7490) will advance by one bit. The IC1 (7446) will decode this BCD output to corresponding the seven segment form and will drive the display to indicate the corresponding digit.
🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to effectively showcase numerical values from 0 to 9 using a seven-segment display, which is a common requirement in digital electronics for applications such as timers, counters, and simple user interfaces. The asynchronous decade counter (7490) is a binary-coded decimal (BCD) counter that counts from 0 to 9 and then resets to 0 upon reaching 10, making it ideal for this application.
The seven-segment display is composed of seven individual LEDs arranged in a figure-eight pattern, allowing for the representation of decimal digits. The common anode configuration means that all anodes of the LEDs are connected to a positive voltage, while the individual cathodes are connected to ground through current-limiting resistors (R1 to R7). These resistors are critical in preventing excess current from flowing through the LEDs, thereby ensuring their longevity and proper operation.
The decoder/driver IC (7446) takes the BCD output from the 7490 counter and converts it into the appropriate signals required to illuminate the correct segments of the display. Each output from the 7446 corresponds to a specific digit, illuminating the necessary segments to form that digit visually.
Clock pulses, which can be generated by an external clock circuit or a microcontroller, provide the timing mechanism for the counter. Each pulse increments the counter, and the decoder interprets the new state of the counter to update the display accordingly. This seamless interaction between the counter, decoder, and display allows for a clear and immediate visual representation of the counted value, making it a versatile solution for various electronic projects requiring numerical output.The circuit shown here is of a simple 0 to 9 display that can be employed in a lot of applications. The circuit is based on asynchronous decade counter 7490(IC2), a 7 segment display (D1), and a seven segment decoder/driver IC 7446 (IC1). The seven segment display consists of 7 LEDs labelled a` through g`. By forward biasing different LEDs, we can display the digits 0 through 9. Seven segment displays are of two types, common cathode and common anode. In common anode type anodes of all the seven LEDs are tied together, while in common cathode type all cathodes are tied together. The seven segment display used here is a common anode type. Resistor R1 to R7 are current limiting resistors. IC 7446 is a decoder/driver IC used to drive the seven segment display. Working of this circuit is very simple. For every clock pulse the BCD output of the IC2 (7490) will advance by one bit. The IC1 (7446) will decode this BCD output to corresponding the seven segment form and will drive the display to indicate the corresponding digit.
🔗 External reference