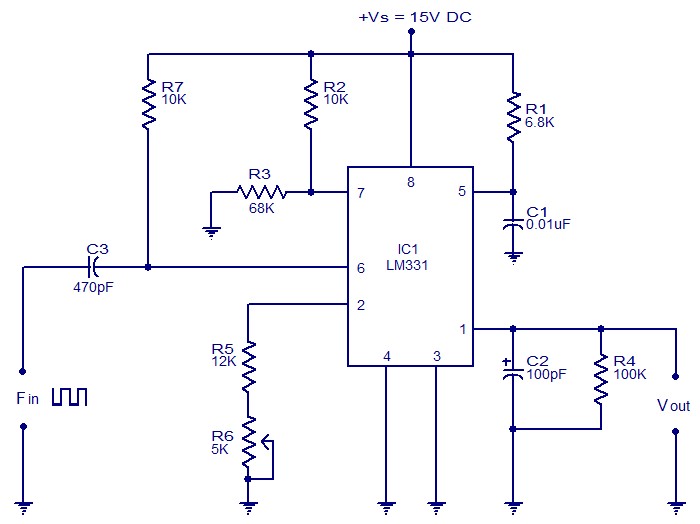
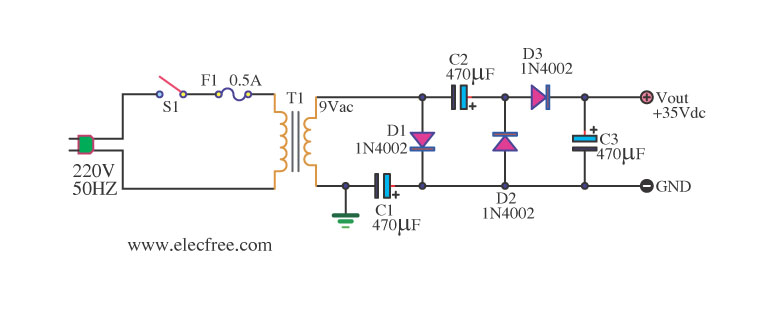
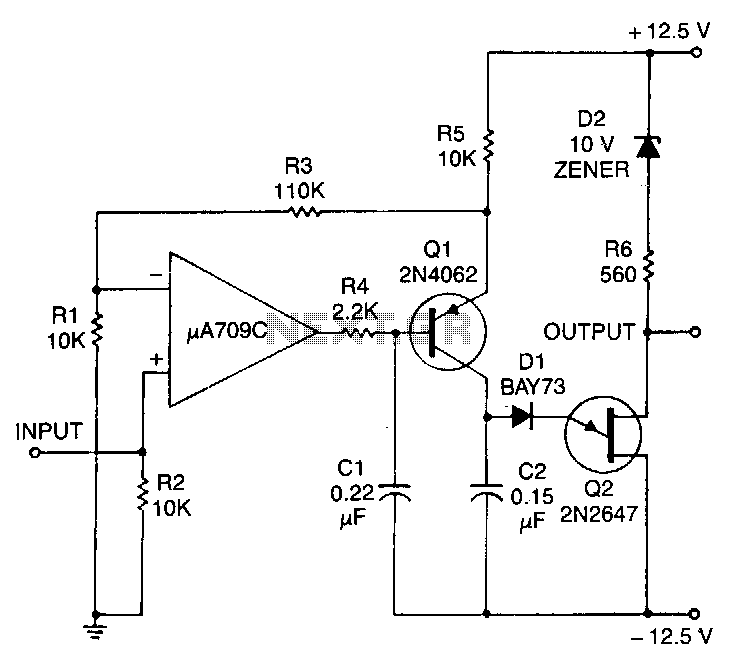
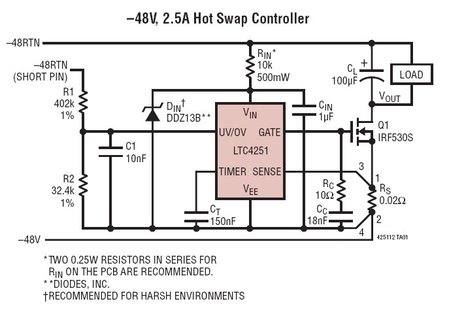
Step down voltage converter 5v with transistor BC337
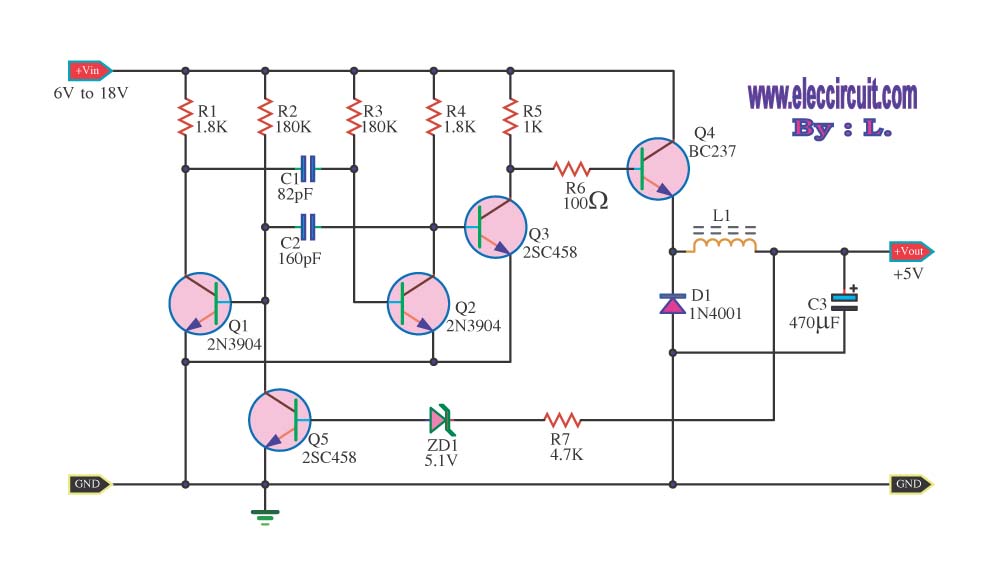
The circuit reduces voltage size or functions as a step-down voltage converter circuit, specifically a DC regulated circuit model using a switching converter. It generates the desired voltage output.
The step-down voltage converter circuit, also known as a buck converter, is designed to efficiently reduce a higher DC voltage to a lower DC voltage while maintaining regulation. This type of circuit is particularly advantageous in applications requiring a stable output voltage from a higher input voltage source, such as battery-powered devices, power supplies, and various electronic systems.
At the core of the buck converter is a switching element, typically a transistor, which rapidly turns on and off to control the energy transfer from the input to the output. The switching action is regulated by a feedback mechanism that monitors the output voltage and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element accordingly. This feedback loop ensures that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in the input voltage or load conditions.
The circuit generally consists of several key components: the input capacitor, switching transistor (often a MOSFET), a diode, an inductor, and an output capacitor. The input capacitor smooths the input voltage and provides a stable supply to the switching element. The inductor stores energy when the transistor is on and releases it to the output when the transistor is off, while the diode ensures current flows in the correct direction during the off phase.
The output capacitor is crucial for filtering the voltage ripple generated during the switching process, providing a smooth DC output voltage. The design of the inductor and capacitors must be carefully selected based on the desired output voltage, current requirements, and switching frequency to optimize performance and efficiency.
In summary, the step-down voltage converter circuit is a vital component in modern electronic designs, offering an efficient means to convert and regulate voltage levels within various applications. Its ability to handle high efficiency and compact size makes it a preferred choice for many electronic devices.The circuit decreases the size voltage or Stepdown Voltage converter circuit be dc regulated circuit model switching converter. The that make voltage output. 🔗 External reference
The step-down voltage converter circuit, also known as a buck converter, is designed to efficiently reduce a higher DC voltage to a lower DC voltage while maintaining regulation. This type of circuit is particularly advantageous in applications requiring a stable output voltage from a higher input voltage source, such as battery-powered devices, power supplies, and various electronic systems.
At the core of the buck converter is a switching element, typically a transistor, which rapidly turns on and off to control the energy transfer from the input to the output. The switching action is regulated by a feedback mechanism that monitors the output voltage and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element accordingly. This feedback loop ensures that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in the input voltage or load conditions.
The circuit generally consists of several key components: the input capacitor, switching transistor (often a MOSFET), a diode, an inductor, and an output capacitor. The input capacitor smooths the input voltage and provides a stable supply to the switching element. The inductor stores energy when the transistor is on and releases it to the output when the transistor is off, while the diode ensures current flows in the correct direction during the off phase.
The output capacitor is crucial for filtering the voltage ripple generated during the switching process, providing a smooth DC output voltage. The design of the inductor and capacitors must be carefully selected based on the desired output voltage, current requirements, and switching frequency to optimize performance and efficiency.
In summary, the step-down voltage converter circuit is a vital component in modern electronic designs, offering an efficient means to convert and regulate voltage levels within various applications. Its ability to handle high efficiency and compact size makes it a preferred choice for many electronic devices.The circuit decreases the size voltage or Stepdown Voltage converter circuit be dc regulated circuit model switching converter. The that make voltage output. 🔗 External reference