Stepper Motor Generator
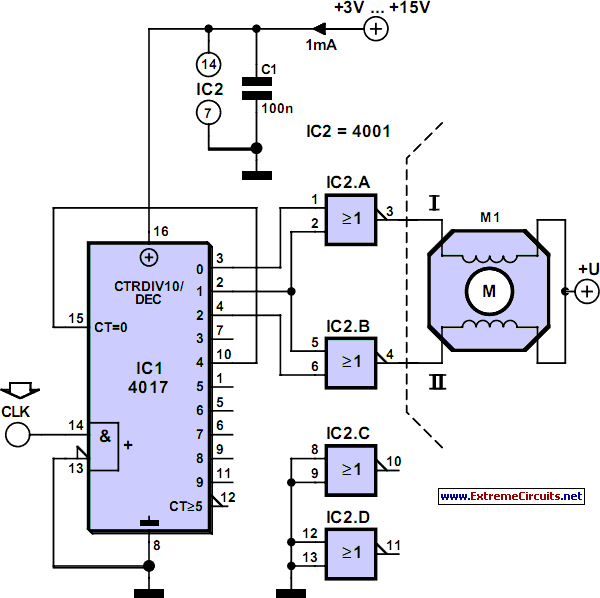
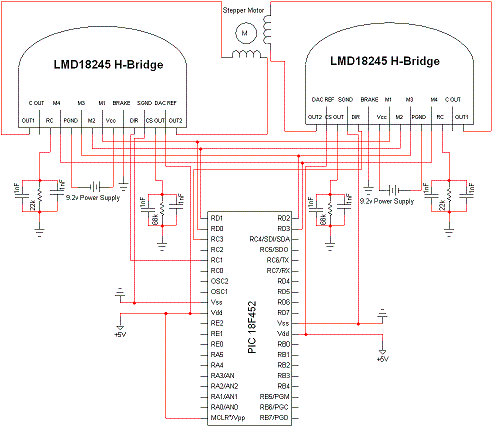
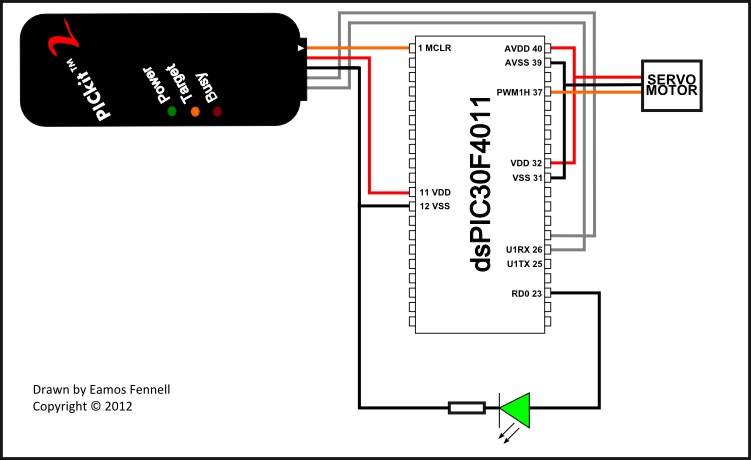
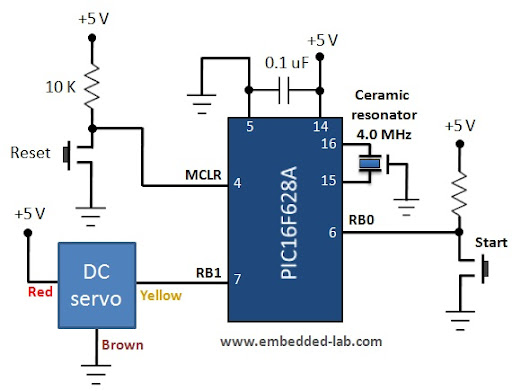
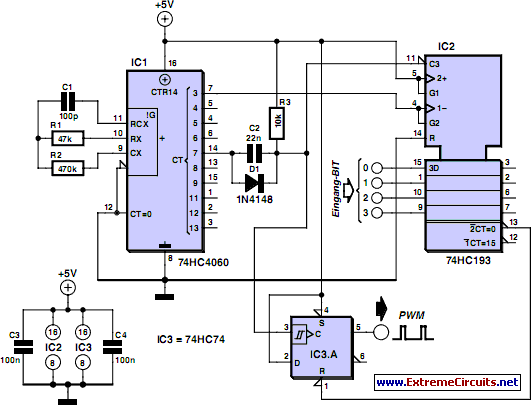
Stepper motors are a recurring subject. This circuit converts a clock signal from a square wave generator into signals with a 90-degree phase shift.
Stepper motors are widely used in applications requiring precise control of angular position, speed, and acceleration. The circuit described facilitates the operation of a stepper motor by transforming a standard clock signal into two output signals that are phase-shifted by 90 degrees. This phase shift is crucial for driving the stepper motor in a coordinated manner, allowing for smooth and accurate stepping.
The circuit typically consists of a square wave generator, which produces a continuous square wave output. This output serves as the input to a phase-shifting network, which can be implemented using various methods, such as using operational amplifiers, RC networks, or digital logic circuits. The phase-shifting network generates two output signals: one that is in phase with the input clock signal and another that leads or lags by 90 degrees.
For example, using an operational amplifier configured as a differentiator can create a 90-degree phase shift. Alternatively, a digital circuit using flip-flops can also achieve the desired phase relationship. The resulting signals are then fed into the stepper motor driver, which interprets these signals to energize the motor coils in the correct sequence, enabling the motor to rotate in a controlled manner.
Proper design considerations for this circuit include ensuring the frequency of the clock signal is suitable for the stepper motor being used, as well as accounting for the required current and voltage levels to drive the motor coils effectively. Additionally, the circuit may include features such as adjustable frequency control to allow for variations in motor speed and performance.Stepper motors are a subject that keeps recurring. This little circuit changes a clock signal (from a square wave generator) into signals with a 90-degree.. 🔗 External reference
Stepper motors are widely used in applications requiring precise control of angular position, speed, and acceleration. The circuit described facilitates the operation of a stepper motor by transforming a standard clock signal into two output signals that are phase-shifted by 90 degrees. This phase shift is crucial for driving the stepper motor in a coordinated manner, allowing for smooth and accurate stepping.
The circuit typically consists of a square wave generator, which produces a continuous square wave output. This output serves as the input to a phase-shifting network, which can be implemented using various methods, such as using operational amplifiers, RC networks, or digital logic circuits. The phase-shifting network generates two output signals: one that is in phase with the input clock signal and another that leads or lags by 90 degrees.
For example, using an operational amplifier configured as a differentiator can create a 90-degree phase shift. Alternatively, a digital circuit using flip-flops can also achieve the desired phase relationship. The resulting signals are then fed into the stepper motor driver, which interprets these signals to energize the motor coils in the correct sequence, enabling the motor to rotate in a controlled manner.
Proper design considerations for this circuit include ensuring the frequency of the clock signal is suitable for the stepper motor being used, as well as accounting for the required current and voltage levels to drive the motor coils effectively. Additionally, the circuit may include features such as adjustable frequency control to allow for variations in motor speed and performance.Stepper motors are a subject that keeps recurring. This little circuit changes a clock signal (from a square wave generator) into signals with a 90-degree.. 🔗 External reference