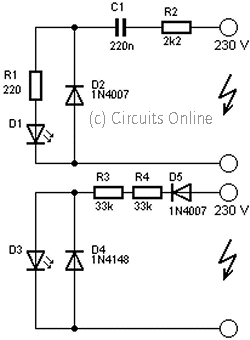
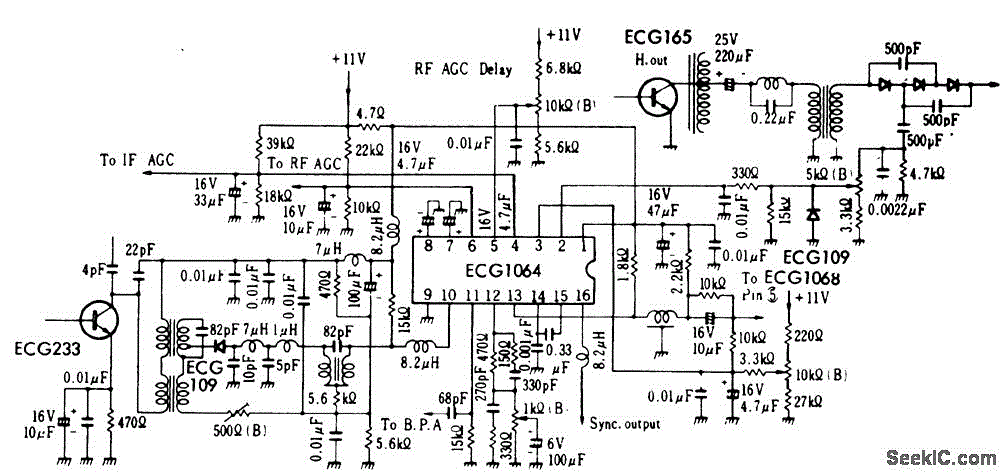
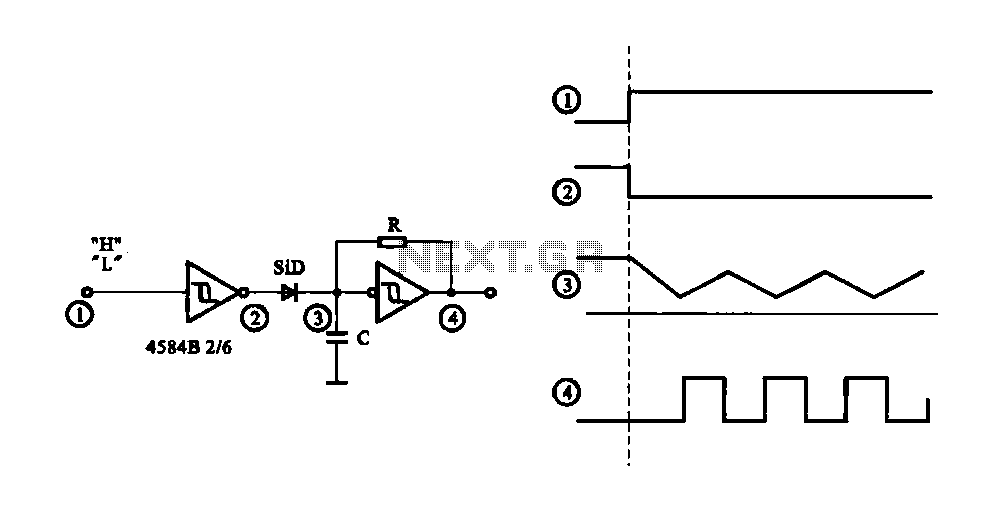
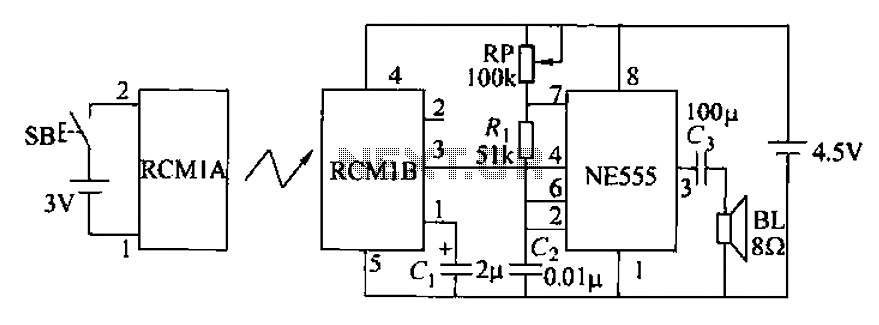
Stereo Headphone Amplifier Circuit
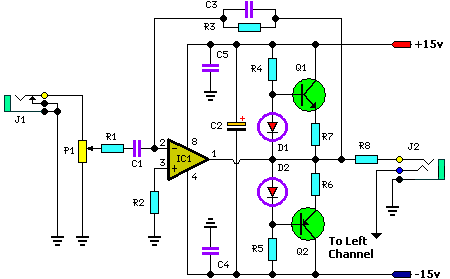
In addition to its primary function as a headphone amplifier, the circuit is suitable for various applications requiring a wide bandwidth low power amplifier. It is constructed using an operational amplifier (op-amp), with its output current enhanced by a pair of transistors.
The described circuit utilizes an operational amplifier as the core component, which is known for its high gain and ability to amplify low-level signals. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting or inverting configuration, depending on the desired application. The circuit's design aims to provide a wide bandwidth, making it ideal for audio applications where fidelity and clarity are essential.
To enhance the output current capabilities of the op-amp, two transistors are employed. These transistors are typically configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing the circuit to drive higher loads without distortion. This configuration also aids in improving the overall efficiency of the amplifier, as it can provide sufficient current to drive headphones or other low-impedance loads effectively.
The power supply for this circuit is usually a dual supply, providing both positive and negative voltages to the op-amp, ensuring that it can handle the full range of audio signals. Bypass capacitors are often included near the power supply pins of the op-amp to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply voltage, which is crucial for maintaining performance.
Input and output coupling capacitors may also be integrated into the design to block DC offsets while allowing AC signals to pass. This is particularly important in audio applications, where any DC component could lead to speaker damage or distortion.
Overall, this circuit design is versatile and can be adapted for various low-power amplification needs, making it a valuable addition to many electronic projects. Its simplicity and effectiveness in amplifying signals while maintaining a wide bandwidth make it an excellent choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.Apart from the obvious usage as a headphone amplifier, the circuit can be used for a range of applications where a wide bandwidth low power amplifier is needed. The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes an operational amplifier as the core component, which is known for its high gain and ability to amplify low-level signals. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting or inverting configuration, depending on the desired application. The circuit's design aims to provide a wide bandwidth, making it ideal for audio applications where fidelity and clarity are essential.
To enhance the output current capabilities of the op-amp, two transistors are employed. These transistors are typically configured in a push-pull arrangement, allowing the circuit to drive higher loads without distortion. This configuration also aids in improving the overall efficiency of the amplifier, as it can provide sufficient current to drive headphones or other low-impedance loads effectively.
The power supply for this circuit is usually a dual supply, providing both positive and negative voltages to the op-amp, ensuring that it can handle the full range of audio signals. Bypass capacitors are often included near the power supply pins of the op-amp to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply voltage, which is crucial for maintaining performance.
Input and output coupling capacitors may also be integrated into the design to block DC offsets while allowing AC signals to pass. This is particularly important in audio applications, where any DC component could lead to speaker damage or distortion.
Overall, this circuit design is versatile and can be adapted for various low-power amplification needs, making it a valuable addition to many electronic projects. Its simplicity and effectiveness in amplifying signals while maintaining a wide bandwidth make it an excellent choice for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.Apart from the obvious usage as a headphone amplifier, the circuit can be used for a range of applications where a wide bandwidth low power amplifier is needed. The circuit is based on an opamp, with its output current boosted by a pair of transistors.. 🔗 External reference