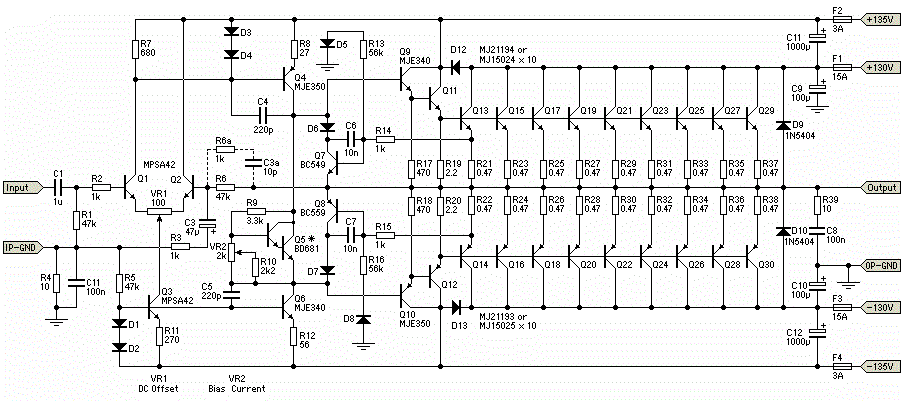
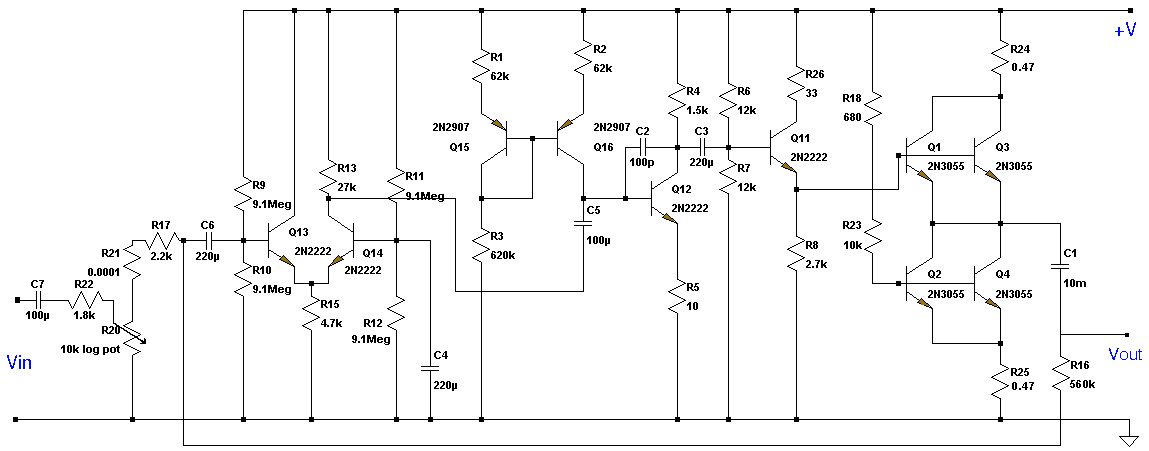
Stereo Preamplifier with adjustment tone
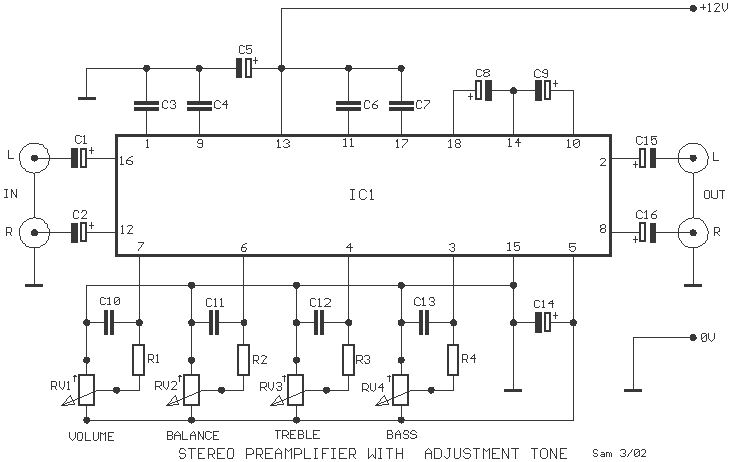
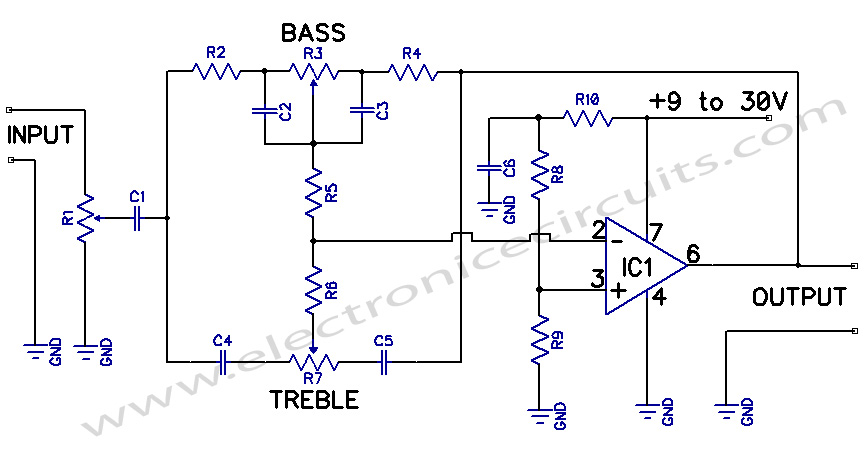
Many times we needed to use a simple circuit of preamplifier, with few components and facility of made. This circuit uses an opamp, the Motorola, TCA5550, that contains a double amplifier, as outputs for the adjust of volume, balance, treble and bass. These adjustments of all parameters come from a line of monophonic linear potentiometers, increasing by far the facility of manufacture. The placement of these potentiometers should be as close as possible to IC1, so that the noise is minimized. The circuit does not require a large current to work.
Additional Content: The preamplifier circuit mentioned is a highly functional and efficient design, utilizing the Motorola TCA5550 opamp. The TCA5550 is a versatile component that includes a dual amplifier, providing the ability to adjust various audio parameters such as volume, balance, treble, and bass. This feature makes the circuit adaptable to a wide range of audio applications.
The circuit's simplicity is highlighted by its minimal component requirement and ease of assembly, making it an ideal choice for both novice and professional electronics engineers. The use of monophonic linear potentiometers for parameter adjustment further simplifies the manufacturing process. These potentiometers are responsible for modifying the circuit's audio output characteristics, providing a high degree of control over the final sound output.
One crucial aspect of this circuit design is the placement of the potentiometers. They should be positioned as close as possible to the IC1 component. This strategic placement helps to minimize noise interference, ensuring a clean and clear audio output.
The circuit operates on a low current, making it energy-efficient and suitable for applications where power consumption is a concern. Despite its low power requirement, it delivers a robust performance, meeting the demands of various audio amplification needs.
Overall, this simple preamplifier circuit design, with its ease of manufacture, versatility, and energy efficiency, offers a reliable solution for various audio amplification applications.Many times we needed to use a simple circuit of preamplifier, with few components and facility of made. This circuit use a opamp. the Motorola, TCA5550, that contains a double amplifier, as outputs for the adjust of volume, balance, treble and bass.
These adjustment of all parameters become from a line monophonic linear potesometers, increasing by far the facility of manufacture. The placement these potesometers should become as much as possible, more near in IC1, so that is minimised the noise.
The circuit does not require big current in order to it work. 🔗 External reference
Additional Content: The preamplifier circuit mentioned is a highly functional and efficient design, utilizing the Motorola TCA5550 opamp. The TCA5550 is a versatile component that includes a dual amplifier, providing the ability to adjust various audio parameters such as volume, balance, treble, and bass. This feature makes the circuit adaptable to a wide range of audio applications.
The circuit's simplicity is highlighted by its minimal component requirement and ease of assembly, making it an ideal choice for both novice and professional electronics engineers. The use of monophonic linear potentiometers for parameter adjustment further simplifies the manufacturing process. These potentiometers are responsible for modifying the circuit's audio output characteristics, providing a high degree of control over the final sound output.
One crucial aspect of this circuit design is the placement of the potentiometers. They should be positioned as close as possible to the IC1 component. This strategic placement helps to minimize noise interference, ensuring a clean and clear audio output.
The circuit operates on a low current, making it energy-efficient and suitable for applications where power consumption is a concern. Despite its low power requirement, it delivers a robust performance, meeting the demands of various audio amplification needs.
Overall, this simple preamplifier circuit design, with its ease of manufacture, versatility, and energy efficiency, offers a reliable solution for various audio amplification applications.Many times we needed to use a simple circuit of preamplifier, with few components and facility of made. This circuit use a opamp. the Motorola, TCA5550, that contains a double amplifier, as outputs for the adjust of volume, balance, treble and bass.
These adjustment of all parameters become from a line monophonic linear potesometers, increasing by far the facility of manufacture. The placement these potesometers should become as much as possible, more near in IC1, so that is minimised the noise.
The circuit does not require big current in order to it work. 🔗 External reference