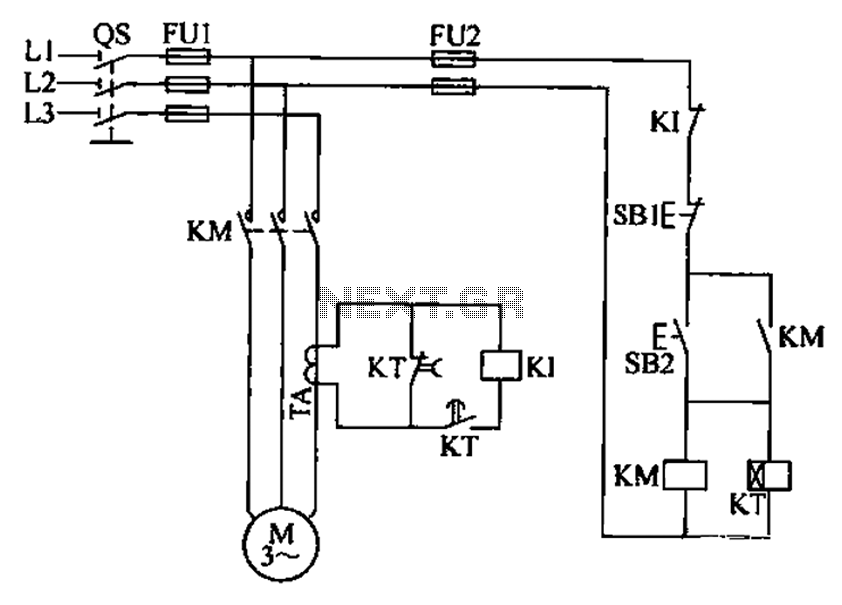
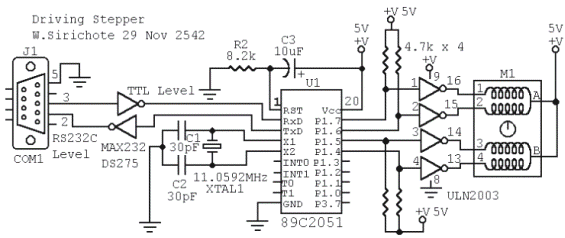
Structure and working principle of brushless motor windings
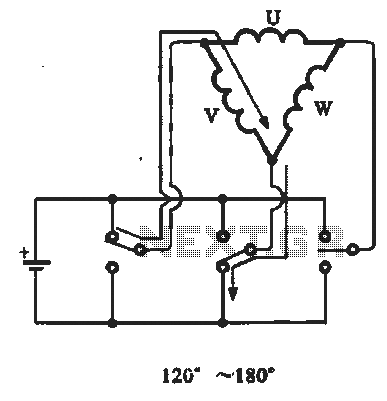
The structure and working principle of brushless motor windings involve the triangular coil configuration. The stator coil can be activated through a switch, resulting in the generation of a rotating magnetic field. The cycling of current and the state of the switch path are illustrated in the accompanying figure. The switching of the transistor is typically responsible for this cycling, and to ensure an orderly transition, a drive control circuit is required.
The brushless motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the interaction between the stator's rotating magnetic field and the rotor's magnetic field generates motion. The triangular coils are arranged in a specific configuration to optimize the magnetic field's efficiency and performance.
In a brushless motor, the stator consists of multiple windings, often arranged in a triangular pattern, which allows for effective magnetic field generation. The switching mechanism, usually implemented through a series of transistors, controls the timing and sequence of current flow through these windings. This control is crucial, as it determines the direction and speed of the rotor's rotation.
A drive control circuit is essential for managing the switching of the transistors. This circuit typically includes a microcontroller or dedicated driver IC that interprets input signals (such as speed commands) and generates the appropriate control signals to the transistors. The design of the control circuit must ensure that the transitions between different states are smooth and efficient, minimizing losses and maximizing performance.
The triangular coil design not only enhances the motor's efficiency but also contributes to its compact size, making brushless motors suitable for a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices to large industrial machinery. The absence of brushes in these motors reduces maintenance needs and increases reliability, further solidifying their preference in modern engineering solutions.Structure and working principle c brushless motor windings Structure and working principle of the triangular coils As shown, through the switch, you can make the stator coil current cycle turned, and the formation of a rotating magnetic field. Can be seen from the figure, the cycle of the week and the current state of the switch path. Is usually caused by switching of the switching transistor, the switch in order to achieve an orderly transition must have a drive control circuit. i class = "else" IC inventory | Part Search | Gallery | Community | 21IC official microblogging |
The brushless motor operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the interaction between the stator's rotating magnetic field and the rotor's magnetic field generates motion. The triangular coils are arranged in a specific configuration to optimize the magnetic field's efficiency and performance.
In a brushless motor, the stator consists of multiple windings, often arranged in a triangular pattern, which allows for effective magnetic field generation. The switching mechanism, usually implemented through a series of transistors, controls the timing and sequence of current flow through these windings. This control is crucial, as it determines the direction and speed of the rotor's rotation.
A drive control circuit is essential for managing the switching of the transistors. This circuit typically includes a microcontroller or dedicated driver IC that interprets input signals (such as speed commands) and generates the appropriate control signals to the transistors. The design of the control circuit must ensure that the transitions between different states are smooth and efficient, minimizing losses and maximizing performance.
The triangular coil design not only enhances the motor's efficiency but also contributes to its compact size, making brushless motors suitable for a wide range of applications, from small electronic devices to large industrial machinery. The absence of brushes in these motors reduces maintenance needs and increases reliability, further solidifying their preference in modern engineering solutions.Structure and working principle c brushless motor windings Structure and working principle of the triangular coils As shown, through the switch, you can make the stator coil current cycle turned, and the formation of a rotating magnetic field. Can be seen from the figure, the cycle of the week and the current state of the switch path. Is usually caused by switching of the switching transistor, the switch in order to achieve an orderly transition must have a drive control circuit. i class = "else" IC inventory | Part Search | Gallery | Community | 21IC official microblogging |