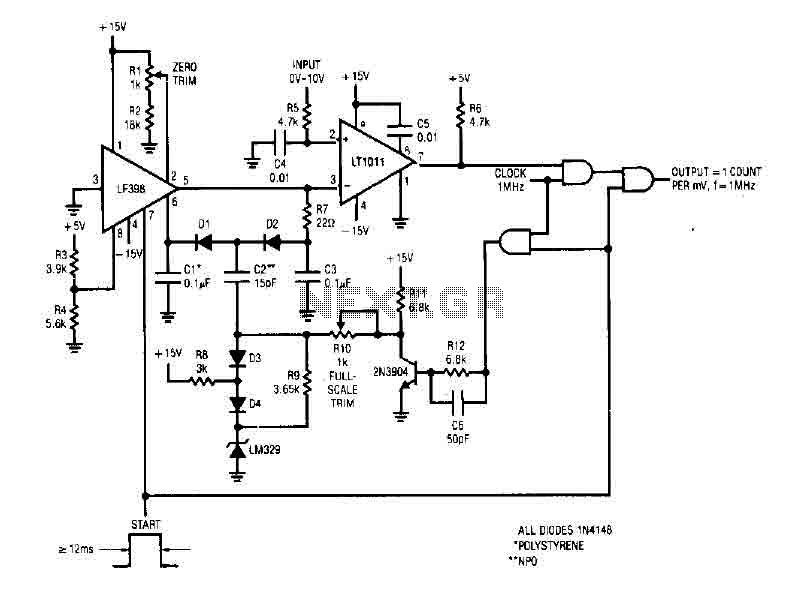
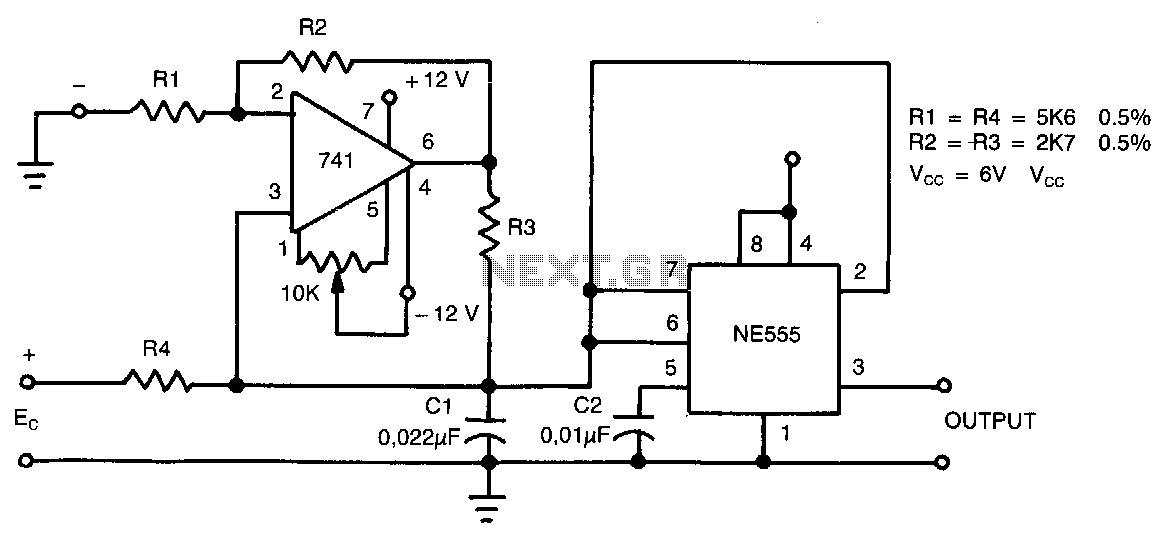
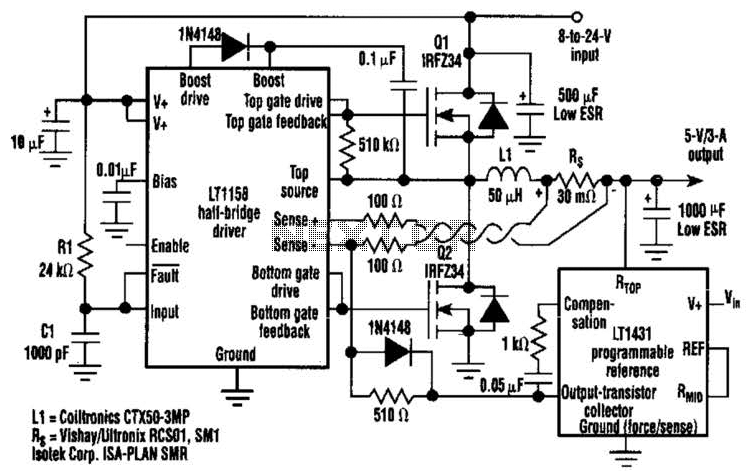
Successive approximation a-d converter
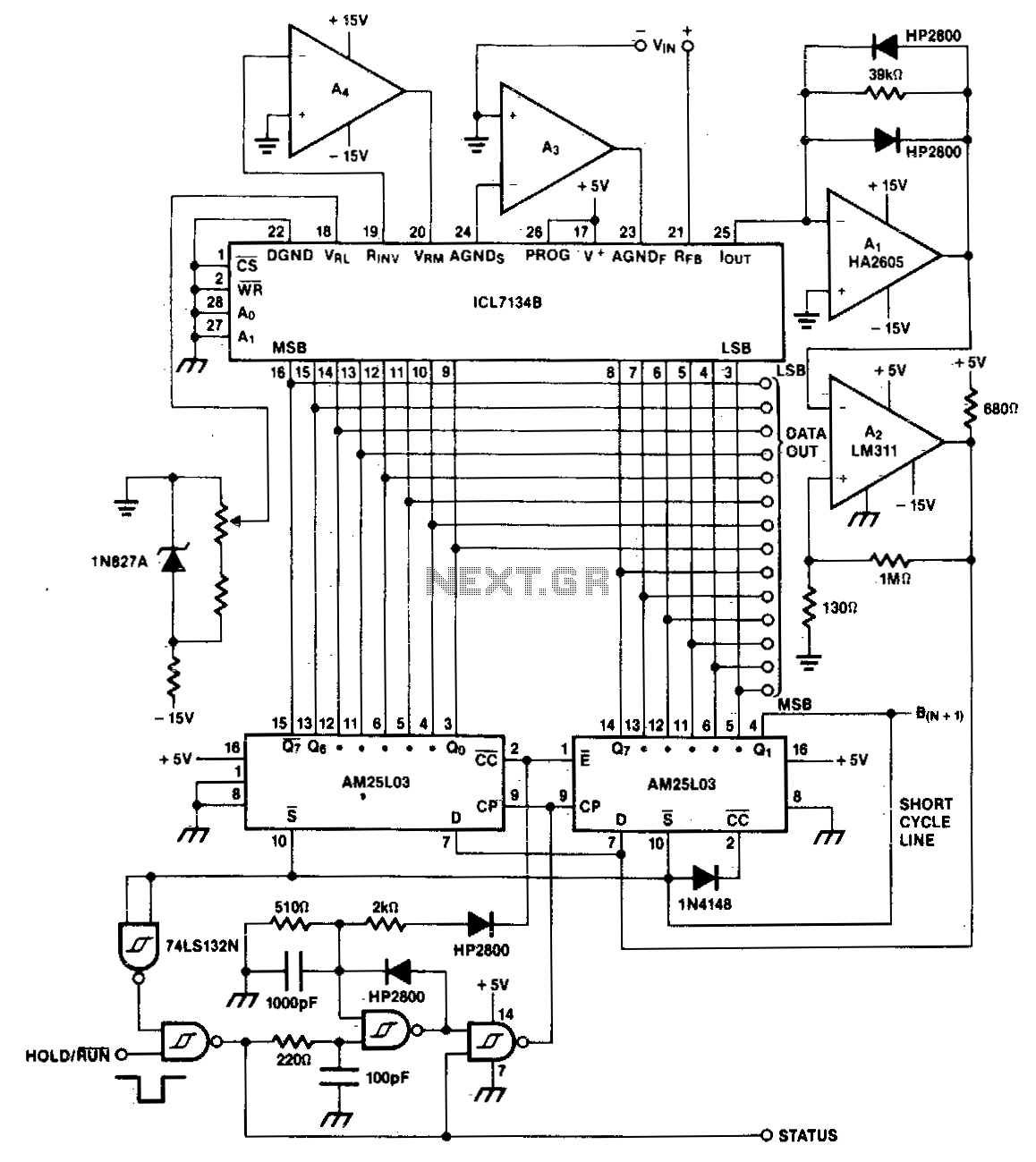
A bipolar input, high-speed A/D converter utilizes two AM25L03 devices to create a 14-bit successive approximation register. The comparator consists of a two-stage circuit featuring an HA2605 front-end amplifier, which is employed to minimize settling time issues at the summing node. It is essential to perform careful offset nulling of this amplifier.
The described A/D converter circuit is designed to achieve high-speed conversion of bipolar signals into a digital format with a resolution of 14 bits. The two AM25L03 components operate in tandem to implement the successive approximation technique, which iteratively narrows down the input signal's digital representation. This method is known for its efficiency in achieving high accuracy with relatively low power consumption.
The comparator's two-stage architecture enhances performance by allowing the HA2605 front-end amplifier to effectively manage the input signal's characteristics before it reaches the decision-making stage of the conversion process. This arrangement is critical for addressing settling time challenges, which can adversely affect the accuracy and speed of the conversion. By reducing the settling time at the summing node, the circuit ensures that the input signal stabilizes quickly, allowing for more rapid successive approximations and thereby increasing the overall throughput of the A/D converter.
Offset nulling is a crucial calibration step for the HA2605 amplifier, as it ensures that any inherent voltage offsets do not introduce errors into the conversion process. This adjustment is vital for maintaining the integrity of the signal being processed, particularly in high-precision applications where even minute discrepancies can lead to significant deviations in the output data.
Overall, this A/D converter design exemplifies a sophisticated approach to high-speed analog-to-digital conversion, leveraging advanced components and careful circuit design to optimize performance and accuracy.A bipolar input, high speed A/D converter uses two AM25L03s to form a 14-bit successive approximation register. The comparator is a two-stage circuit with an HA2605 front-end amplifier used to reduce settling time problems at the summing node
Careful offset-nulling of this amplifier is needed.
The described A/D converter circuit is designed to achieve high-speed conversion of bipolar signals into a digital format with a resolution of 14 bits. The two AM25L03 components operate in tandem to implement the successive approximation technique, which iteratively narrows down the input signal's digital representation. This method is known for its efficiency in achieving high accuracy with relatively low power consumption.
The comparator's two-stage architecture enhances performance by allowing the HA2605 front-end amplifier to effectively manage the input signal's characteristics before it reaches the decision-making stage of the conversion process. This arrangement is critical for addressing settling time challenges, which can adversely affect the accuracy and speed of the conversion. By reducing the settling time at the summing node, the circuit ensures that the input signal stabilizes quickly, allowing for more rapid successive approximations and thereby increasing the overall throughput of the A/D converter.
Offset nulling is a crucial calibration step for the HA2605 amplifier, as it ensures that any inherent voltage offsets do not introduce errors into the conversion process. This adjustment is vital for maintaining the integrity of the signal being processed, particularly in high-precision applications where even minute discrepancies can lead to significant deviations in the output data.
Overall, this A/D converter design exemplifies a sophisticated approach to high-speed analog-to-digital conversion, leveraging advanced components and careful circuit design to optimize performance and accuracy.A bipolar input, high speed A/D converter uses two AM25L03s to form a 14-bit successive approximation register. The comparator is a two-stage circuit with an HA2605 front-end amplifier used to reduce settling time problems at the summing node
Careful offset-nulling of this amplifier is needed.