SINE WAVE TO SQUARE WAVE CONVERTER
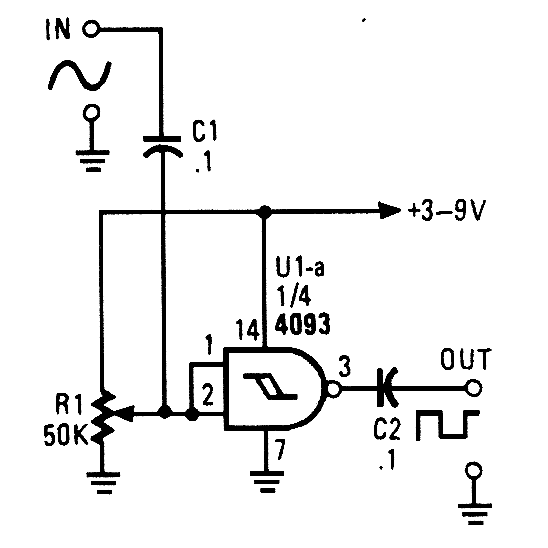
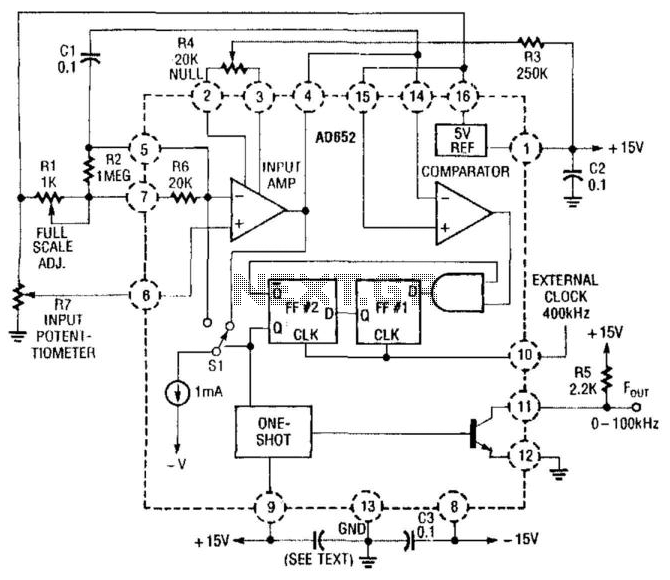
This circuit converts a sine wave into a square wave. It consists of a single 2-input NAND Schmitt trigger configured as an inverter, with a trigger level adjustment at its input. As the input voltage exceeds the gate's trigger point, the output transitions to its alternate state, generating a square-wave output.
The circuit operates by utilizing the characteristics of a Schmitt trigger, which provides hysteresis in its switching behavior. This hysteresis allows the circuit to effectively handle noisy input signals, ensuring that the output remains stable and free from oscillations that could occur with a standard inverter.
In this configuration, the Schmitt trigger's two inputs are connected in such a way that one input serves as the actual signal input, while the other is used for feedback to establish the trigger levels. The trigger levels can be adjusted by modifying the resistor values in the feedback loop, allowing for flexibility in determining the precise voltage thresholds at which the output state changes.
When a sine wave is applied to the input, the voltage gradually increases and decreases, crossing the predefined trigger thresholds. As the sine wave rises and crosses the upper threshold, the output of the Schmitt trigger switches from low to high, producing a square wave that corresponds to the rising edge of the input signal. Conversely, as the sine wave descends and crosses the lower threshold, the output switches back from high to low, completing the square wave cycle.
The resulting output is a clean square wave that can be used in various applications, such as clock signals in digital circuits, waveform shaping, or as a trigger signal for other electronic components. The simplicity of this circuit, combined with the effectiveness of the Schmitt trigger in providing stable switching, makes it an ideal choice for converting analog waveforms into digital signals.This circuit tums a sine wave into a square wave. It is comprised of a single 2-input NAND Schmitt trigger that`s conftgured as an inverter with a trigger level adjustment at its input. As the input voltage rises above the gate`s trigger point, the output snaps to its alternate state, producing a square-wave output.
🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the characteristics of a Schmitt trigger, which provides hysteresis in its switching behavior. This hysteresis allows the circuit to effectively handle noisy input signals, ensuring that the output remains stable and free from oscillations that could occur with a standard inverter.
In this configuration, the Schmitt trigger's two inputs are connected in such a way that one input serves as the actual signal input, while the other is used for feedback to establish the trigger levels. The trigger levels can be adjusted by modifying the resistor values in the feedback loop, allowing for flexibility in determining the precise voltage thresholds at which the output state changes.
When a sine wave is applied to the input, the voltage gradually increases and decreases, crossing the predefined trigger thresholds. As the sine wave rises and crosses the upper threshold, the output of the Schmitt trigger switches from low to high, producing a square wave that corresponds to the rising edge of the input signal. Conversely, as the sine wave descends and crosses the lower threshold, the output switches back from high to low, completing the square wave cycle.
The resulting output is a clean square wave that can be used in various applications, such as clock signals in digital circuits, waveform shaping, or as a trigger signal for other electronic components. The simplicity of this circuit, combined with the effectiveness of the Schmitt trigger in providing stable switching, makes it an ideal choice for converting analog waveforms into digital signals.This circuit tums a sine wave into a square wave. It is comprised of a single 2-input NAND Schmitt trigger that`s conftgured as an inverter with a trigger level adjustment at its input. As the input voltage rises above the gate`s trigger point, the output snaps to its alternate state, producing a square-wave output.
🔗 External reference