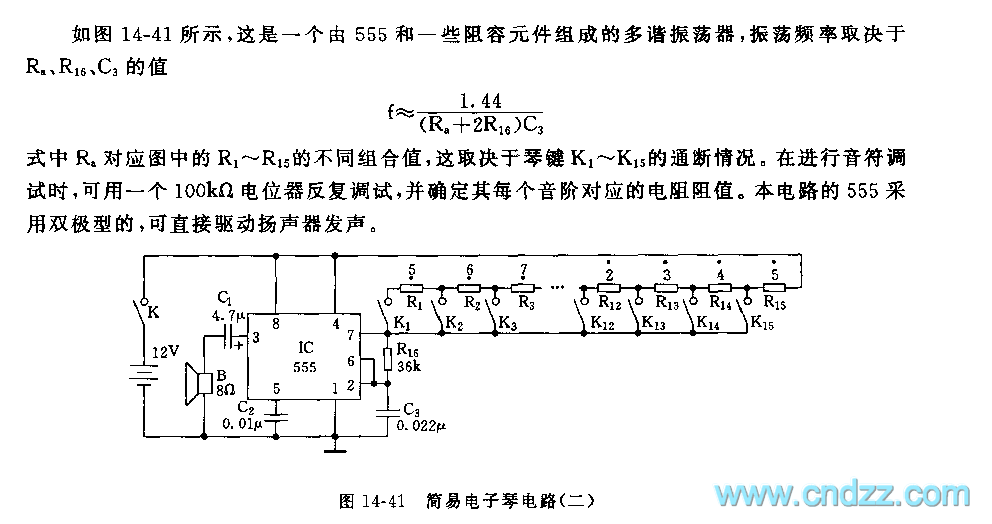
Super Simple Inverter
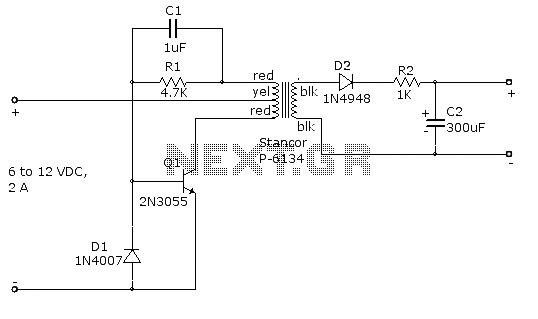
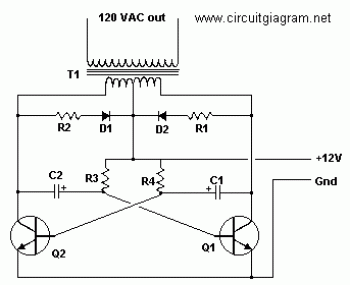
This is an example of a simple inverter that can be used to power a fluorescent lamp and a small strobe. This circuit will produce over 400 VDC from a 12 VDC, 2.5 A.
The described inverter circuit is designed to convert a low voltage direct current (DC) input into a high voltage direct current output, suitable for powering devices such as fluorescent lamps and small strobe lights. The circuit typically operates by utilizing a transformer to step up the voltage from the input level of 12 VDC to an output exceeding 400 VDC.
Key components of this inverter may include a switching element, such as a transistor or MOSFET, which is responsible for turning the current on and off rapidly to create an alternating current (AC) signal. This AC signal is then fed into a transformer, which increases the voltage to the desired level. The output is rectified to provide a stable DC voltage suitable for the load.
The inverter circuit may also incorporate additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to ensure stable operation, manage voltage levels, and filter noise. A feedback mechanism may be included to regulate the output voltage and maintain consistency under varying load conditions.
Safety precautions are critical when designing and implementing this inverter, particularly due to the high voltages involved. Proper insulation, circuit protection, and adherence to safety standards are essential to prevent electrical hazards.
Overall, this inverter circuit represents a practical solution for applications requiring high voltage DC power from a low voltage DC source, making it versatile for various electronic projects.This is example of a simple inverter that can be used to power fluorescent lamp and a small strobe. This circuit will produce over 400VDC from a 12 VDC, 2.5 A.. 🔗 External reference
The described inverter circuit is designed to convert a low voltage direct current (DC) input into a high voltage direct current output, suitable for powering devices such as fluorescent lamps and small strobe lights. The circuit typically operates by utilizing a transformer to step up the voltage from the input level of 12 VDC to an output exceeding 400 VDC.
Key components of this inverter may include a switching element, such as a transistor or MOSFET, which is responsible for turning the current on and off rapidly to create an alternating current (AC) signal. This AC signal is then fed into a transformer, which increases the voltage to the desired level. The output is rectified to provide a stable DC voltage suitable for the load.
The inverter circuit may also incorporate additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes to ensure stable operation, manage voltage levels, and filter noise. A feedback mechanism may be included to regulate the output voltage and maintain consistency under varying load conditions.
Safety precautions are critical when designing and implementing this inverter, particularly due to the high voltages involved. Proper insulation, circuit protection, and adherence to safety standards are essential to prevent electrical hazards.
Overall, this inverter circuit represents a practical solution for applications requiring high voltage DC power from a low voltage DC source, making it versatile for various electronic projects.This is example of a simple inverter that can be used to power fluorescent lamp and a small strobe. This circuit will produce over 400VDC from a 12 VDC, 2.5 A.. 🔗 External reference