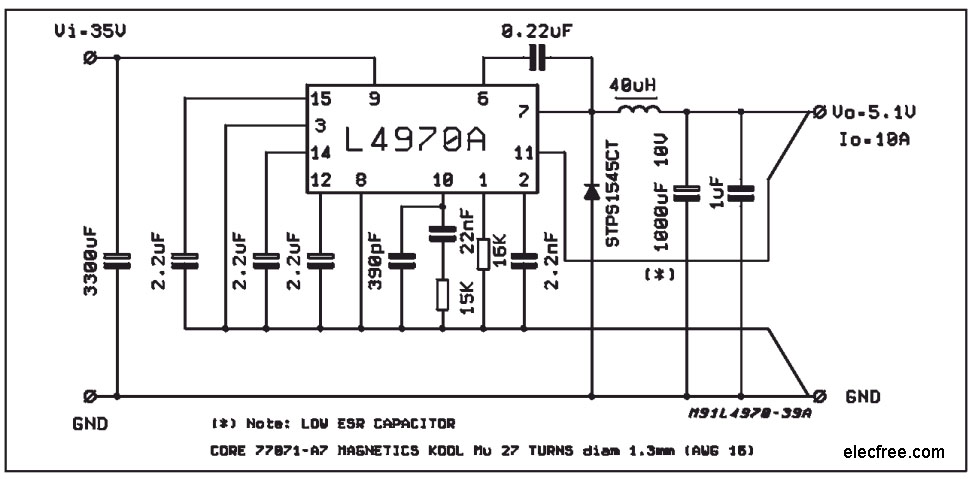
Switching Improves Regulator Efficiency
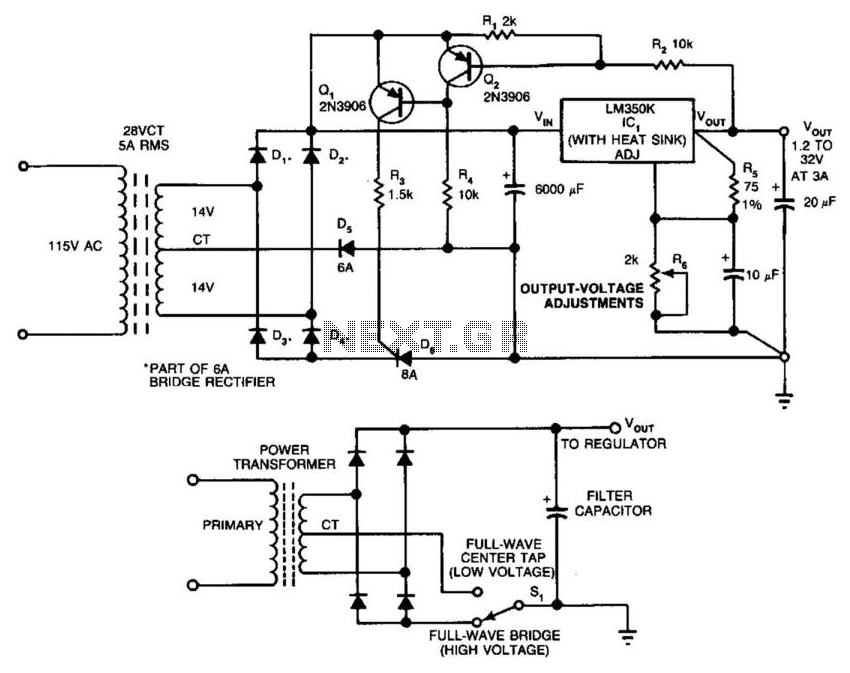
In this circuit, a full-wave bridge is switched to a full-wave center tap to reduce regulator dissipation. SCR D6 switches between configurations. When D6 is off, the circuit is an FWCT rectifier using D1, D2, and D5. It applies 17 V plus ripple to the regulator input. The drop across the regulator supplies base drive to Q2. If Q2 is on, Q1 is off, and D6 is off. If the regulator voltage drops below about 3 V, Q2 turns off, and turns Q1 on, which turns on D6. This changes the circuit to an FW bridge using D1 through D4.
The circuit operates by utilizing a combination of a full-wave center tap (FWCT) rectifier and a full-wave bridge rectifier configuration to optimize the efficiency of the voltage regulation process. The central component, SCR D6, acts as a switch that toggles between these two configurations based on the voltage levels detected at the regulator output.
In the FWCT mode, with SCR D6 turned off, diodes D1, D2, and D5 conduct, allowing the circuit to convert the AC input voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. This configuration generates an output voltage of approximately 17 V, which includes a ripple component due to the nature of rectification. The pulsating DC voltage is fed into the voltage regulator, which is responsible for maintaining a stable output voltage.
The voltage drop across the regulator is critical as it provides the necessary base drive to transistor Q2. When Q2 is active (turned on), it prevents Q1 from conducting, effectively keeping SCR D6 off and maintaining the FWCT operation. This mode is efficient under normal load conditions, as it minimizes power dissipation within the regulator.
However, if the load demand increases and the output voltage of the regulator falls below a threshold of approximately 3 V, Q2 will deactivate. This action allows Q1 to turn on, which in turn activates SCR D6. Once D6 is on, the circuit transitions to the full-wave bridge configuration utilizing diodes D1 through D4. This configuration provides a more robust output by allowing current to flow through all four diodes, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable even under varying load conditions.
The switching mechanism between the two configurations enhances the circuit's overall efficiency and reliability. By dynamically adjusting the rectification method based on the output voltage, the design minimizes losses and optimizes performance across a range of operational scenarios. This approach is particularly beneficial in applications where maintaining a stable voltage is critical, such as in power supplies for sensitive electronic devices. In this circuit, a full-wave bridge is switched to a full-wave center tap to reduce regulator dissi pation. SCR D6 switches between configurations. When D6 is off, the circuit is an FWCT rectifier using Dl, D2, and D5. It applies 17 V plus ripple to the regulator input. The drop across the regulator supplies base drive to Q2. If Q2 is on, Ql is off, and D6 is off. If the regulator voltage drops below about 3 V, Q2 turns off, and turns Ql on, which turns on D6. This changes the circuit to an FW bridge using Dl through D4.
The circuit operates by utilizing a combination of a full-wave center tap (FWCT) rectifier and a full-wave bridge rectifier configuration to optimize the efficiency of the voltage regulation process. The central component, SCR D6, acts as a switch that toggles between these two configurations based on the voltage levels detected at the regulator output.
In the FWCT mode, with SCR D6 turned off, diodes D1, D2, and D5 conduct, allowing the circuit to convert the AC input voltage into a pulsating DC voltage. This configuration generates an output voltage of approximately 17 V, which includes a ripple component due to the nature of rectification. The pulsating DC voltage is fed into the voltage regulator, which is responsible for maintaining a stable output voltage.
The voltage drop across the regulator is critical as it provides the necessary base drive to transistor Q2. When Q2 is active (turned on), it prevents Q1 from conducting, effectively keeping SCR D6 off and maintaining the FWCT operation. This mode is efficient under normal load conditions, as it minimizes power dissipation within the regulator.
However, if the load demand increases and the output voltage of the regulator falls below a threshold of approximately 3 V, Q2 will deactivate. This action allows Q1 to turn on, which in turn activates SCR D6. Once D6 is on, the circuit transitions to the full-wave bridge configuration utilizing diodes D1 through D4. This configuration provides a more robust output by allowing current to flow through all four diodes, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable even under varying load conditions.
The switching mechanism between the two configurations enhances the circuit's overall efficiency and reliability. By dynamically adjusting the rectification method based on the output voltage, the design minimizes losses and optimizes performance across a range of operational scenarios. This approach is particularly beneficial in applications where maintaining a stable voltage is critical, such as in power supplies for sensitive electronic devices. In this circuit, a full-wave bridge is switched to a full-wave center tap to reduce regulator dissi pation. SCR D6 switches between configurations. When D6 is off, the circuit is an FWCT rectifier using Dl, D2, and D5. It applies 17 V plus ripple to the regulator input. The drop across the regulator supplies base drive to Q2. If Q2 is on, Ql is off, and D6 is off. If the regulator voltage drops below about 3 V, Q2 turns off, and turns Ql on, which turns on D6. This changes the circuit to an FW bridge using Dl through D4.