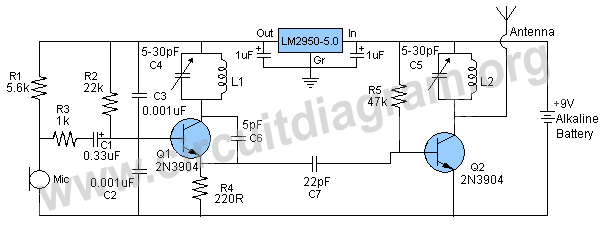
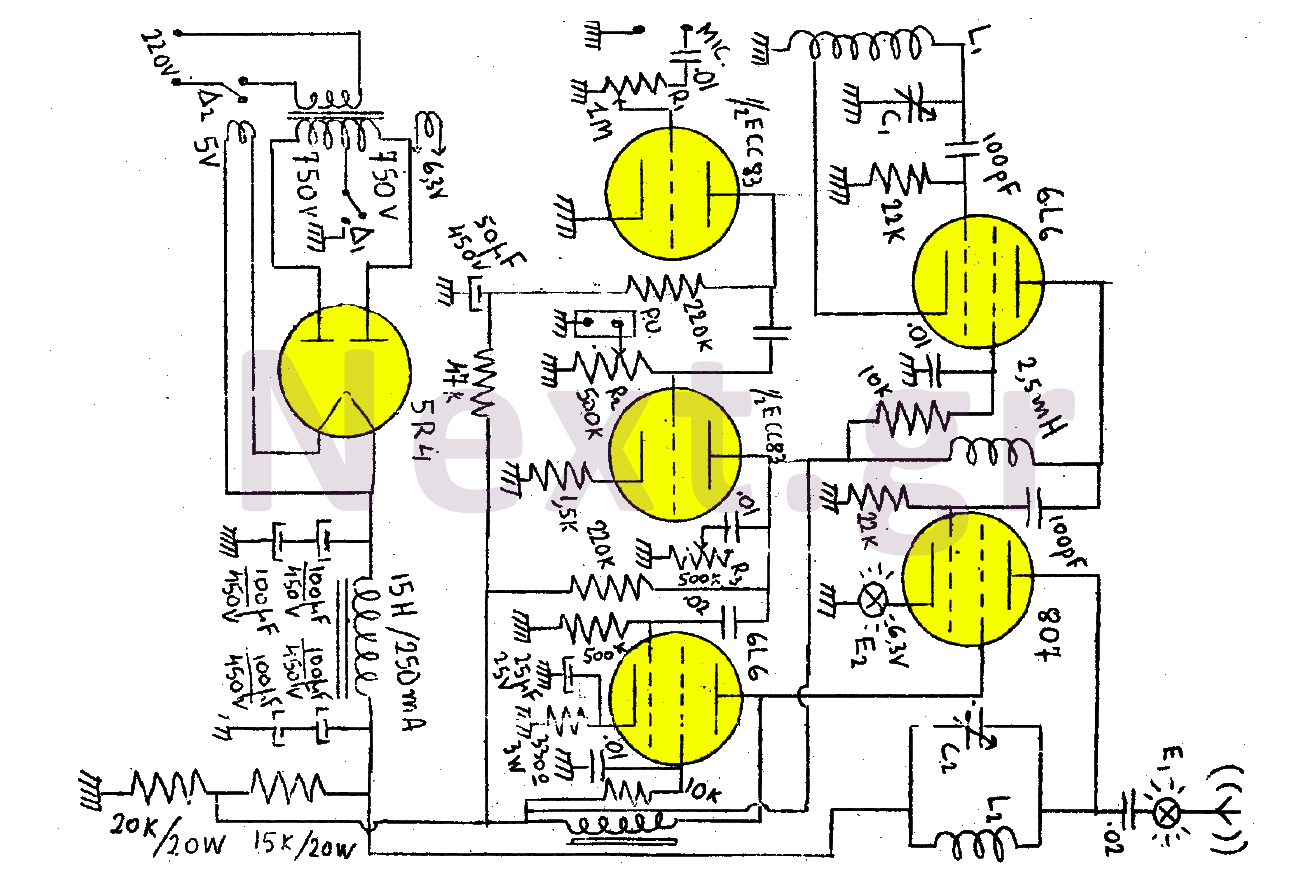
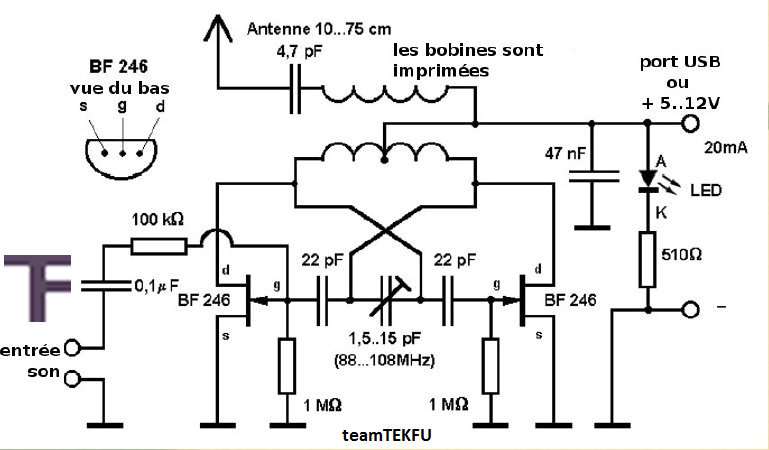
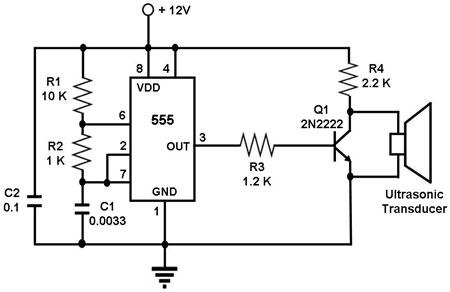
Synchronizing Multiple High-Speed Multiplexed DACs for Transmit Applications
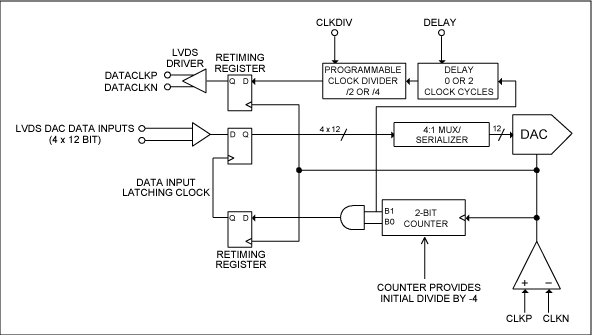
This application note provides insight into how to synchronize multiple high-speed DACs in transmitter applications.
This document outlines the techniques and methodologies for synchronizing multiple high-speed Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs) in various transmitter applications. Synchronization is crucial in systems where multiple DACs are used to ensure that the signal outputs are coherent and aligned in time, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity and performance.
The synchronization process typically involves the use of a common clock signal distributed to all DACs to ensure that they operate in unison. This can be achieved through various methods, including the use of phase-locked loops (PLLs) to generate a stable clock signal, or by utilizing a master-slave configuration where one DAC acts as the master clock source for the others.
In addition to clock synchronization, the application note may also cover techniques for managing data alignment between the DACs. This can involve buffering data streams to ensure that they are processed simultaneously, thereby preventing any potential delays that could lead to phase discrepancies in the output signals.
Furthermore, the document may discuss the importance of considering the layout and design of the PCB when implementing multiple DACs. Proper grounding, power distribution, and signal routing are critical to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the synchronized DACs.
The application note serves as a valuable resource for engineers and designers working with high-speed DACs in transmitter applications, providing practical guidance on achieving effective synchronization to enhance overall system performance.This application note provides insight into how synchronize multiple multiplext high-speed DACs in transmitter applications.. 🔗 External reference
This document outlines the techniques and methodologies for synchronizing multiple high-speed Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs) in various transmitter applications. Synchronization is crucial in systems where multiple DACs are used to ensure that the signal outputs are coherent and aligned in time, which is essential for maintaining signal integrity and performance.
The synchronization process typically involves the use of a common clock signal distributed to all DACs to ensure that they operate in unison. This can be achieved through various methods, including the use of phase-locked loops (PLLs) to generate a stable clock signal, or by utilizing a master-slave configuration where one DAC acts as the master clock source for the others.
In addition to clock synchronization, the application note may also cover techniques for managing data alignment between the DACs. This can involve buffering data streams to ensure that they are processed simultaneously, thereby preventing any potential delays that could lead to phase discrepancies in the output signals.
Furthermore, the document may discuss the importance of considering the layout and design of the PCB when implementing multiple DACs. Proper grounding, power distribution, and signal routing are critical to minimize noise and interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the synchronized DACs.
The application note serves as a valuable resource for engineers and designers working with high-speed DACs in transmitter applications, providing practical guidance on achieving effective synchronization to enhance overall system performance.This application note provides insight into how synchronize multiple multiplext high-speed DACs in transmitter applications.. 🔗 External reference