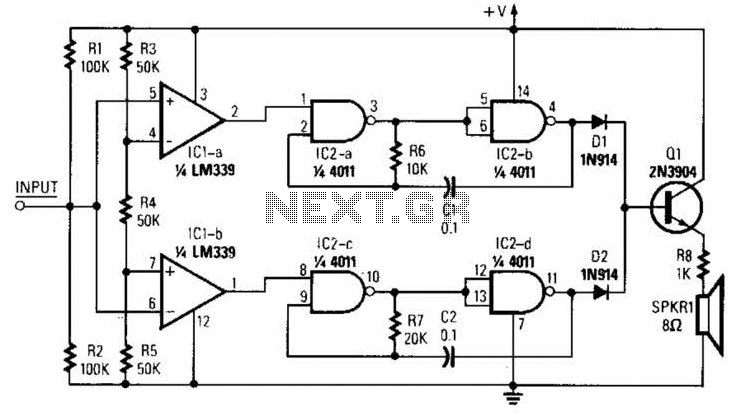
XTR112 114 isolated transmit receive circuit diagram of the ring
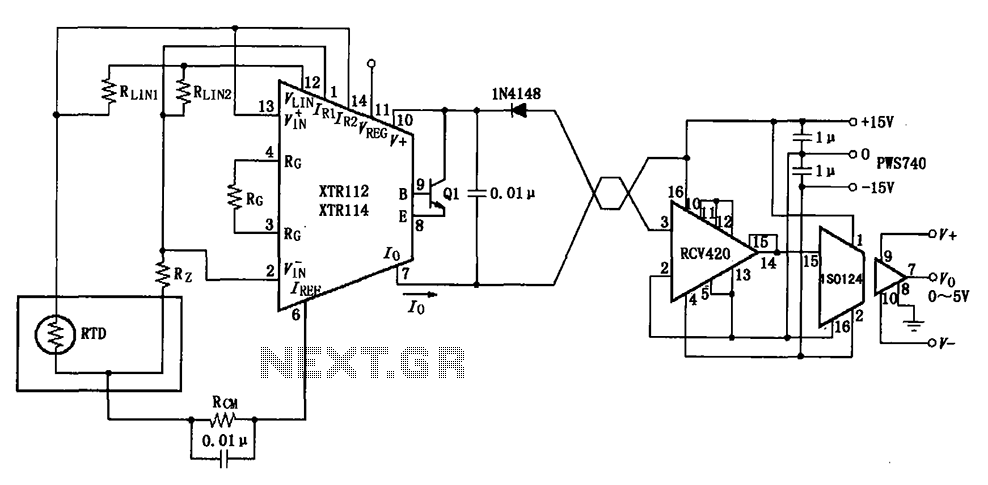
The RTD temperature data collected at the scene is converted into a voltage using the XTR112/114. This voltage is further transformed into a 4 to 20 mA current output, which is then transmitted via a twisted pair. The RCV420 receives the signal, and an ISO124 isolation amplifier is utilized to provide an output of 0 to 5V. The circuit exhibits excellent anti-jamming performance, making it suitable for long-distance transmission in environments with significant interference. The schematic illustrates a three-wire RTD connection; if a two-wire RTD is used, RLIN2 should be removed.
The circuit design begins with the RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), which is a temperature sensor that provides a resistance change proportional to temperature. The XTR112/114 is an integrated circuit specifically designed for converting the resistance change from the RTD into a corresponding voltage signal. This voltage is then converted into a standard 4 to 20 mA current loop output, which is a common industrial standard for signal transmission, allowing for long-distance signal integrity.
The twisted pair wiring used for transmission minimizes electromagnetic interference, which is crucial in industrial environments. Upon reaching the receiving end, the RCV420 module is employed to capture the 4 to 20 mA signal, ensuring that the signal is accurately interpreted. The ISO124 isolation amplifier serves to electrically isolate the output from the input, providing protection against surges and noise, and converting the current signal into a 0 to 5V voltage output suitable for further processing or display.
The circuit's design incorporates robust anti-jamming features, making it ideal for use in environments with substantial electrical noise, such as factories or near heavy machinery. The inclusion of a three-wire RTD configuration in the schematic allows for improved accuracy by compensating for lead resistance. In cases where a two-wire RTD is implemented, the design stipulates the removal of the RLIN2 resistor to maintain proper functionality and accuracy. This adaptability enhances the circuit's versatility in various applications, ensuring reliable temperature measurement and monitoring. As shown, collected at the scene RTD temperature, it is converted into a voltage by the XTR112/114 voltage is converted into 4 ~ 20mA current output, and then the twisted pair transmission, RCV420 reception, isolation amplifier ISO124 isolation amplifier, the output 0 ~ 5V voltage. Excellent anti-jamming performance of the circuit can be applied to long-distance transmission interference or big occasions.
The figure for the three-wire RTD connection, if the connection with the two-wire RTD, then remove RLIN2.
The circuit design begins with the RTD (Resistance Temperature Detector), which is a temperature sensor that provides a resistance change proportional to temperature. The XTR112/114 is an integrated circuit specifically designed for converting the resistance change from the RTD into a corresponding voltage signal. This voltage is then converted into a standard 4 to 20 mA current loop output, which is a common industrial standard for signal transmission, allowing for long-distance signal integrity.
The twisted pair wiring used for transmission minimizes electromagnetic interference, which is crucial in industrial environments. Upon reaching the receiving end, the RCV420 module is employed to capture the 4 to 20 mA signal, ensuring that the signal is accurately interpreted. The ISO124 isolation amplifier serves to electrically isolate the output from the input, providing protection against surges and noise, and converting the current signal into a 0 to 5V voltage output suitable for further processing or display.
The circuit's design incorporates robust anti-jamming features, making it ideal for use in environments with substantial electrical noise, such as factories or near heavy machinery. The inclusion of a three-wire RTD configuration in the schematic allows for improved accuracy by compensating for lead resistance. In cases where a two-wire RTD is implemented, the design stipulates the removal of the RLIN2 resistor to maintain proper functionality and accuracy. This adaptability enhances the circuit's versatility in various applications, ensuring reliable temperature measurement and monitoring. As shown, collected at the scene RTD temperature, it is converted into a voltage by the XTR112/114 voltage is converted into 4 ~ 20mA current output, and then the twisted pair transmission, RCV420 reception, isolation amplifier ISO124 isolation amplifier, the output 0 ~ 5V voltage. Excellent anti-jamming performance of the circuit can be applied to long-distance transmission interference or big occasions.
The figure for the three-wire RTD connection, if the connection with the two-wire RTD, then remove RLIN2.