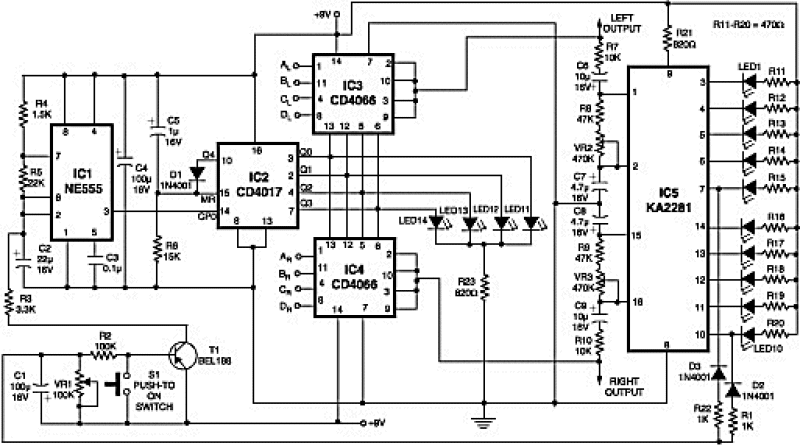
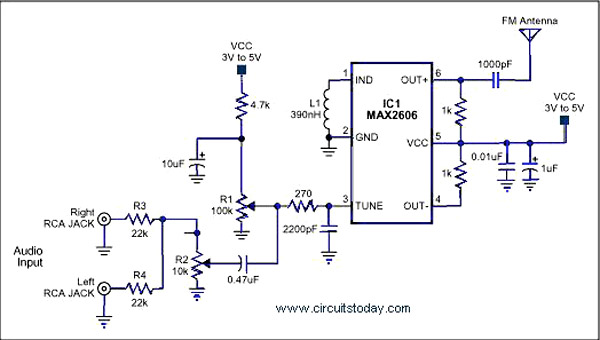
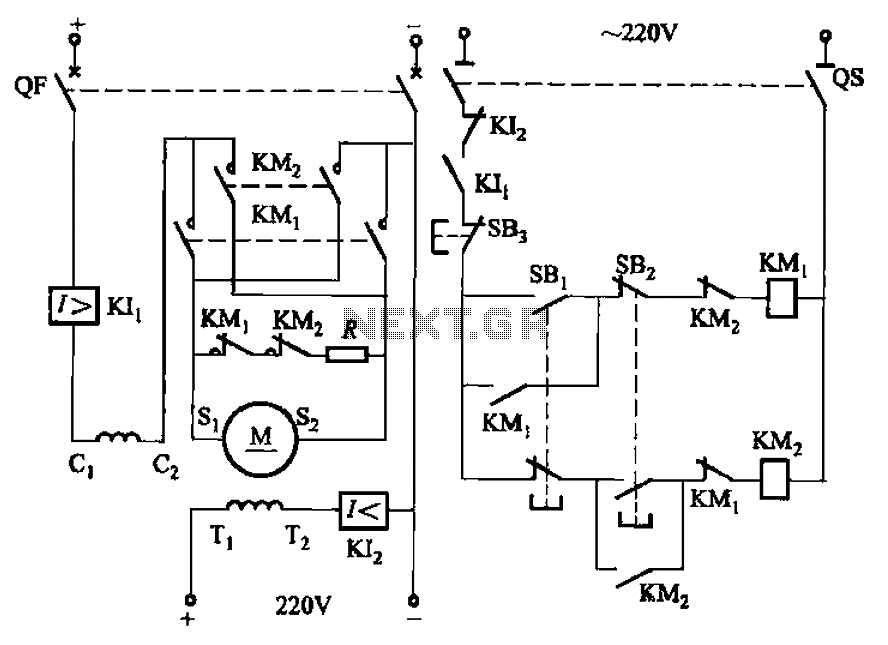
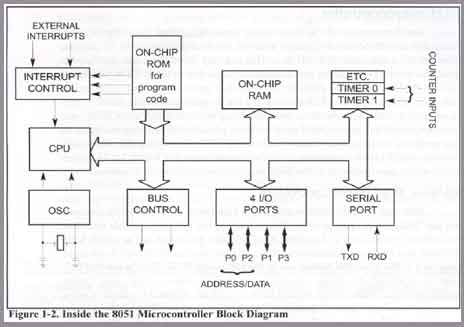
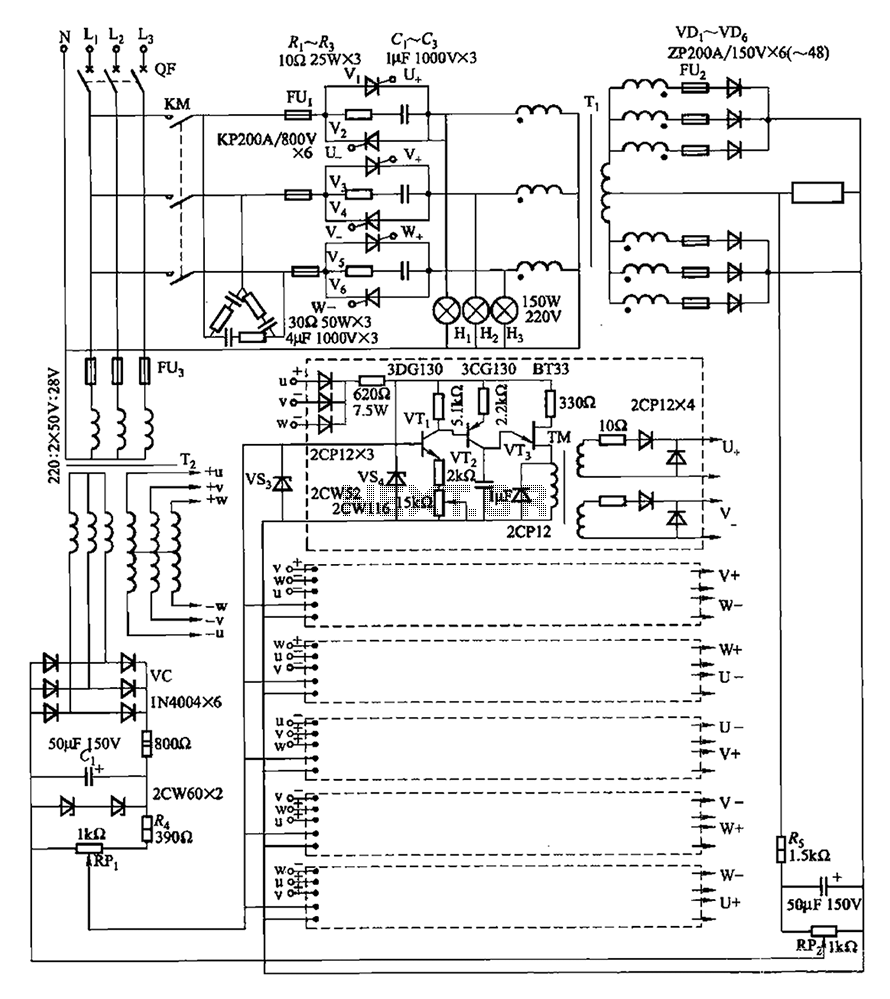
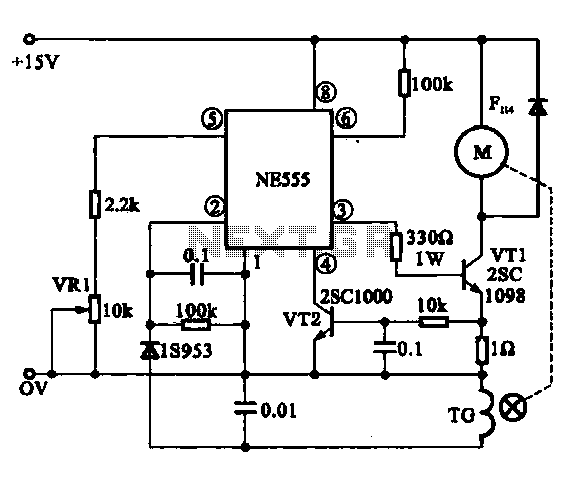
Simple dimming lights circuit diagram
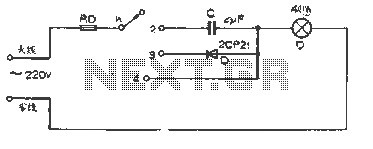
The figure illustrates a basic dimming lights circuit. The light intensity is controlled by a multi-speed control switch, designated as K. When switch K is set to position "1," the lights are turned off. In position "2," the light emits a shimmering effect due to a capacitive connection. At position "3," the circuit utilizes half-wave rectification through a diode, supplying approximately half the usual power to the lamp, resulting in reduced brightness. Finally, when K is set to position "4," the lamp operates at its rated voltage, achieving maximum brightness.
This circuit employs a multi-speed control switch to adjust the brightness of a connected lamp through various operational modes. The switch K allows for four distinct settings, each altering the electrical characteristics supplied to the lamp.
In position "1," the circuit is open, effectively disconnecting the power supply from the lamp and resulting in no light output. This position is useful for completely turning off the lamp without needing to unplug it.
Position "2" introduces a capacitive coupling, which allows a small amount of current to pass through, creating a shimmering light effect. This is achieved by using a capacitor in series with the lamp, which charges and discharges, providing an alternating current (AC) effect that gives the lamp a flickering appearance. This setting can be particularly useful for decorative lighting or ambiance.
In position "3," the circuit employs a diode for half-wave rectification. The diode permits current to flow in only one direction, effectively reducing the power supplied to the lamp to about 50% of its rated value. This results in a dimmer light output, suitable for situations where less brightness is desired while still maintaining a steady light without flickering.
Position "4" connects the lamp directly to the power supply at its rated voltage, allowing it to operate at full brightness. This configuration is ideal for scenarios requiring maximum illumination, such as in workspaces or areas needing bright lighting.
Overall, this dimming circuit provides versatility in light control, allowing users to select the desired brightness level according to their needs. The use of capacitive coupling and rectification techniques ensures that different light effects can be achieved while maintaining simplicity in the circuit design.The figure is a simple dimming lights line, the light is adjusted by the multi-speed control switch K. When K to position "1" lights out; when K to position "2", the light shimmering through the capacitive connection; when K to position "3", the half-wave rectified by the diode power to the lamp power supply, lamp brightness about half the usual; when K to position "4", the lamp at rated voltage, the brightness of the brightest.
This circuit employs a multi-speed control switch to adjust the brightness of a connected lamp through various operational modes. The switch K allows for four distinct settings, each altering the electrical characteristics supplied to the lamp.
In position "1," the circuit is open, effectively disconnecting the power supply from the lamp and resulting in no light output. This position is useful for completely turning off the lamp without needing to unplug it.
Position "2" introduces a capacitive coupling, which allows a small amount of current to pass through, creating a shimmering light effect. This is achieved by using a capacitor in series with the lamp, which charges and discharges, providing an alternating current (AC) effect that gives the lamp a flickering appearance. This setting can be particularly useful for decorative lighting or ambiance.
In position "3," the circuit employs a diode for half-wave rectification. The diode permits current to flow in only one direction, effectively reducing the power supplied to the lamp to about 50% of its rated value. This results in a dimmer light output, suitable for situations where less brightness is desired while still maintaining a steady light without flickering.
Position "4" connects the lamp directly to the power supply at its rated voltage, allowing it to operate at full brightness. This configuration is ideal for scenarios requiring maximum illumination, such as in workspaces or areas needing bright lighting.
Overall, this dimming circuit provides versatility in light control, allowing users to select the desired brightness level according to their needs. The use of capacitive coupling and rectification techniques ensures that different light effects can be achieved while maintaining simplicity in the circuit design.The figure is a simple dimming lights line, the light is adjusted by the multi-speed control switch K. When K to position "1" lights out; when K to position "2", the light shimmering through the capacitive connection; when K to position "3", the half-wave rectified by the diode power to the lamp power supply, lamp brightness about half the usual; when K to position "4", the lamp at rated voltage, the brightness of the brightest.