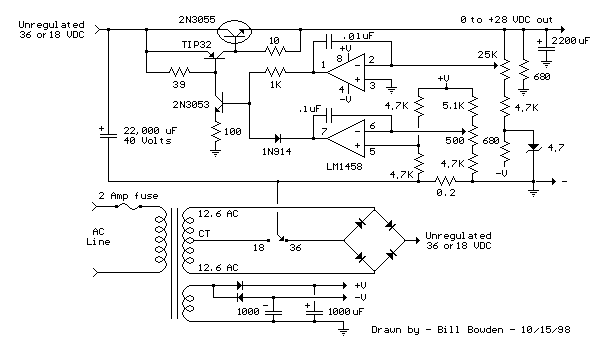
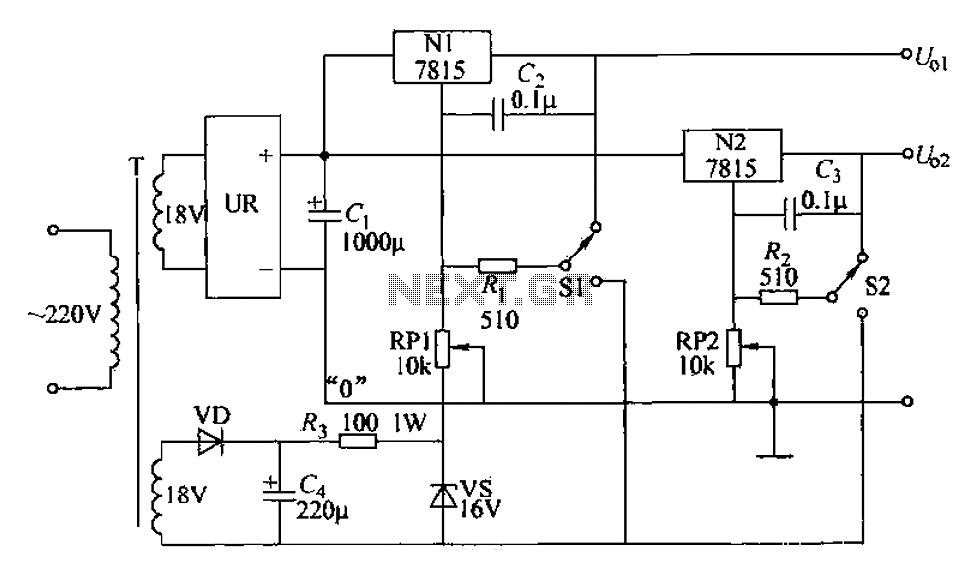
Temperature compensation of the symmetrical power supply 7812 F007C

The circuit is a temperature-compensated power supply that generates a negative voltage to track positive voltage changes in a symmetrical voltage integrated power supply. It features a three-terminal regulator connected with two identical transistors, leveraging the temperature characteristics of the transistor PN junction for temperature compensation. This results in a positive voltage output that exhibits high temperature stability and accuracy. The circuit employs an operational amplifier and the F007C regulator (BG4, 3AD30B) to ensure that the negative voltage accurately follows the positive voltage variations, maintaining strict symmetry and high accuracy in the output voltages. This power supply is designed for applications requiring precise symmetry between positive and negative voltage levels in advanced electronic circuits.
The described circuit operates as a precision voltage regulator, utilizing a combination of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) for temperature compensation. The two transistors are configured in a way that their temperature coefficients offset each other, minimizing drift in the output voltage due to temperature variations. This configuration is critical in applications where voltage stability is paramount, such as in analog signal processing and precision measurement systems.
The operational amplifier in this circuit serves as a feedback controller, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and responds accurately to changes in load conditions. By employing the F007C regulator, which is known for its low dropout voltage and high output current capability, the circuit can maintain regulation even under varying input conditions. The symmetrical output makes this design particularly advantageous for differential signaling applications, where both positive and negative voltages are required to maintain signal integrity.
In summary, this temperature-compensated power supply circuit is a robust solution for providing stable and symmetrical voltage outputs, making it ideal for high-precision electronic applications. Its design ensures that both the positive and negative outputs are tightly regulated and maintain high accuracy across a range of operating temperatures. As shown in Figure it is a temperature compensated with a negative voltage to follow the positive changes in the symmetrical voltage integrated power supply. This circuit is ch aracterized by: three-terminal regulator regulator circuit is connected with two of the same type transistors, using the temperature characteristics of the transistor PN junction temperature compensation with each other, so that a positive voltage output of the power supply has a high temperature stability and accuracy. Utilize the op amp and F007C regulator BG4 (3AD30B), the negative voltage accurately tracks the positive voltage changes, so that the positive and negative output voltage strictly symmetrical, and has a high accuracy.
The power supply is suitable for the symmetry of the positive and negative voltage requirements for higher electronic circuits.
The described circuit operates as a precision voltage regulator, utilizing a combination of bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) for temperature compensation. The two transistors are configured in a way that their temperature coefficients offset each other, minimizing drift in the output voltage due to temperature variations. This configuration is critical in applications where voltage stability is paramount, such as in analog signal processing and precision measurement systems.
The operational amplifier in this circuit serves as a feedback controller, ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and responds accurately to changes in load conditions. By employing the F007C regulator, which is known for its low dropout voltage and high output current capability, the circuit can maintain regulation even under varying input conditions. The symmetrical output makes this design particularly advantageous for differential signaling applications, where both positive and negative voltages are required to maintain signal integrity.
In summary, this temperature-compensated power supply circuit is a robust solution for providing stable and symmetrical voltage outputs, making it ideal for high-precision electronic applications. Its design ensures that both the positive and negative outputs are tightly regulated and maintain high accuracy across a range of operating temperatures. As shown in Figure it is a temperature compensated with a negative voltage to follow the positive changes in the symmetrical voltage integrated power supply. This circuit is ch aracterized by: three-terminal regulator regulator circuit is connected with two of the same type transistors, using the temperature characteristics of the transistor PN junction temperature compensation with each other, so that a positive voltage output of the power supply has a high temperature stability and accuracy. Utilize the op amp and F007C regulator BG4 (3AD30B), the negative voltage accurately tracks the positive voltage changes, so that the positive and negative output voltage strictly symmetrical, and has a high accuracy.
The power supply is suitable for the symmetry of the positive and negative voltage requirements for higher electronic circuits.