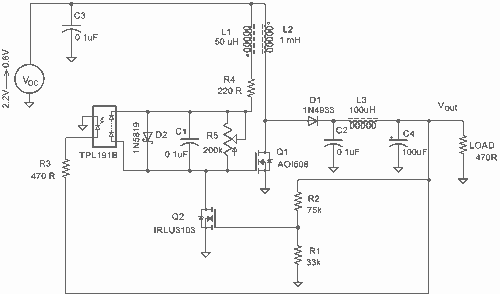
temperature detection voltage-frequency switch circuit
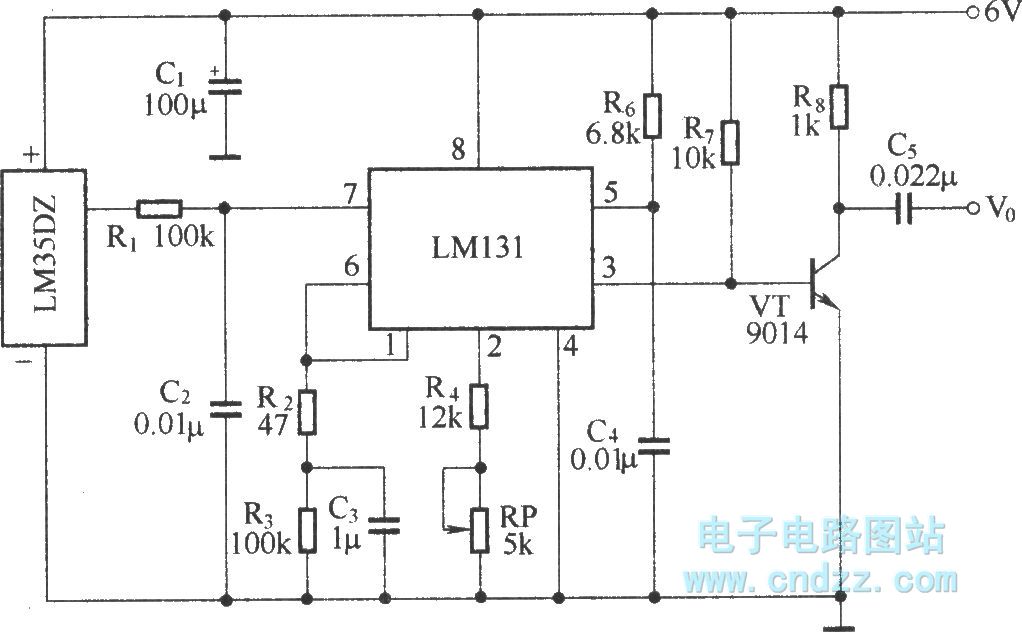
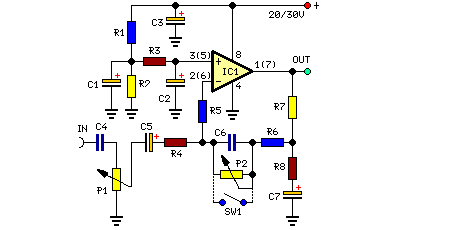
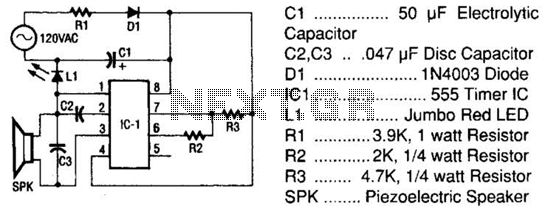
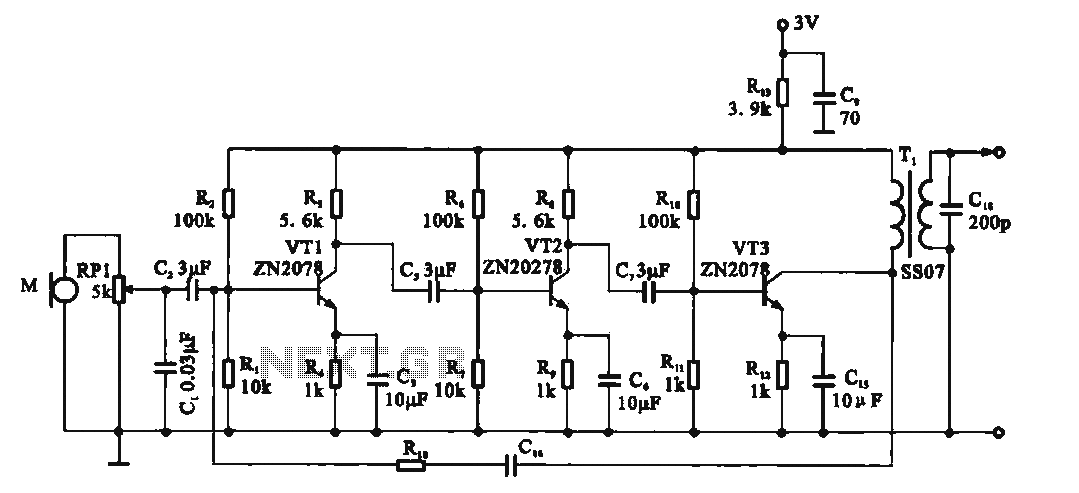
The circuit depicted in the figure integrates a temperature detection system, a temperature-voltage switch, and a voltage-frequency switch to enable remote temperature monitoring. This circuit is connected to a wireless transmission circuit, creating a remote control temperature detection system. The temperature detection and temperature-voltage switch utilize integrated components.
The described circuit serves as a comprehensive solution for remote temperature monitoring applications. The temperature detection component typically employs a thermistor or a thermocouple to sense temperature changes. These sensors produce an analog signal that corresponds to the temperature, which is then processed by the temperature-voltage switch. This switch converts the analog signal into a proportional voltage level, suitable for further processing or transmission.
The voltage-frequency switch is responsible for modulating the output signal into a frequency-based format. This modulation is crucial for wireless transmission, as it allows the signal to be sent over longer distances with reduced interference. The integration of these components ensures that temperature readings are converted into a format that can be easily transmitted and subsequently received by a remote monitoring system.
To enhance the reliability of the circuit, additional features such as noise filtering and signal amplification may be included. Noise filtering can be achieved through the use of capacitors and inductors, which help to stabilize the output signal. Signal amplification can be accomplished using operational amplifiers, ensuring that the transmitted signal maintains its integrity over long distances.
In summary, this circuit design effectively combines temperature sensing, signal conditioning, and wireless transmission to facilitate remote temperature monitoring. Its modular approach allows for easy integration into various applications, from industrial monitoring systems to consumer electronics.As shown in the figure, the temperature detection, temperature-voltage switch and voltage-frequency switch circuit is used to remote detect temperature. We connect the circuit and wireless transmitting circuit forming a temperature detection remote control transmitting circuit.
In the circuit, temperature detection and temperature-voltage switch adopt integr.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit serves as a comprehensive solution for remote temperature monitoring applications. The temperature detection component typically employs a thermistor or a thermocouple to sense temperature changes. These sensors produce an analog signal that corresponds to the temperature, which is then processed by the temperature-voltage switch. This switch converts the analog signal into a proportional voltage level, suitable for further processing or transmission.
The voltage-frequency switch is responsible for modulating the output signal into a frequency-based format. This modulation is crucial for wireless transmission, as it allows the signal to be sent over longer distances with reduced interference. The integration of these components ensures that temperature readings are converted into a format that can be easily transmitted and subsequently received by a remote monitoring system.
To enhance the reliability of the circuit, additional features such as noise filtering and signal amplification may be included. Noise filtering can be achieved through the use of capacitors and inductors, which help to stabilize the output signal. Signal amplification can be accomplished using operational amplifiers, ensuring that the transmitted signal maintains its integrity over long distances.
In summary, this circuit design effectively combines temperature sensing, signal conditioning, and wireless transmission to facilitate remote temperature monitoring. Its modular approach allows for easy integration into various applications, from industrial monitoring systems to consumer electronics.As shown in the figure, the temperature detection, temperature-voltage switch and voltage-frequency switch circuit is used to remote detect temperature. We connect the circuit and wireless transmitting circuit forming a temperature detection remote control transmitting circuit.
In the circuit, temperature detection and temperature-voltage switch adopt integr.. 🔗 External reference