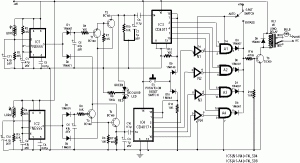
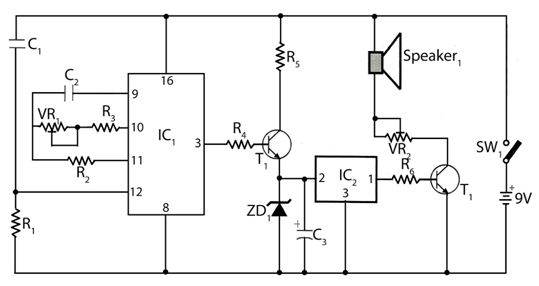
The easiest musical voice lights
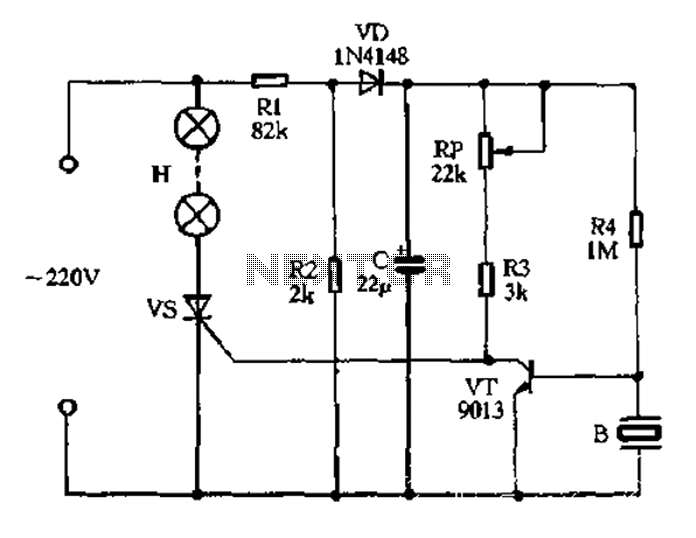
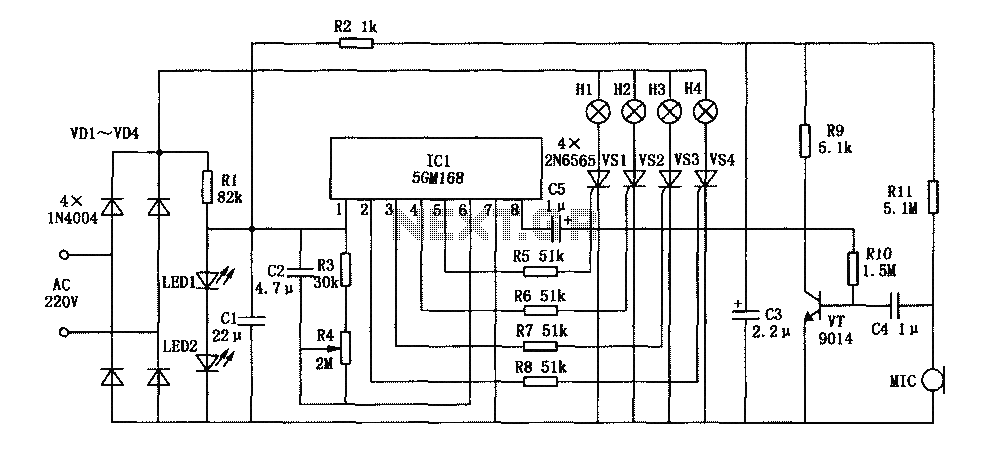
The circuit operates on 220V AC, utilizing resistors R1 and R2 to create a partial voltage drop. A VD half-wave rectifier converts this AC voltage to approximately 3V DC across capacitor C. An adjustment potentiometer RP is incorporated to control the conduction state of tube VT. When VT is in conduction, the SCR gate and cathode have a very short path, preventing trigger current and keeping the circuit in an off state, which results in the color lights being off. The piezoelectric ceramics (designated as B) convert acoustic signals from the environment into corresponding electrical signals. These electrical signals are applied to the base and emitter of transistor VT. During the negative half-cycle of the signal, three diodes conduct, raising the gate potential of SCR vs, which turns it on and illuminates the lights. This allows the lantern to synchronize with music and respond to acoustic signals. The potentiometer RP adjusts the sensitivity of the circuit to sound. When RP is tuned to a lower setting, the conduction depth of transistor VT is shallow, allowing for high sensitivity to sound. Conversely, a higher setting on RP causes deeper saturation of VT, requiring a larger base signal to trigger conduction, resulting in lower sensitivity to sound.
The described circuit is a sound-activated light system that employs basic electronic components to achieve its functionality. The use of resistors R1 and R2 creates a voltage divider, which is essential for stepping down the 220V AC to a manageable level for the rectifier. The half-wave rectifier, denoted by VD, allows only one half of the AC waveform to pass, which is then smoothed by capacitor C to provide a steady DC voltage for the circuit's operation.
The adjustment potentiometer RP serves a critical role in fine-tuning the sensitivity of the sound detection mechanism. By varying the resistance, it alters the voltage at the base of transistor VT, which controls its conduction state. This responsiveness to sound is facilitated by the piezoelectric component B, which efficiently converts acoustic energy into an electrical signal. The interaction between the acoustic signal and the electronic components enables the system to respond dynamically to environmental sounds.
When the system detects a sound, the resulting electrical signal triggers the conduction of the transistor VT, which in turn activates the SCR vs. The SCR acts as a switch that allows current to flow to the light source, illuminating it in response to the detected sound. The configuration of three diodes ensures that the signal is appropriately processed to maintain consistent operation.
This circuit design is suitable for applications such as decorative lighting that responds to music or ambient noise, creating an engaging visual experience. The ability to adjust sensitivity through potentiometer RP allows for customization based on the environment, making it versatile for different settings. Overall, this sound-activated lighting system exemplifies a practical application of basic electronic principles to achieve an interactive and visually appealing effect.220V AC by Rl and R2 partial pressure, VD half-wave rectifier, the capacitor C in the left ends of about 3V DC voltage right. Adjustment potentiometer RP, so that the three-pol e tube VT just in the conduction state, then SCR vs gate and cathode is between the transistor VT ce very short road, vs, no trigger current in the off state, the color lights not bright. B for the piezoelectric ceramics, it receives into the environment after the acoustic signal output corresponding electrical signal, the electrical signal applied to the VT base and emitter, a negative half cycle of the signal so that the three diodes exit conducting state, which set That electrode vs SCR gate potential rises, vs open, lights on the light.
So lantern can with the music and sparkling acoustic environment. Potentiometer RP can be used to adjust the voice sensitivity. RP tune hours, the transistor VT conduction shallow depth, VT easy to withdraw a short guide state, so the voice is high sensitivity {On the contrary, when the big tune RP, VT deep saturation, VT exit to the conduction state needs to enter a larger base signal, dare voice low sensitivity.
The described circuit is a sound-activated light system that employs basic electronic components to achieve its functionality. The use of resistors R1 and R2 creates a voltage divider, which is essential for stepping down the 220V AC to a manageable level for the rectifier. The half-wave rectifier, denoted by VD, allows only one half of the AC waveform to pass, which is then smoothed by capacitor C to provide a steady DC voltage for the circuit's operation.
The adjustment potentiometer RP serves a critical role in fine-tuning the sensitivity of the sound detection mechanism. By varying the resistance, it alters the voltage at the base of transistor VT, which controls its conduction state. This responsiveness to sound is facilitated by the piezoelectric component B, which efficiently converts acoustic energy into an electrical signal. The interaction between the acoustic signal and the electronic components enables the system to respond dynamically to environmental sounds.
When the system detects a sound, the resulting electrical signal triggers the conduction of the transistor VT, which in turn activates the SCR vs. The SCR acts as a switch that allows current to flow to the light source, illuminating it in response to the detected sound. The configuration of three diodes ensures that the signal is appropriately processed to maintain consistent operation.
This circuit design is suitable for applications such as decorative lighting that responds to music or ambient noise, creating an engaging visual experience. The ability to adjust sensitivity through potentiometer RP allows for customization based on the environment, making it versatile for different settings. Overall, this sound-activated lighting system exemplifies a practical application of basic electronic principles to achieve an interactive and visually appealing effect.220V AC by Rl and R2 partial pressure, VD half-wave rectifier, the capacitor C in the left ends of about 3V DC voltage right. Adjustment potentiometer RP, so that the three-pol e tube VT just in the conduction state, then SCR vs gate and cathode is between the transistor VT ce very short road, vs, no trigger current in the off state, the color lights not bright. B for the piezoelectric ceramics, it receives into the environment after the acoustic signal output corresponding electrical signal, the electrical signal applied to the VT base and emitter, a negative half cycle of the signal so that the three diodes exit conducting state, which set That electrode vs SCR gate potential rises, vs open, lights on the light.
So lantern can with the music and sparkling acoustic environment. Potentiometer RP can be used to adjust the voice sensitivity. RP tune hours, the transistor VT conduction shallow depth, VT easy to withdraw a short guide state, so the voice is high sensitivity {On the contrary, when the big tune RP, VT deep saturation, VT exit to the conduction state needs to enter a larger base signal, dare voice low sensitivity.