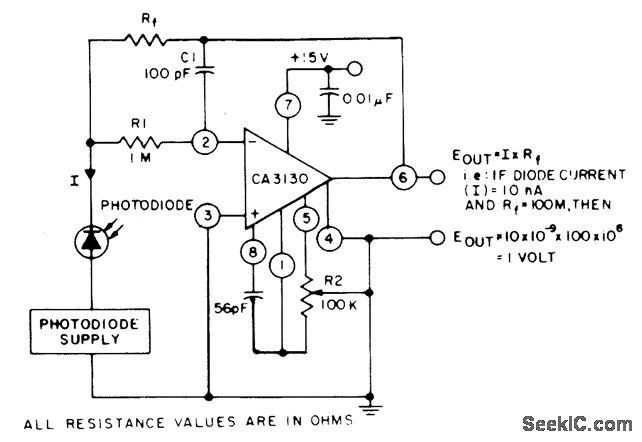
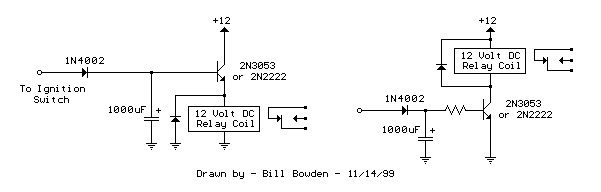
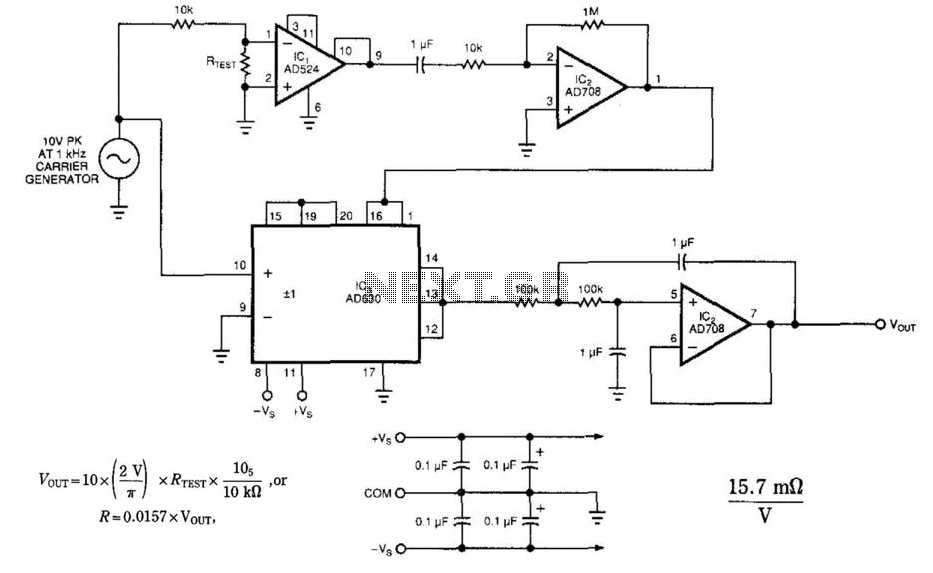
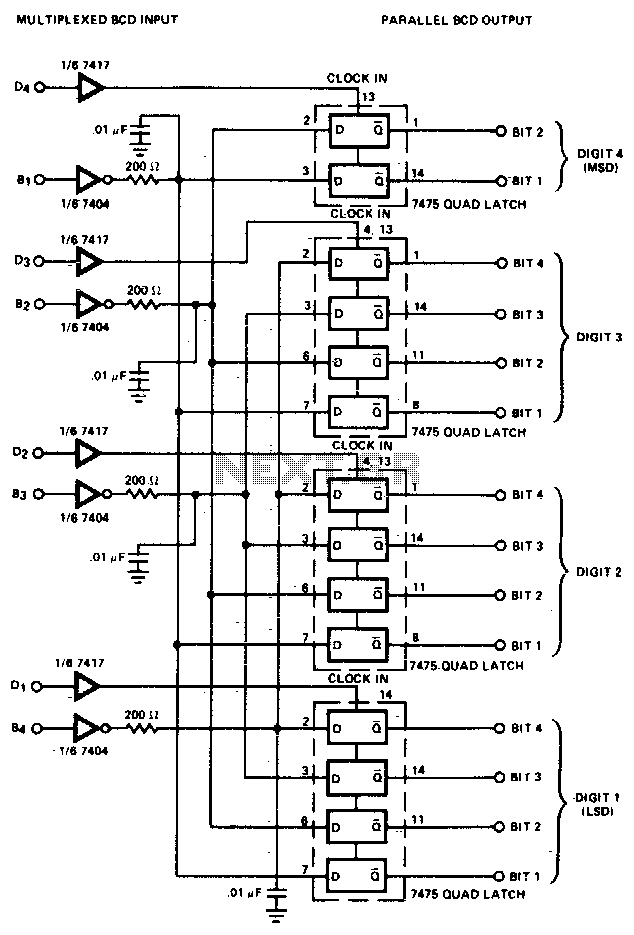
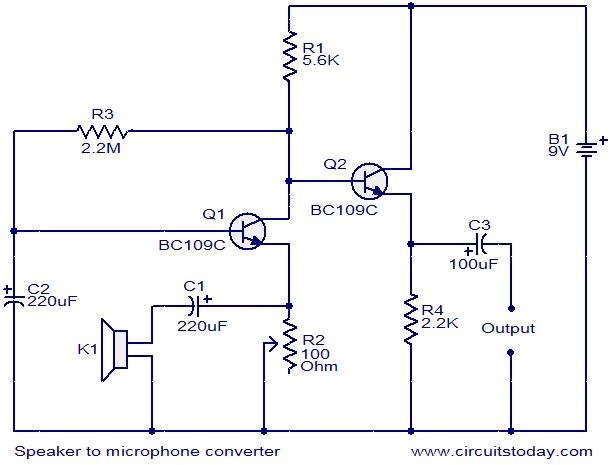
The Effects of Turning off a Converter with Self-Driven Synchronous Rectifiers
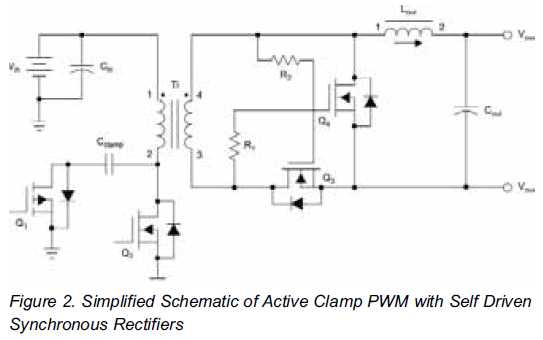
This type of circuit cannot be employed in a load-sharing configuration. Synchronous rectification is one of the most effective methods to enhance the efficiency of low-voltage systems.
Synchronous rectification is a technique employed in power conversion circuits, particularly in DC-DC converters and power supplies, to improve efficiency by reducing conduction losses. Unlike traditional diode rectification, where diodes are used to convert AC to DC, synchronous rectification utilizes active switching devices, typically MOSFETs, to perform the rectification process. This approach significantly minimizes the forward voltage drop associated with diodes, leading to lower power dissipation and improved thermal performance.
In a synchronous rectifier circuit, the control mechanism is crucial for determining the optimal timing for switching the MOSFETs. This is often achieved through feedback loops that monitor the output voltage and adjust the gate signals of the MOSFETs accordingly. The synchronous rectifier operates in conjunction with a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller, which regulates the duty cycle of the switching devices to maintain the desired output voltage level.
The implementation of synchronous rectification is particularly beneficial in low-voltage applications, where the efficiency gains can result in significant power savings and reduced heat generation. However, it is important to note that synchronous rectification circuits typically require more complex control strategies and may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring load-sharing configurations. In such scenarios, careful design considerations must be made to ensure stability and reliability in the power delivery system.This type of circuit can never be used in a load-share configuration Synchronous rectification is one of the best ways to improve the efficiency of the low-voltage.. 🔗 External reference
Synchronous rectification is a technique employed in power conversion circuits, particularly in DC-DC converters and power supplies, to improve efficiency by reducing conduction losses. Unlike traditional diode rectification, where diodes are used to convert AC to DC, synchronous rectification utilizes active switching devices, typically MOSFETs, to perform the rectification process. This approach significantly minimizes the forward voltage drop associated with diodes, leading to lower power dissipation and improved thermal performance.
In a synchronous rectifier circuit, the control mechanism is crucial for determining the optimal timing for switching the MOSFETs. This is often achieved through feedback loops that monitor the output voltage and adjust the gate signals of the MOSFETs accordingly. The synchronous rectifier operates in conjunction with a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller, which regulates the duty cycle of the switching devices to maintain the desired output voltage level.
The implementation of synchronous rectification is particularly beneficial in low-voltage applications, where the efficiency gains can result in significant power savings and reduced heat generation. However, it is important to note that synchronous rectification circuits typically require more complex control strategies and may not be suitable for all applications, particularly those requiring load-sharing configurations. In such scenarios, careful design considerations must be made to ensure stability and reliability in the power delivery system.This type of circuit can never be used in a load-share configuration Synchronous rectification is one of the best ways to improve the efficiency of the low-voltage.. 🔗 External reference