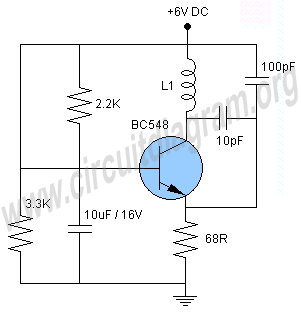
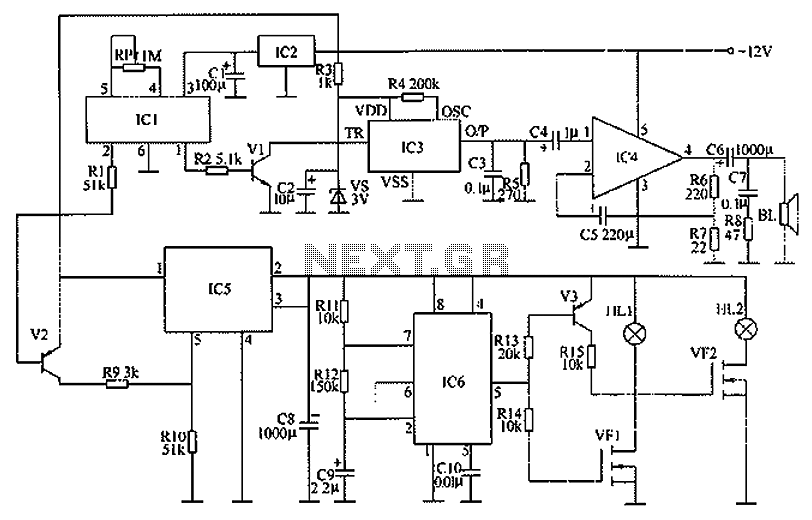
The simplest Metal detector with one BC548

This is the circuit diagram of a low cost metal detector using a single transistor circuit and an old pocket radio. This is nothing but a Colpitts oscillator working in the medium band frequency and a radio tuned to the same frequency. First, the radio and the circuit are placed close. Then the radio is tuned so that there is no sound from the radio. In this condition, the radio and the circuit will be in the same frequency and same frequencies beat off to produce no sound. When the metal detector circuit is placed near to a metal object, the inductance of its coil changes, and so do the frequency of oscillations. Now the two frequencies will be different; there will be no canceling, and the radio produces a hissing sound. The metal is detected. To make L1, make 60 turns of 36SWG enameled Copper wire on a 1 cm PVC tube. Powering the circuit using an adapter rather than a battery induces noise. It is always good to power radio projects from a battery.
The circuit described is a simple yet effective metal detector that utilizes a Colpitts oscillator configuration. The core component of this design is a single transistor, which serves as the active element for generating oscillations. The oscillator operates at medium band frequencies, which are typically around the AM radio frequency range. The circuit is designed to work in conjunction with an old pocket radio, which acts as a receiver for the oscillations produced by the metal detector circuit.
In the initial setup, the radio is tuned to a specific frequency where it does not produce any sound, indicating that it is in resonance with the oscillator circuit. The proximity of the metal detector circuit to a metal object alters the inductance of the coil (L1), which is constructed by winding 60 turns of 36 SWG enameled copper wire around a 1 cm PVC tube. This change in inductance leads to a shift in the frequency of the oscillations generated by the Colpitts oscillator. As a result, the frequency of the metal detector circuit diverges from that of the radio, creating a situation where the two frequencies no longer cancel each other out. This results in the radio producing a hissing sound, which serves as an audible indication that metal has been detected.
It is important to note that powering the circuit with an adapter may introduce unwanted noise, which can interfere with the detection capabilities of the metal detector. Therefore, it is advisable to use a battery as the power source for this project, as it provides a cleaner power supply that enhances the performance of the radio and the metal detector circuit. Overall, this design represents an accessible and practical approach to metal detection, leveraging basic electronic principles and readily available components.This is the circuit diagram of a low cost metal detector using a single transistor circuit and an old pocket radio..This is nothing but a Colpitts oscillator working in the medium band frequency and a radio tuned to the same frequency.First the radio and the circuit are placed close.Then the radio is tuned so that there is no sound from radio.In this condition the radio and the circuit will be in same frequency and same frequencies beat off to produce no sound. This is the set up.When the metal detector circuit is placed near to a metal object the inductance of its coil changes , and so do the frequency of oscillations.Now the two frequency will be different , there will be no canceling and radio produces a hissing sound.The metal is detected. To make L1 make 60 turns of 36SWG enameled Copper wire on a 1 cm PVC tube. Powering the circuit using a adapter rather than a battery induces noise. It is always good to power radio projects from battery. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described is a simple yet effective metal detector that utilizes a Colpitts oscillator configuration. The core component of this design is a single transistor, which serves as the active element for generating oscillations. The oscillator operates at medium band frequencies, which are typically around the AM radio frequency range. The circuit is designed to work in conjunction with an old pocket radio, which acts as a receiver for the oscillations produced by the metal detector circuit.
In the initial setup, the radio is tuned to a specific frequency where it does not produce any sound, indicating that it is in resonance with the oscillator circuit. The proximity of the metal detector circuit to a metal object alters the inductance of the coil (L1), which is constructed by winding 60 turns of 36 SWG enameled copper wire around a 1 cm PVC tube. This change in inductance leads to a shift in the frequency of the oscillations generated by the Colpitts oscillator. As a result, the frequency of the metal detector circuit diverges from that of the radio, creating a situation where the two frequencies no longer cancel each other out. This results in the radio producing a hissing sound, which serves as an audible indication that metal has been detected.
It is important to note that powering the circuit with an adapter may introduce unwanted noise, which can interfere with the detection capabilities of the metal detector. Therefore, it is advisable to use a battery as the power source for this project, as it provides a cleaner power supply that enhances the performance of the radio and the metal detector circuit. Overall, this design represents an accessible and practical approach to metal detection, leveraging basic electronic principles and readily available components.This is the circuit diagram of a low cost metal detector using a single transistor circuit and an old pocket radio..This is nothing but a Colpitts oscillator working in the medium band frequency and a radio tuned to the same frequency.First the radio and the circuit are placed close.Then the radio is tuned so that there is no sound from radio.In this condition the radio and the circuit will be in same frequency and same frequencies beat off to produce no sound. This is the set up.When the metal detector circuit is placed near to a metal object the inductance of its coil changes , and so do the frequency of oscillations.Now the two frequency will be different , there will be no canceling and radio produces a hissing sound.The metal is detected. To make L1 make 60 turns of 36SWG enameled Copper wire on a 1 cm PVC tube. Powering the circuit using a adapter rather than a battery induces noise. It is always good to power radio projects from battery. 🔗 External reference