Thermally Operated Direction Detector

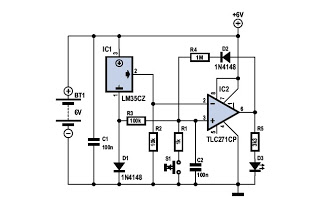
A heat-sensitive sensor can be utilized to create a direction detector. This type of sensor responds to minimal heat. The specific sensor used in this design features a sensitive surface that has been divided into two sections. Consequently, it can differentiate whether heat is approaching from the left or the right. The indication for cold objects is, of course, the opposite. Circuit IC1B provides a symmetric supply. The terminal 's' of the sensor serves as its output. The signal at 's' is amplified in IC1A by a factor of approximately 70 before it is available at the output of the detector. To achieve optimal directivity, it is preferable to position the sensor behind a single narrow slit instead of the conventional raster of a multifaceted mirror. The circuit consumes only a few milliamperes from a 5-V power supply.
The described heat-sensitive sensor direction detector operates based on differential heat detection. The sensor's surface is divided into two distinct areas, allowing it to detect variations in thermal radiation from different directions. When heat sources are detected, the sensor outputs a voltage signal that corresponds to the intensity of heat received by each section of the sensor. This output is then fed into an operational amplifier, IC1A, which amplifies the signal by a factor of 70, ensuring that even minimal changes in heat can be accurately detected and processed.
The output from IC1A can be used to drive additional circuitry, such as an LED indicator or a microcontroller, to provide visual or digital feedback regarding the direction of the detected heat source. The choice of using a single narrow slit instead of a multifaceted mirror enhances the sensor's ability to pinpoint the direction of the heat source more accurately, reducing interference from ambient thermal noise.
The use of a symmetric supply circuit, IC1B, ensures stable operation of the sensor and amplifier, minimizing fluctuations that could affect detection accuracy. The low power consumption of the entire circuit, drawing only a few milliamperes from a 5-V supply, makes it suitable for battery-operated applications, extending the operational life of portable devices utilizing this technology.
In summary, this design effectively leverages the properties of heat-sensitive sensors and amplifiers to create a compact and efficient direction detection system, ideal for applications in security, robotics, or any field requiring thermal monitoring and directional awareness. A heat-sensitive sensor can be used to construct a direction detector. Such a sensor reacts to all an imal heat. The one used in this design has a sensitive surface that has been divided into two. It, therefore, makes a difference, whether the heat approaches from the left or the right. The indication for cold objects is, of course, exactly the opposite. Circuit IC1B forms a symmetric supply. Terminal s of the sensor is its output. The signal at s is amplified in IC1A by a factor of about 70 before it is available at the output of the detector. To obtain good directivity, it is best to place the sensor behind a single narrow slit, rather than behind the usual raster of a multifacetted mirror.
The circuit draws a current of only a few mA from a 5-V supply.
The described heat-sensitive sensor direction detector operates based on differential heat detection. The sensor's surface is divided into two distinct areas, allowing it to detect variations in thermal radiation from different directions. When heat sources are detected, the sensor outputs a voltage signal that corresponds to the intensity of heat received by each section of the sensor. This output is then fed into an operational amplifier, IC1A, which amplifies the signal by a factor of 70, ensuring that even minimal changes in heat can be accurately detected and processed.
The output from IC1A can be used to drive additional circuitry, such as an LED indicator or a microcontroller, to provide visual or digital feedback regarding the direction of the detected heat source. The choice of using a single narrow slit instead of a multifaceted mirror enhances the sensor's ability to pinpoint the direction of the heat source more accurately, reducing interference from ambient thermal noise.
The use of a symmetric supply circuit, IC1B, ensures stable operation of the sensor and amplifier, minimizing fluctuations that could affect detection accuracy. The low power consumption of the entire circuit, drawing only a few milliamperes from a 5-V supply, makes it suitable for battery-operated applications, extending the operational life of portable devices utilizing this technology.
In summary, this design effectively leverages the properties of heat-sensitive sensors and amplifiers to create a compact and efficient direction detection system, ideal for applications in security, robotics, or any field requiring thermal monitoring and directional awareness. A heat-sensitive sensor can be used to construct a direction detector. Such a sensor reacts to all an imal heat. The one used in this design has a sensitive surface that has been divided into two. It, therefore, makes a difference, whether the heat approaches from the left or the right. The indication for cold objects is, of course, exactly the opposite. Circuit IC1B forms a symmetric supply. Terminal s of the sensor is its output. The signal at s is amplified in IC1A by a factor of about 70 before it is available at the output of the detector. To obtain good directivity, it is best to place the sensor behind a single narrow slit, rather than behind the usual raster of a multifacetted mirror.
The circuit draws a current of only a few mA from a 5-V supply.