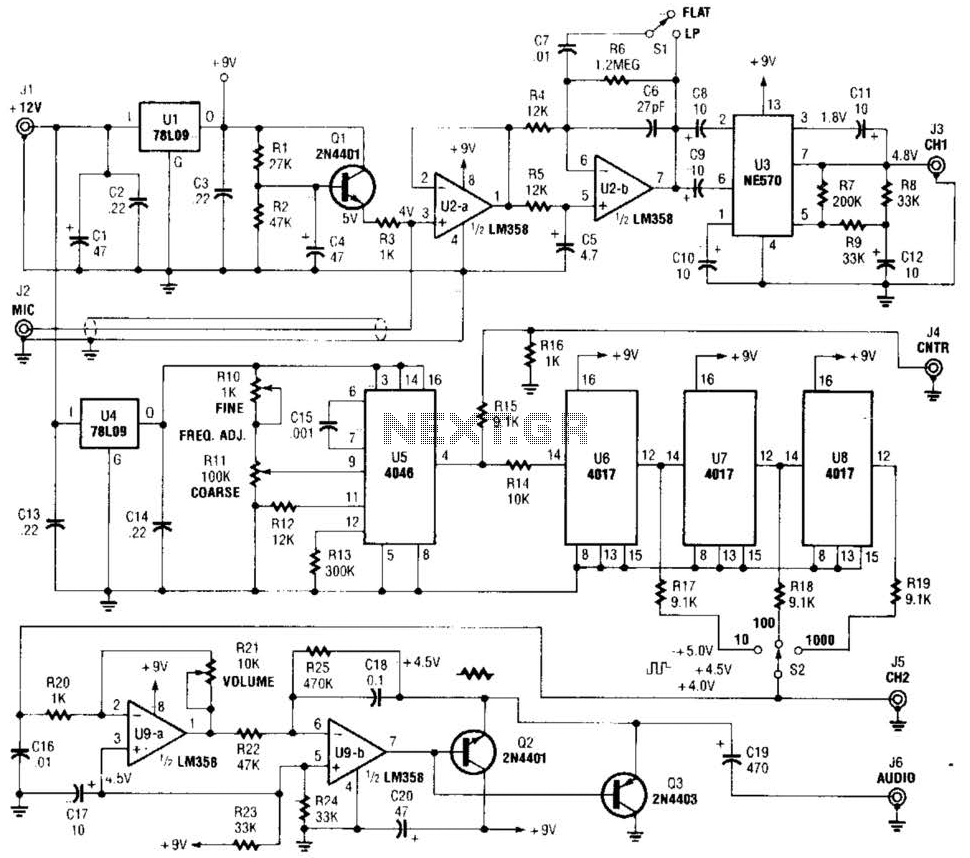
Thermocouple amplifier gain circuit
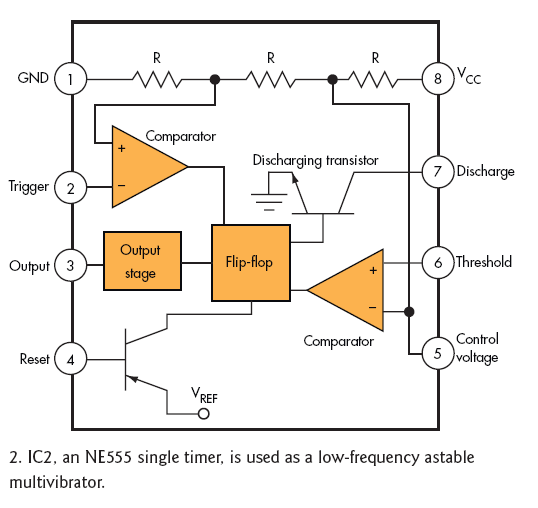
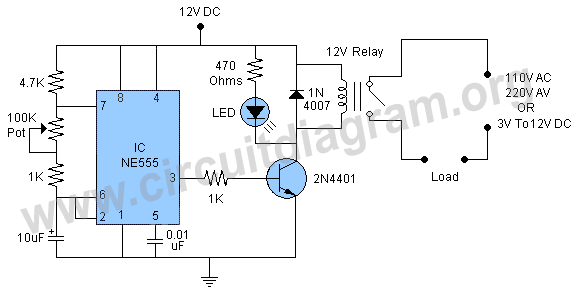
The OP07 is a low drift operational amplifier with a maximum voltage drift of 30 µV/°C and a maximum drift of 0.6 mV/V/°C. It features low noise characteristics with a maximum noise level of 0.6 pV/√Hz, offering ultra-stability with a maximum drift of 0.6 µV/°C over months. The amplifier operates within a wide supply voltage range of ±3V to ±18V. The OP27 and OP07 share similar parameters, as detailed in the accompanying table. Their pin functions are illustrated in Figure LO-1, with the application circuit depicted in the referenced figure. When resistors R3 and R4 are equal, and R1 equals R2, the OP07 can be configured as a differential instrumentation amplifier, with the amplifier gain determined by the ratio of R3 to R1. Figures 10-2 and 10-3 present two configurations of a standard operational amplifier circuit, which retains a structure similar to general operational amplifier designs. This circuit is capable of amplifying the input signal from a sensor and converting it into a 4 to 20 mA current output. The operational amplifier, along with a reference voltage source and output transistors, facilitates this conversion. The input voltage is processed through the operational amplifier, with the V driven by the sampling resistor R6 and the load resistance R1. The relationship between the output current and input voltage is given by the equation I_out = (V_IN * R_s / R_z + 5 * R_s / R_1) / R6, with the specific output current equation being I_out = (16 * V_IN / 100) + 4.0 mA.
The OP07 operational amplifier is designed for precision applications requiring minimal drift and noise, making it suitable for instrumentation and industrial sensor applications. Its low voltage drift and noise specifications ensure that the output remains stable over temperature variations and extended periods, which is critical in environments where accuracy is paramount.
In the differential instrumentation amplifier configuration, the resistors R3 and R1 play a vital role in setting the gain of the amplifier, allowing for fine-tuning of the output based on the specific application requirements. The ability to convert voltage signals into a standard current output (4-20 mA) is particularly beneficial in industrial settings where current loops are commonly used for signal transmission over long distances, minimizing the effects of noise and interference.
The circuit's performance can be further enhanced by selecting precision resistors for R1, R2, R3, and R4, which will help maintain the desired gain accuracy and linearity. Additionally, the choice of the reference voltage source is crucial for ensuring that the output current is consistently within the desired range, particularly under varying load conditions.
Overall, the OP07 operational amplifier, with its low drift, low noise, and flexible configuration options, serves as a robust solution for high-performance analog signal processing tasks in various electronic applications.OP07 low drift (maximum voltage drift 30 FLV, maximum drift 0.6vV / aC), low noise (maximum 0.6 pLVp.P), ultra-stability (maximum 0.6yV / qC. Months), wide supply voltage range (t3 ~ + 18V), high-performance operational amplifiers. OP27 and OP07 closer parameters (see table). Their pin functions shown in Figure LO-l, the application circuit as shown in FIG. When R3: R4, Ri = R2 when, OP07 constitute a differential instrumentation amplifier, the amplifier gain is determined by R3 / RI. Figure 10-2, Figure 10-3 are two cases of common operation amplifier circuit, the circuit configuration of the operational amplifier and the general structure of the same.
The circuit can be amplified input signal of the sensor is converted to 4 ~ 20mA current output circuit mainly by the operational amplifier, a reference voltage source, the output tubes. Input voltage through the operational amplifier, V driven by the sampling resistor R6 , the load resistance Ri.
In the form of a current output. Output current and input voltage relationship between the / ou-r = (VIN Rs / Rz + 5Rs / R,) / R6 according to the figure parameter / ourr = (16VlN / JOO) + 4.O (mA)
The OP07 operational amplifier is designed for precision applications requiring minimal drift and noise, making it suitable for instrumentation and industrial sensor applications. Its low voltage drift and noise specifications ensure that the output remains stable over temperature variations and extended periods, which is critical in environments where accuracy is paramount.
In the differential instrumentation amplifier configuration, the resistors R3 and R1 play a vital role in setting the gain of the amplifier, allowing for fine-tuning of the output based on the specific application requirements. The ability to convert voltage signals into a standard current output (4-20 mA) is particularly beneficial in industrial settings where current loops are commonly used for signal transmission over long distances, minimizing the effects of noise and interference.
The circuit's performance can be further enhanced by selecting precision resistors for R1, R2, R3, and R4, which will help maintain the desired gain accuracy and linearity. Additionally, the choice of the reference voltage source is crucial for ensuring that the output current is consistently within the desired range, particularly under varying load conditions.
Overall, the OP07 operational amplifier, with its low drift, low noise, and flexible configuration options, serves as a robust solution for high-performance analog signal processing tasks in various electronic applications.OP07 low drift (maximum voltage drift 30 FLV, maximum drift 0.6vV / aC), low noise (maximum 0.6 pLVp.P), ultra-stability (maximum 0.6yV / qC. Months), wide supply voltage range (t3 ~ + 18V), high-performance operational amplifiers. OP27 and OP07 closer parameters (see table). Their pin functions shown in Figure LO-l, the application circuit as shown in FIG. When R3: R4, Ri = R2 when, OP07 constitute a differential instrumentation amplifier, the amplifier gain is determined by R3 / RI. Figure 10-2, Figure 10-3 are two cases of common operation amplifier circuit, the circuit configuration of the operational amplifier and the general structure of the same.
The circuit can be amplified input signal of the sensor is converted to 4 ~ 20mA current output circuit mainly by the operational amplifier, a reference voltage source, the output tubes. Input voltage through the operational amplifier, V driven by the sampling resistor R6 , the load resistance Ri.
In the form of a current output. Output current and input voltage relationship between the / ou-r = (VIN Rs / Rz + 5Rs / R,) / R6 according to the figure parameter / ourr = (16VlN / JOO) + 4.O (mA)