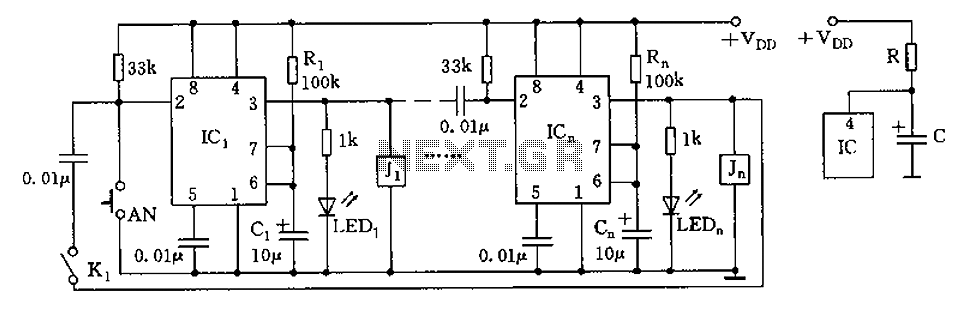
three channel audio splitter
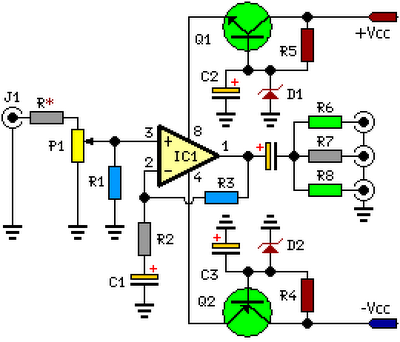
This circuit is designed to amplify and distribute audio signals. The input audio signal is connected to J1 and, after passing through P1, it is buffered and amplified by IC1 for redistribution. It features three outputs that can drive three audio lines with an impedance of 300 ohms.
The circuit operates by first receiving the audio signal at connector J1, which serves as the input interface. The signal then travels through potentiometer P1, allowing for adjustable gain control. This component is crucial for fine-tuning the amplitude of the audio signal before it reaches the amplifier stage.
Following the potentiometer, the signal is directed to integrated circuit IC1, which functions as the main amplification unit. This IC is selected for its ability to provide high fidelity amplification while maintaining low distortion levels. The output from IC1 is split into three separate paths, enabling the circuit to drive multiple audio lines simultaneously. Each output is designed to maintain a consistent impedance of 300 ohms, ensuring compatibility with standard audio equipment and minimizing signal loss.
The circuit may also include bypass capacitors and filtering components to eliminate noise and enhance the overall audio quality. The layout should be carefully designed to minimize interference and ensure stable operation across various audio frequencies. Proper grounding and shielding practices should be implemented to further improve performance and reliability in real-world applications.This circuit is suitable to amplify and distribute the audio signals. The input audio signal is applied to the J1 and after passing through the P1, It is buffered and amplified by the IC1 prepared to redistribute. It has 3 outputs to drive 3 audio lines with 300 ohms impedance.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by first receiving the audio signal at connector J1, which serves as the input interface. The signal then travels through potentiometer P1, allowing for adjustable gain control. This component is crucial for fine-tuning the amplitude of the audio signal before it reaches the amplifier stage.
Following the potentiometer, the signal is directed to integrated circuit IC1, which functions as the main amplification unit. This IC is selected for its ability to provide high fidelity amplification while maintaining low distortion levels. The output from IC1 is split into three separate paths, enabling the circuit to drive multiple audio lines simultaneously. Each output is designed to maintain a consistent impedance of 300 ohms, ensuring compatibility with standard audio equipment and minimizing signal loss.
The circuit may also include bypass capacitors and filtering components to eliminate noise and enhance the overall audio quality. The layout should be carefully designed to minimize interference and ensure stable operation across various audio frequencies. Proper grounding and shielding practices should be implemented to further improve performance and reliability in real-world applications.This circuit is suitable to amplify and distribute the audio signals. The input audio signal is applied to the J1 and after passing through the P1, It is buffered and amplified by the IC1 prepared to redistribute. It has 3 outputs to drive 3 audio lines with 300 ohms impedance.. 🔗 External reference