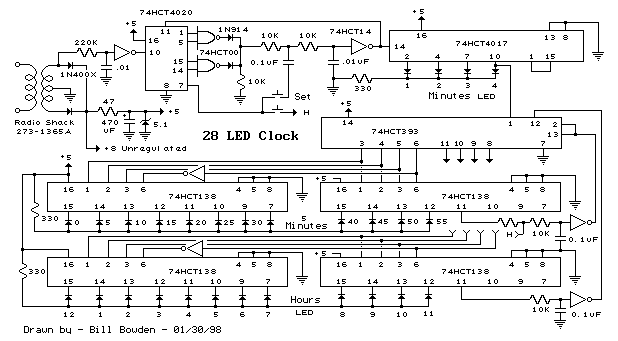
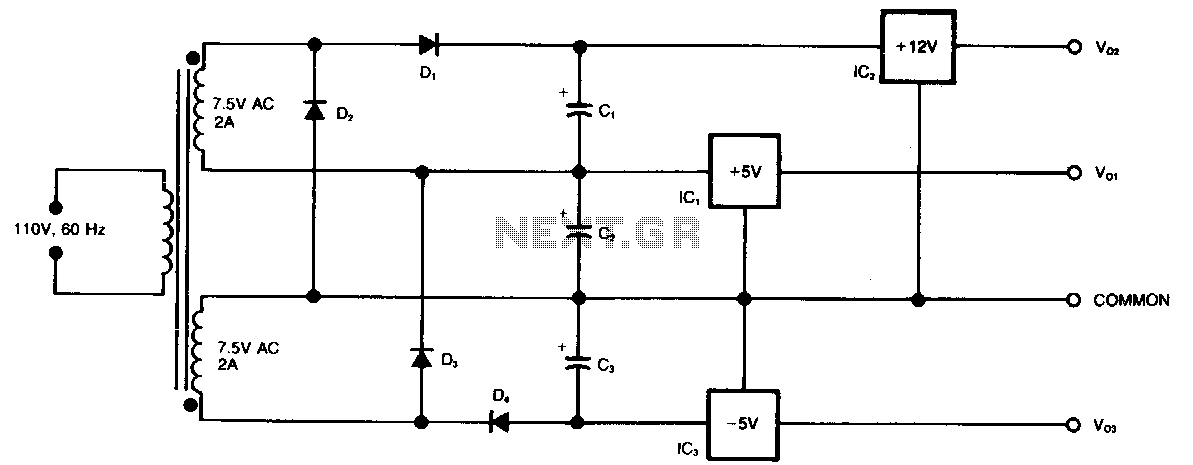
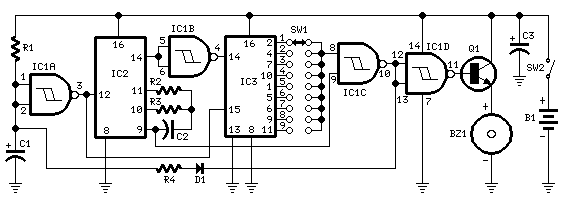
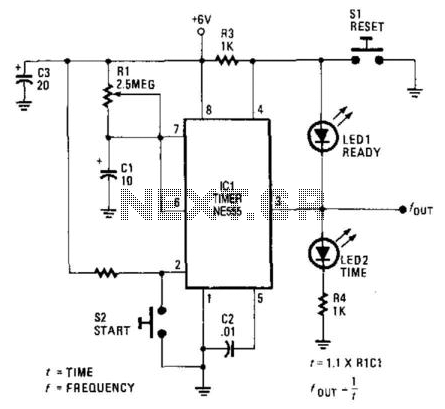
Three Hour Timer

Manufacturers of cordless drills typically recommend a battery charging time of three hours. Once this charging time is complete, the battery must be disconnected from the charger to prevent the risk of overcharging. This circuit, positioned between the charger and the battery socket, mitigates that risk. The relay contact Re1 interrupts the charging current once the three-hour period has elapsed. Additionally, ten LEDs indicate the remaining charging time in increments of 20 minutes. The timer resets each time power is applied, preparing it for a new cycle. When power is supplied, IC3 is reset through C4 and R5. After the designated charging time, Q9 (pin 11) goes high, activating the relay and cutting off the charging current. Q9 connects to the active-low EN (enable) input, ensuring the counter remains in this state. The charging duration can be adjusted from approximately 2 hours 15 minutes to 4 hours 30 minutes using P1. The author configured P1 to 30 k, resulting in a charging time of 3 hours 7 minutes. Increasing the resistance of P1 leads to a shorter charging time. While the timing of the circuit is not highly precise, its accuracy suffices for the intended purpose. It is important to note that the first clock cycle after the circuit is powered on (transitioning from Q0 to Q1) is longer than subsequent cycles due to the need for capacitor C3 to charge to around half the supply voltage.
This circuit serves as an effective battery management system for cordless drill chargers, ensuring safe operation and preventing overcharging. The relay Re1 acts as a crucial component in controlling the charging current, providing a physical disconnection once the battery has been charged for the predetermined duration. The use of ten LEDs for visual feedback is particularly advantageous, as it allows users to monitor charging progress in real-time, enhancing user experience and safety.
The timing mechanism relies on an integrated circuit (IC3) and associated passive components, including resistors (R5) and capacitors (C4 and C3), to create a reliable timing function. The adjustable potentiometer P1 enables customization of the charging duration, accommodating different battery specifications and user preferences. The design acknowledges the inherent limitations of timing accuracy but ensures that the error margin is tolerable for practical applications.
Upon initial power-up, the circuit experiences a unique behavior where the first timing cycle is extended. This phenomenon is due to the charging characteristics of capacitor C3, which must reach a specific voltage level before the timing sequence stabilizes. This characteristic should be considered during the design and testing phases to ensure that the circuit performs optimally under various conditions.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a practical solution for managing battery charging in cordless drills, integrating user-friendly features with essential safety mechanisms.Manufacturers of cordless drills generally recommend a battery charging time of three hours. Once the charging time is up the battery must be disconnected from the charger: if you forget to do this there is a danger of overcharging the battery. This circuit, which sits between the charger circuit and its battery socket, prevents that possibility:
the contact of relay Re1 interrupts the charging current when the three hours are up. Ten LEDs show the remaining charging time in steps of 20 minutes. The timer is reset each time power is applied and it is then ready for a new cycle. When power is applied IC3 is reset via C4 and R5. When the charging time has elapsed, Q9 (pin 11) goes high, which turns the relay on and interrupts the charging current. Since Q9 is connected to the active-low EN (enable) input, the counter will now remain in this state.
The charging time can be adjusted from about 2 hours 15 minutes to 4 hours 30 minutes using P1. The author set P1 to 30 k, giving a charging time of 3 hours 7minutes. The greater the resistance of P1, the shorter the charging time. The timing of the circuit is not particularly precise, but its accuracy is entirely adequate for the job. When adjusting the charging time it is worth noting that therst clock cycle after the circuit is turned on (from Q0 to Q1) is longer than the subsequent ones.
This is because initially capacitor C3 has to be charged to around half the supply voltage. 🔗 External reference
This circuit serves as an effective battery management system for cordless drill chargers, ensuring safe operation and preventing overcharging. The relay Re1 acts as a crucial component in controlling the charging current, providing a physical disconnection once the battery has been charged for the predetermined duration. The use of ten LEDs for visual feedback is particularly advantageous, as it allows users to monitor charging progress in real-time, enhancing user experience and safety.
The timing mechanism relies on an integrated circuit (IC3) and associated passive components, including resistors (R5) and capacitors (C4 and C3), to create a reliable timing function. The adjustable potentiometer P1 enables customization of the charging duration, accommodating different battery specifications and user preferences. The design acknowledges the inherent limitations of timing accuracy but ensures that the error margin is tolerable for practical applications.
Upon initial power-up, the circuit experiences a unique behavior where the first timing cycle is extended. This phenomenon is due to the charging characteristics of capacitor C3, which must reach a specific voltage level before the timing sequence stabilizes. This characteristic should be considered during the design and testing phases to ensure that the circuit performs optimally under various conditions.
Overall, this circuit design exemplifies a practical solution for managing battery charging in cordless drills, integrating user-friendly features with essential safety mechanisms.Manufacturers of cordless drills generally recommend a battery charging time of three hours. Once the charging time is up the battery must be disconnected from the charger: if you forget to do this there is a danger of overcharging the battery. This circuit, which sits between the charger circuit and its battery socket, prevents that possibility:
the contact of relay Re1 interrupts the charging current when the three hours are up. Ten LEDs show the remaining charging time in steps of 20 minutes. The timer is reset each time power is applied and it is then ready for a new cycle. When power is applied IC3 is reset via C4 and R5. When the charging time has elapsed, Q9 (pin 11) goes high, which turns the relay on and interrupts the charging current. Since Q9 is connected to the active-low EN (enable) input, the counter will now remain in this state.
The charging time can be adjusted from about 2 hours 15 minutes to 4 hours 30 minutes using P1. The author set P1 to 30 k, giving a charging time of 3 hours 7minutes. The greater the resistance of P1, the shorter the charging time. The timing of the circuit is not particularly precise, but its accuracy is entirely adequate for the job. When adjusting the charging time it is worth noting that therst clock cycle after the circuit is turned on (from Q0 to Q1) is longer than the subsequent ones.
This is because initially capacitor C3 has to be charged to around half the supply voltage. 🔗 External reference