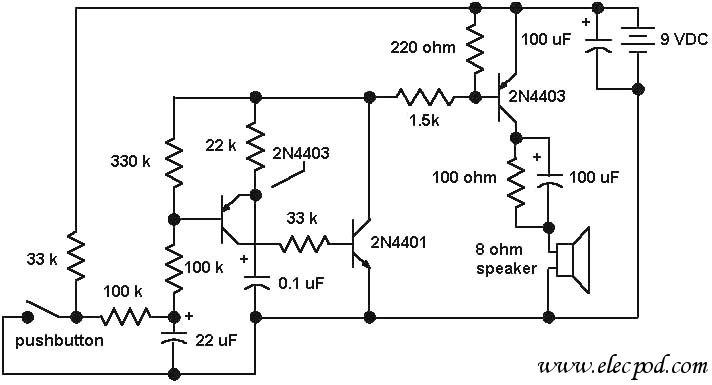
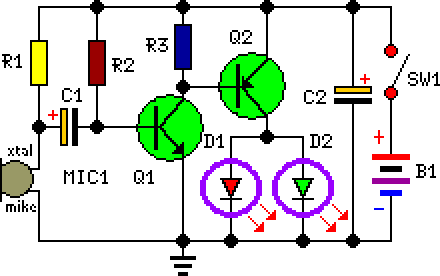
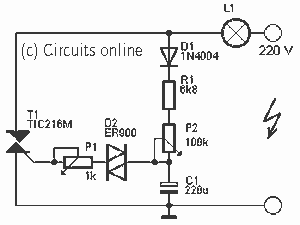
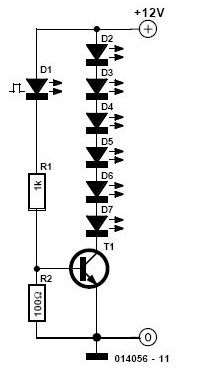
To simulate the Gyralite (dual flashing headlights).
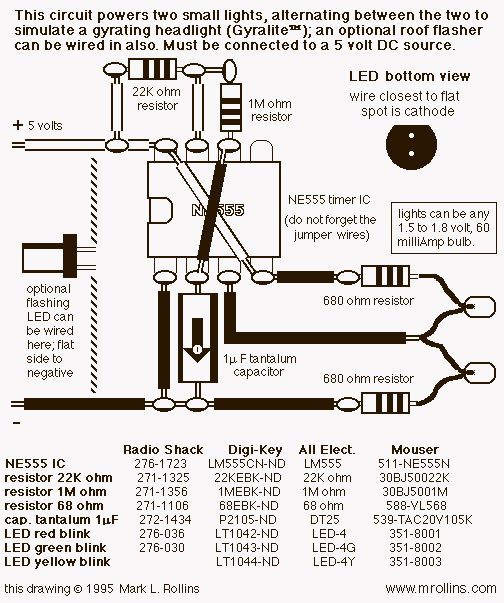
This circuit must be connected to a 5 volt DC source. See my RR page for several 5 volt supplies. Note the flashing LED is optional, but looks so good on the top of a locomotive.
The circuit described is designed to operate from a 5-volt DC power supply, which is a common voltage level for many electronic applications. The circuit may include a flashing LED, which serves as an indicator or decorative element, particularly suitable for model trains or locomotives.
To construct the circuit, a reliable 5-volt DC source should be selected, which can be derived from various power supplies such as voltage regulators, battery packs, or USB power adapters. The power source must be capable of delivering sufficient current for the components in the circuit, especially if multiple LEDs or other devices are used.
The optional flashing LED can be implemented using a simple astable multivibrator circuit, which can be constructed with a 555 timer IC. The 555 timer can be configured to produce a square wave output, causing the LED to turn on and off at a specified rate. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values in the timer circuit.
For the LED itself, it is important to include a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED to prevent excess current from damaging it. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
Overall, this circuit provides a simple yet effective means of adding visual appeal to a model locomotive while ensuring compatibility with standard 5-volt power supplies.This circuit must be connected to a 5 volt DC source. See my RR page for several 5 volt supplies. Note the flashing LED is optional, but looks s-o-o-o-o good on the top of a locomotive. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described is designed to operate from a 5-volt DC power supply, which is a common voltage level for many electronic applications. The circuit may include a flashing LED, which serves as an indicator or decorative element, particularly suitable for model trains or locomotives.
To construct the circuit, a reliable 5-volt DC source should be selected, which can be derived from various power supplies such as voltage regulators, battery packs, or USB power adapters. The power source must be capable of delivering sufficient current for the components in the circuit, especially if multiple LEDs or other devices are used.
The optional flashing LED can be implemented using a simple astable multivibrator circuit, which can be constructed with a 555 timer IC. The 555 timer can be configured to produce a square wave output, causing the LED to turn on and off at a specified rate. The frequency of the flashing can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values in the timer circuit.
For the LED itself, it is important to include a current-limiting resistor in series with the LED to prevent excess current from damaging it. The value of this resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
Overall, this circuit provides a simple yet effective means of adding visual appeal to a model locomotive while ensuring compatibility with standard 5-volt power supplies.This circuit must be connected to a 5 volt DC source. See my RR page for several 5 volt supplies. Note the flashing LED is optional, but looks s-o-o-o-o good on the top of a locomotive. 🔗 External reference