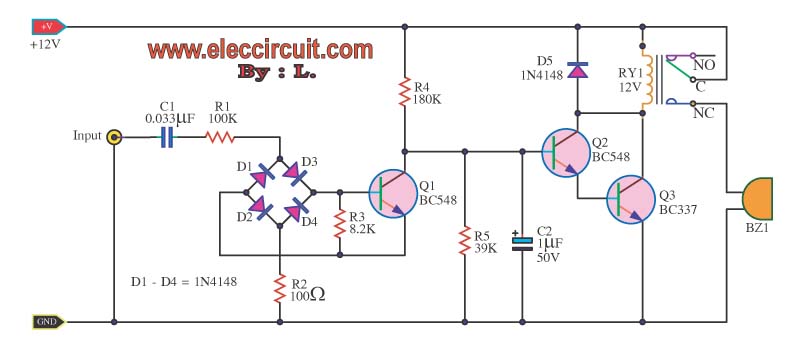
Transistor common emitter amplifier circuit
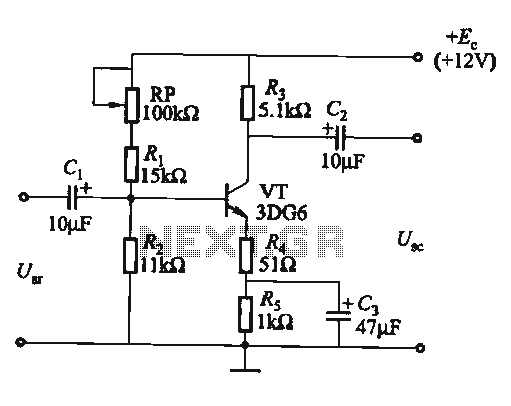
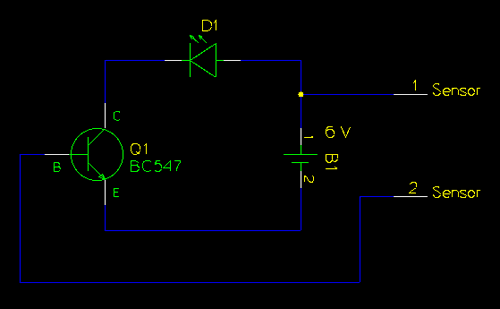
The circuit is a bias circuit for automatic stabilizers that maintains a stable quiescent operating point with good thermal stability. It utilizes a three-pole tube with an NPN type transistor, characterized by a small Iceo. An adjustment potentiometer, RP, is employed to modify the quiescent point. Figure (a) illustrates the use of a sub-pressure emitter bias circuit, while Figure (b) features a thermistor, R, to compensate for variations in the operating point.
The described circuit functions as a biasing mechanism to ensure consistent performance in electronic devices, particularly in amplifiers. The NPN transistor is integral to the operation, as its characteristics, including a low collector-emitter leakage current (Iceo), contribute to improved thermal stability. This stability is crucial in preventing drift in the quiescent operating point due to temperature fluctuations or component aging.
The adjustment potentiometer, RP, allows for fine-tuning of the quiescent point, enabling the circuit to adapt to varying conditions and maintain optimal performance. By adjusting this potentiometer, the user can set the desired operating point to ensure that the transistor operates in its linear region, thereby minimizing distortion and maximizing efficiency.
In Figure (a), the sub-pressure emitter bias circuit is depicted. This configuration typically involves a resistor network that establishes a stable voltage at the emitter of the NPN transistor, which helps to maintain consistent biasing despite changes in supply voltage or temperature. The emitter resistor provides negative feedback, further enhancing stability by reducing the gain as the temperature increases, thus counteracting the effects of thermal runaway.
Figure (b) introduces a thermistor, R, as a temperature-dependent resistor that alters its resistance with temperature changes. This component is crucial for compensating for variations in the operating point caused by thermal effects. As the temperature rises, the thermistor's resistance decreases, which can adjust the biasing conditions dynamically, ensuring that the quiescent point remains stable across a range of operating temperatures.
Overall, this circuit design is essential for applications requiring reliable and stable operation, particularly in environments where temperature variations may impact performance. The combination of an NPN transistor, adjustable potentiometer, and thermistor creates a robust biasing solution that enhances the reliability and efficiency of electronic circuits.Circuit bias circuit automatic stabilizers quiescent operating point, good thermal stability. Three-pole tube with NPN type (Iceo small). Adjustment potentiometer RP can change the quiescent point. Figure (a) use of sub-pressure emitter bias circuit; Fig. (B) thermistor R. To compensate for changes in the operating point.
The described circuit functions as a biasing mechanism to ensure consistent performance in electronic devices, particularly in amplifiers. The NPN transistor is integral to the operation, as its characteristics, including a low collector-emitter leakage current (Iceo), contribute to improved thermal stability. This stability is crucial in preventing drift in the quiescent operating point due to temperature fluctuations or component aging.
The adjustment potentiometer, RP, allows for fine-tuning of the quiescent point, enabling the circuit to adapt to varying conditions and maintain optimal performance. By adjusting this potentiometer, the user can set the desired operating point to ensure that the transistor operates in its linear region, thereby minimizing distortion and maximizing efficiency.
In Figure (a), the sub-pressure emitter bias circuit is depicted. This configuration typically involves a resistor network that establishes a stable voltage at the emitter of the NPN transistor, which helps to maintain consistent biasing despite changes in supply voltage or temperature. The emitter resistor provides negative feedback, further enhancing stability by reducing the gain as the temperature increases, thus counteracting the effects of thermal runaway.
Figure (b) introduces a thermistor, R, as a temperature-dependent resistor that alters its resistance with temperature changes. This component is crucial for compensating for variations in the operating point caused by thermal effects. As the temperature rises, the thermistor's resistance decreases, which can adjust the biasing conditions dynamically, ensuring that the quiescent point remains stable across a range of operating temperatures.
Overall, this circuit design is essential for applications requiring reliable and stable operation, particularly in environments where temperature variations may impact performance. The combination of an NPN transistor, adjustable potentiometer, and thermistor creates a robust biasing solution that enhances the reliability and efficiency of electronic circuits.Circuit bias circuit automatic stabilizers quiescent operating point, good thermal stability. Three-pole tube with NPN type (Iceo small). Adjustment potentiometer RP can change the quiescent point. Figure (a) use of sub-pressure emitter bias circuit; Fig. (B) thermistor R. To compensate for changes in the operating point.