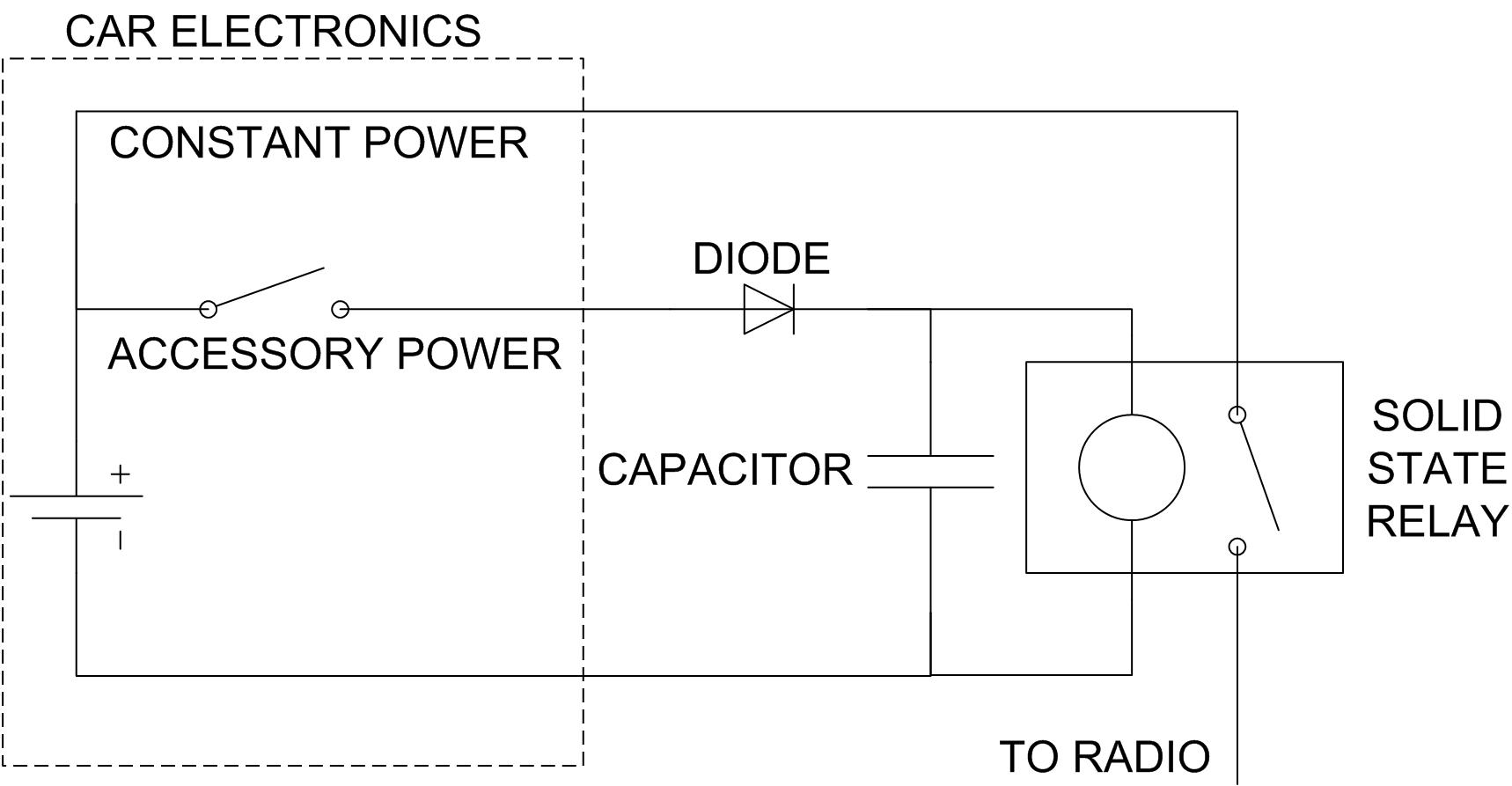
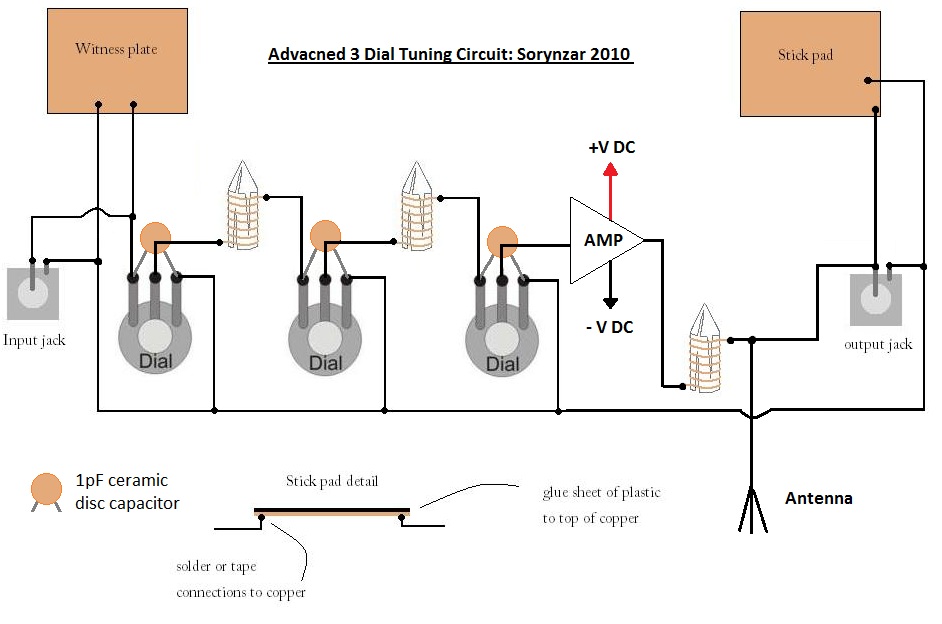
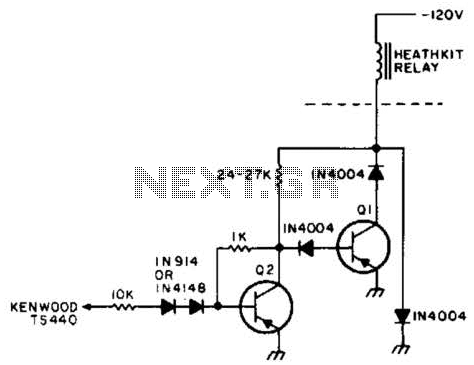
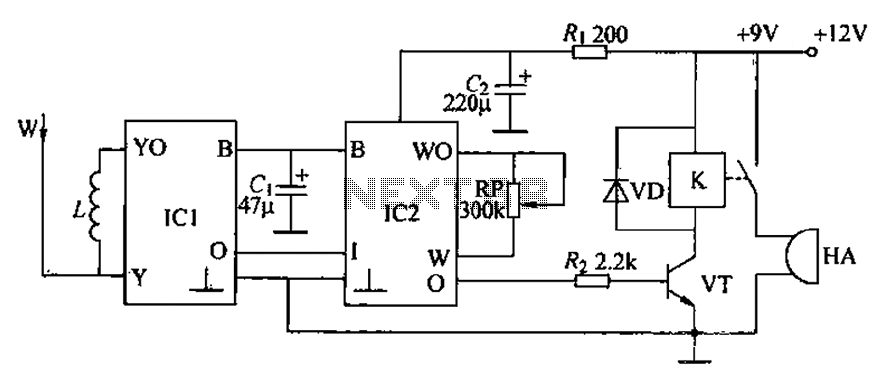
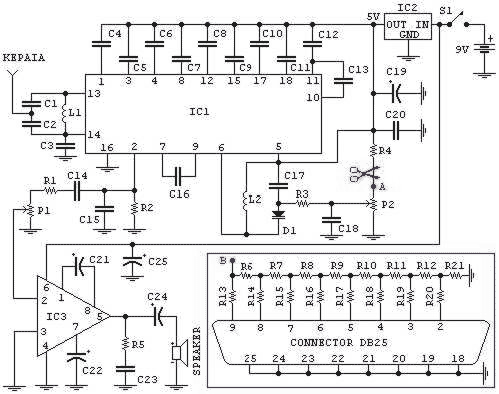
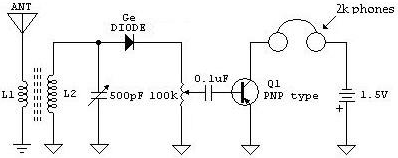
TRANSISTORIZED AM RADIO
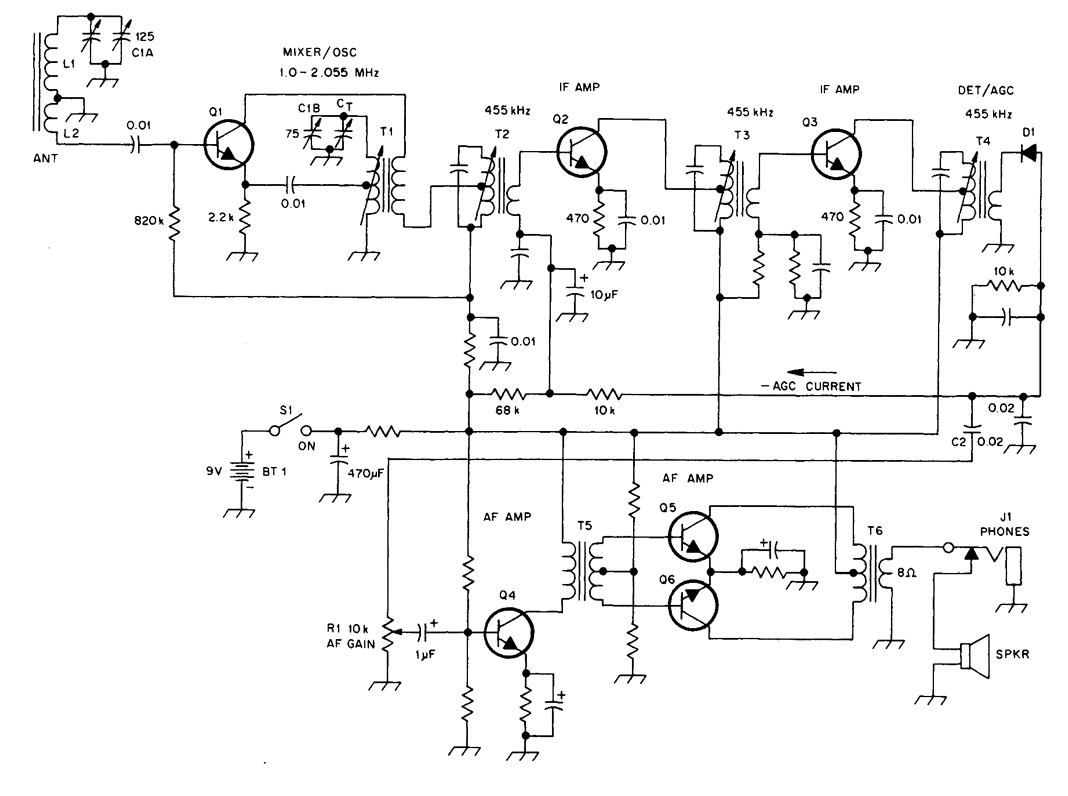
The schematic illustrates a standard AM radio circuit utilizing NPN transistors. This generic circuit does not provide specific values for all components, serving instead as a reference point for experimenters to begin their projects.
The schematic of a typical transistor AM radio circuit primarily consists of several key components: an antenna, RF amplifier, mixer, local oscillator, IF amplifier, detector, and audio amplifier. The use of NPN transistors in this design allows for efficient signal amplification and processing.
The antenna captures the radio frequency signals and feeds them into the RF amplifier, which boosts the weak signals. The amplified RF signal is then sent to the mixer, where it is combined with a signal from the local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This mixing process is crucial for demodulating the AM signal.
The IF amplifier further amplifies the intermediate frequency signal, enhancing the quality of the audio output. The detector circuit extracts the audio information from the IF signal, converting it back into an audible format. Finally, the audio amplifier increases the volume of the detected audio signal, allowing it to be heard through speakers or headphones.
Due to the generic nature of the schematic, component values such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors are not specified. This omission is intentional, as it encourages experimenters to modify and customize the circuit based on their specific requirements and available components. For those looking to build or experiment with an AM radio circuit, the schematic serves as a foundational guide, illustrating the essential stages of signal processing in a straightforward and accessible manner.Shown is a schematic of a typical transistor AM radio. This circuit uses npn transistors. The circuit is generic; therefore, no specific values are given for some components. This circuit is for ref-erence, to serve as a starting point for experimenters.. 🔗 External reference
The schematic of a typical transistor AM radio circuit primarily consists of several key components: an antenna, RF amplifier, mixer, local oscillator, IF amplifier, detector, and audio amplifier. The use of NPN transistors in this design allows for efficient signal amplification and processing.
The antenna captures the radio frequency signals and feeds them into the RF amplifier, which boosts the weak signals. The amplified RF signal is then sent to the mixer, where it is combined with a signal from the local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency (IF) signal. This mixing process is crucial for demodulating the AM signal.
The IF amplifier further amplifies the intermediate frequency signal, enhancing the quality of the audio output. The detector circuit extracts the audio information from the IF signal, converting it back into an audible format. Finally, the audio amplifier increases the volume of the detected audio signal, allowing it to be heard through speakers or headphones.
Due to the generic nature of the schematic, component values such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors are not specified. This omission is intentional, as it encourages experimenters to modify and customize the circuit based on their specific requirements and available components. For those looking to build or experiment with an AM radio circuit, the schematic serves as a foundational guide, illustrating the essential stages of signal processing in a straightforward and accessible manner.Shown is a schematic of a typical transistor AM radio. This circuit uses npn transistors. The circuit is generic; therefore, no specific values are given for some components. This circuit is for ref-erence, to serve as a starting point for experimenters.. 🔗 External reference