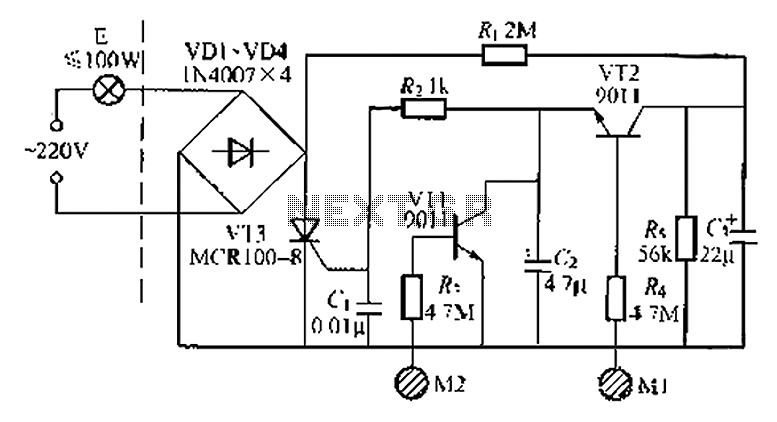
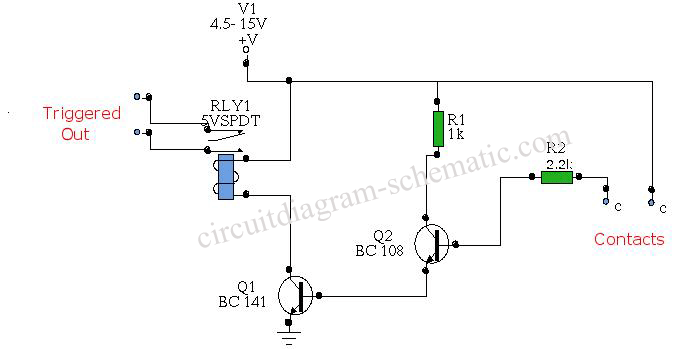
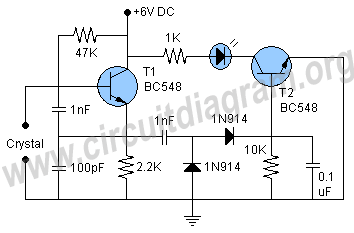
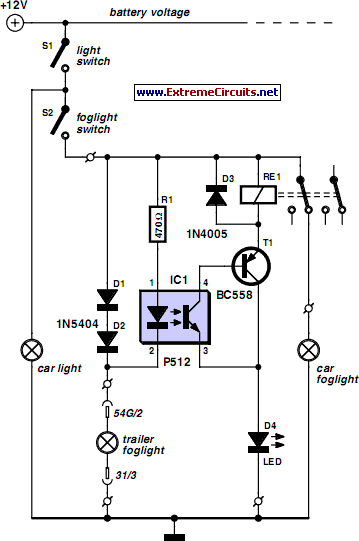
Transistorized Am Radio Circuit
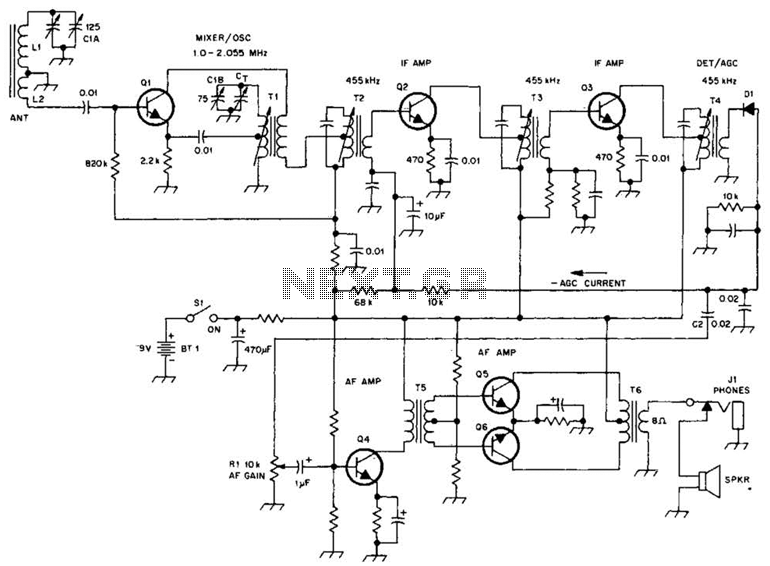
A schematic of a typical transistor AM radio is presented. This circuit utilizes npn transistors. It is a generic circuit; hence, specific values for some components are not provided. This circuit serves as a reference point for experimenters.
The schematic features a basic AM radio receiver design that leverages the properties of npn transistors for signal amplification and demodulation. The circuit typically consists of an antenna, a tuning circuit, an amplifier stage, and a demodulation section.
The antenna captures radio frequency (RF) signals, which are then filtered and tuned to the desired frequency using an LC circuit composed of an inductor and a variable capacitor. This tuning circuit is crucial as it allows the user to select the specific AM station frequency.
Once the RF signal is tuned, it is fed into the base of the first npn transistor, which acts as a common-emitter amplifier. This stage provides initial amplification of the weak RF signal. The output from this transistor is then connected to the next stage, which may include additional amplification stages or a demodulator.
The demodulation process is typically achieved through envelope detection, where the amplified RF signal is rectified to recover the audio signal. This can be done using a diode connected to the output of the amplifier stage, followed by a low-pass filter to smooth out the rectified signal and extract the audio frequency component.
Power supply considerations are also critical in such circuits, often provided by batteries or a regulated power supply. Bypass capacitors may be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply to the transistors.
Overall, this schematic serves as a foundational design for hobbyists and experimenters interested in building their own AM radio receivers, allowing for modifications and enhancements based on specific project requirements. Shown is a schematic of a typical transistor AM radio. This circuit uses npn transistors. The circuit is generic; therefore, no specific values are given for some components. This circuit is for reference, to serve as a starting point for experimenters.
The schematic features a basic AM radio receiver design that leverages the properties of npn transistors for signal amplification and demodulation. The circuit typically consists of an antenna, a tuning circuit, an amplifier stage, and a demodulation section.
The antenna captures radio frequency (RF) signals, which are then filtered and tuned to the desired frequency using an LC circuit composed of an inductor and a variable capacitor. This tuning circuit is crucial as it allows the user to select the specific AM station frequency.
Once the RF signal is tuned, it is fed into the base of the first npn transistor, which acts as a common-emitter amplifier. This stage provides initial amplification of the weak RF signal. The output from this transistor is then connected to the next stage, which may include additional amplification stages or a demodulator.
The demodulation process is typically achieved through envelope detection, where the amplified RF signal is rectified to recover the audio signal. This can be done using a diode connected to the output of the amplifier stage, followed by a low-pass filter to smooth out the rectified signal and extract the audio frequency component.
Power supply considerations are also critical in such circuits, often provided by batteries or a regulated power supply. Bypass capacitors may be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply to the transistors.
Overall, this schematic serves as a foundational design for hobbyists and experimenters interested in building their own AM radio receivers, allowing for modifications and enhancements based on specific project requirements. Shown is a schematic of a typical transistor AM radio. This circuit uses npn transistors. The circuit is generic; therefore, no specific values are given for some components. This circuit is for reference, to serve as a starting point for experimenters.