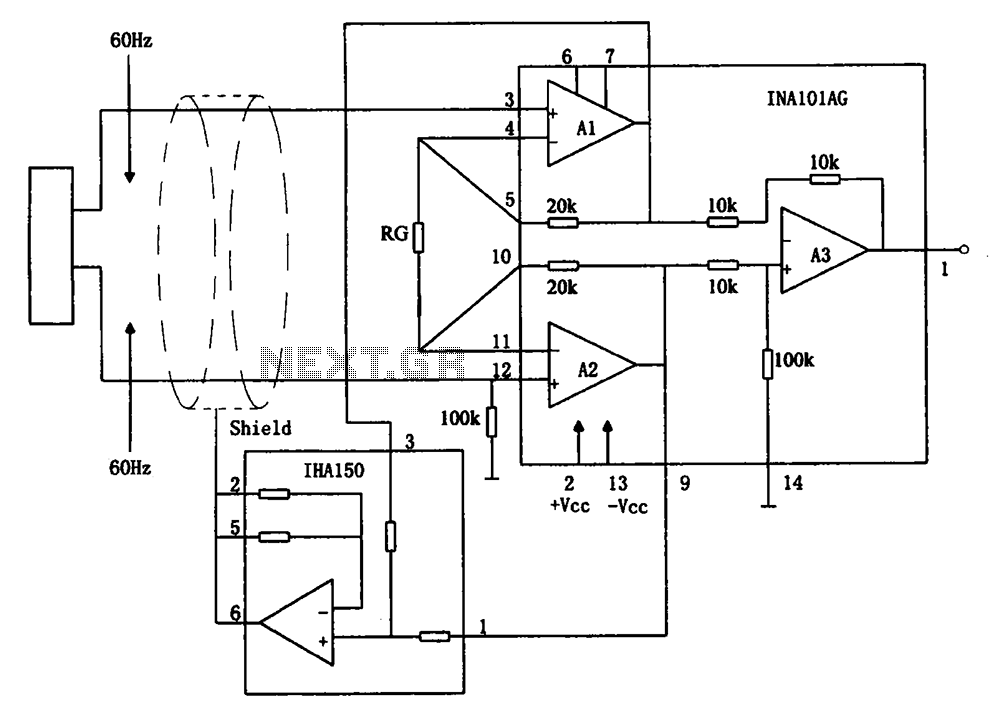
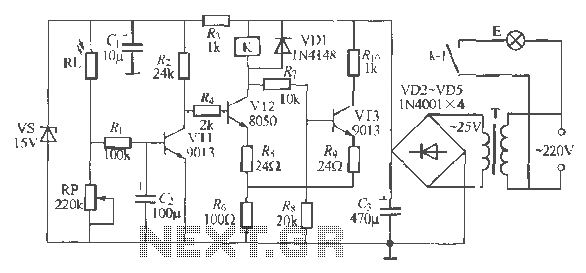
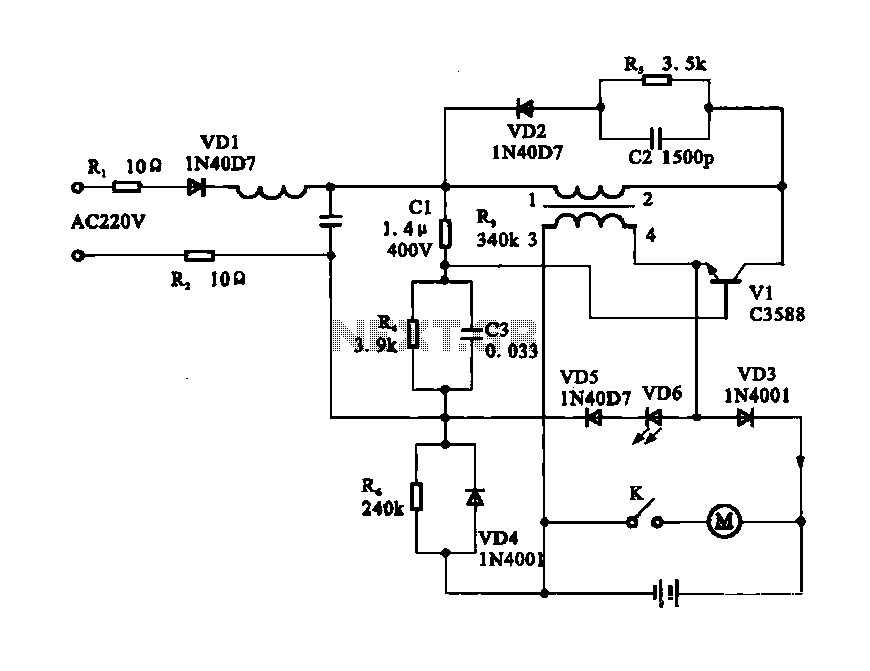
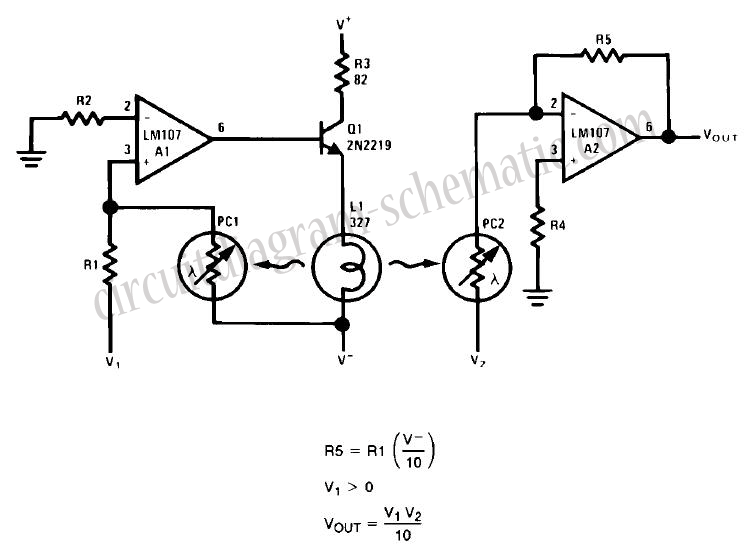
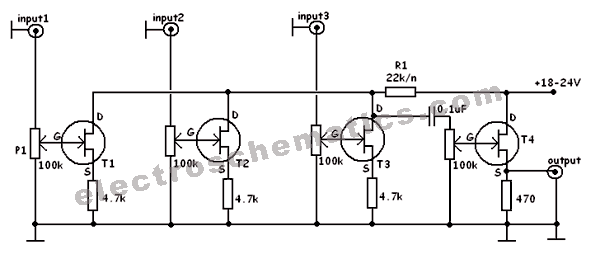
Tremolo Circuit
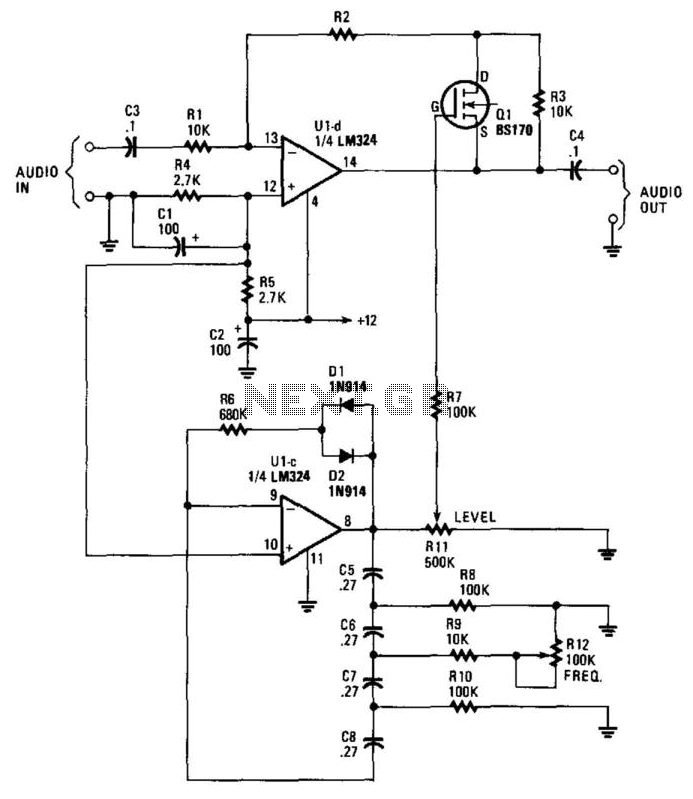
This circuit incorporates a Very Low Frequency (VLF) Amplitude Modulation (AM) component into an audio signal. This effect is commonly utilized in musical instruments. U1C, a phase-shift oscillator functioning at a few Hertz, generates a signal that modulates the gain of U1D. Resistor R11 adjusts the level of the effect, while resistor R12 modifies the frequency.
The circuit operates by leveraging a phase-shift oscillator (U1C) that produces a low-frequency oscillation. This oscillator typically consists of an operational amplifier configured in a feedback loop that introduces phase shifts to create a sine wave output at a frequency in the range of a few Hertz. The output of U1C is fed to transistor Q1, which acts as a modulator. The modulation of the gain of U1D is achieved by varying the control voltage applied to its input, influenced by the oscillating signal from Q1.
Resistor R11 plays a critical role in controlling the depth of the modulation effect. By adjusting R11, the user can increase or decrease the amplitude of the modulation signal, thus altering how pronounced the VLF AM effect is on the audio signal. A higher resistance value will result in a subtler effect, while a lower value will yield a more pronounced modulation.
Resistor R12 is responsible for adjusting the frequency of the modulation effect. Changing the resistance value alters the feedback network of the phase-shift oscillator, which in turn modifies the frequency of the oscillation. This allows for a range of modulation frequencies to be selected, enabling the user to tailor the sound to their preferences.
Overall, this circuit design is beneficial for musicians and sound designers looking to incorporate unique modulation effects into their audio signals, enhancing the sonic characteristics of their instruments or audio production. Proper implementation of the circuit components and careful tuning of R11 and R12 can yield a wide variety of creative sound effects. This circuit adds a VLF AM component to an audio signal. This effect is widely used in musical instruments. U1C, a phase-sh ift oscillator operating at a few Hz applies a signal to Ql, which modulates the gain of U1D. Rll varies the level of the effect, while R12 varies the frequency.
The circuit operates by leveraging a phase-shift oscillator (U1C) that produces a low-frequency oscillation. This oscillator typically consists of an operational amplifier configured in a feedback loop that introduces phase shifts to create a sine wave output at a frequency in the range of a few Hertz. The output of U1C is fed to transistor Q1, which acts as a modulator. The modulation of the gain of U1D is achieved by varying the control voltage applied to its input, influenced by the oscillating signal from Q1.
Resistor R11 plays a critical role in controlling the depth of the modulation effect. By adjusting R11, the user can increase or decrease the amplitude of the modulation signal, thus altering how pronounced the VLF AM effect is on the audio signal. A higher resistance value will result in a subtler effect, while a lower value will yield a more pronounced modulation.
Resistor R12 is responsible for adjusting the frequency of the modulation effect. Changing the resistance value alters the feedback network of the phase-shift oscillator, which in turn modifies the frequency of the oscillation. This allows for a range of modulation frequencies to be selected, enabling the user to tailor the sound to their preferences.
Overall, this circuit design is beneficial for musicians and sound designers looking to incorporate unique modulation effects into their audio signals, enhancing the sonic characteristics of their instruments or audio production. Proper implementation of the circuit components and careful tuning of R11 and R12 can yield a wide variety of creative sound effects. This circuit adds a VLF AM component to an audio signal. This effect is widely used in musical instruments. U1C, a phase-sh ift oscillator operating at a few Hz applies a signal to Ql, which modulates the gain of U1D. Rll varies the level of the effect, while R12 varies the frequency.