Triac regulation of mains voltage
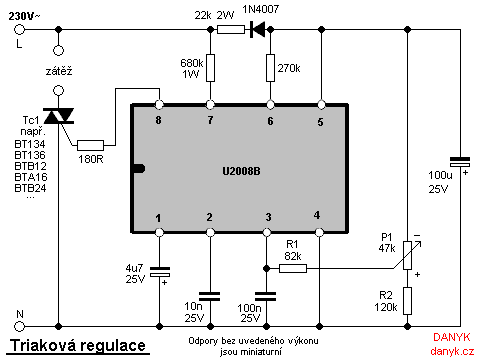
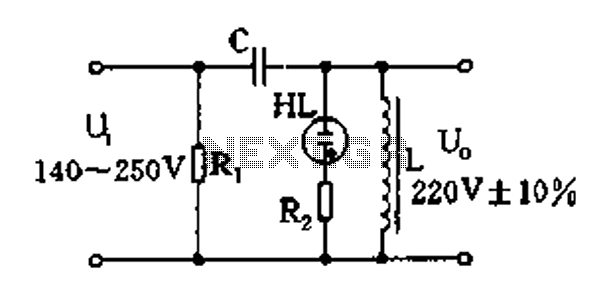
Triac regulation is designed to control the power of mains appliances. It can adjust the brightness of incandescent light bulbs, halogen lamps, dimmable energy savers, heaters, and other thermal devices, as well as regulate motors. The power can be easily adjusted from 0 to 100% using a potentiometer. This regulation utilizes a triac as the switching element, which is triggered at a specific phase by a pulse to the control electrode (G or Gate) and remains conductive until the line voltage reaches zero. While some regulators are built with discrete components, the integrated circuit U2008B is found to be the most reliable option. The schematic diagram provided illustrates a triac regulation circuit for 220V, 230V, or 240V mains voltages. Power adjustment is achieved through P1, and if the regulation does not cover the full range, adjustments can be made to R1 or R2. The triac operates in quadrants II and III. It is important to note that the electrolytic capacitors in the diagram have their positive terminal connected to neutral. The resistors without specified wattage are miniature types. The triac (Tc1) must be appropriately rated based on the load; for higher power applications, it should be mounted on a heatsink. Suitable triacs include BT134, BT136 (rated for 4A), BTB12 (12A), BTA16 (16A), or BTB24 (24A). The triac should also have a voltage rating of at least 600V. A warning is issued that the entire circuit operates at mains voltage. Therefore, it is crucial to use a suitable potentiometer with a plastic shaft for safety. The metal case of the triac is not isolated from the mains, and any connected appliance should be treated as live, even if the power regulation is set to zero.
Triac regulation circuits are essential for controlling the power delivered to various electrical devices, allowing for a versatile range of applications in home and industrial settings. The triac functions as a semiconductor switch, enabling precise control over the power output by adjusting the phase angle of the AC waveform. This method of control is particularly effective for resistive loads like incandescent bulbs and heating elements, where the power can be smoothly varied without introducing significant harmonic distortion.
The use of the integrated circuit U2008B enhances the reliability and performance of the circuit, providing a robust control mechanism for the triac. The circuit design must consider the thermal management of the triac, as excessive heat can lead to failure. Therefore, adequate heatsinking is necessary for high-power applications, ensuring that the triac operates within its specified temperature range.
The circuit's safety features are paramount, given the high voltages involved. The recommendation to use a potentiometer with a plastic shaft minimizes the risk of electric shock, while the note regarding the non-isolated metal case of the triac serves as a crucial reminder for proper handling and installation practices. All components should be rated for the expected electrical loads and voltages to maintain circuit integrity and safety.
In summary, the triac regulation circuit provides a practical solution for controlling the power of various electrical appliances, combining effective performance with necessary safety considerations. Proper component selection, circuit design, and adherence to safety protocols are essential for successful implementation in real-world applications.Triac regulation suited to regulate the power of mains appliances. It can regulate the brightness of incadescent light bulbs, halogen, dimmable energy savers, the power of heaters and other thermal appliances, engine (motor) regulation, etc. Fits as well to regulate certain types of Tesla transformer (eg SSTC). Power can be easily ad justed from 0 to 100% by simply turning the potentiometer. Triac regulation uses the triac as a switching element. Triac is triggered at some phase by pulse to the control electrode G (Gate) and remains conductive until the line passes zero voltage. There are also some regulators made of discrete components, but as the most reliable I found the involvement of an integrated circuit U2008B.
The schematic diagram below shows triac regulation circuit for 220V / 230V / 240V mains voltages. Power is adjusted by P1. If the regulations does not regulate in full range, adjust R1 or R2. The triac operates in quadrants II and III. Caution - note that the electrolytes in the diagram have positive pole at neutral. The resistors with no wattage noted are miniature. Triac Tc1 has to be sufficiently dimensioned according to the load. For higher powers, place it on the heatsink. You can use for example BT134, BT136 to 4A, BTB12 to 12A, BTA16 to 16A or BTB24 to 24A. Triac must also be rated to sufficient voltage, I recommend at least 600V. Warning: The whole circuit is at mains voltage! To ensure safety, it is necessary to use suitable potentiometer (with plastic shaft). Metal case of triac is not isolated from the mains! Connected appliance should always be treated as live, even if the regulation is set to zero power. The appliance is still under voltage! 🔗 External reference
Triac regulation circuits are essential for controlling the power delivered to various electrical devices, allowing for a versatile range of applications in home and industrial settings. The triac functions as a semiconductor switch, enabling precise control over the power output by adjusting the phase angle of the AC waveform. This method of control is particularly effective for resistive loads like incandescent bulbs and heating elements, where the power can be smoothly varied without introducing significant harmonic distortion.
The use of the integrated circuit U2008B enhances the reliability and performance of the circuit, providing a robust control mechanism for the triac. The circuit design must consider the thermal management of the triac, as excessive heat can lead to failure. Therefore, adequate heatsinking is necessary for high-power applications, ensuring that the triac operates within its specified temperature range.
The circuit's safety features are paramount, given the high voltages involved. The recommendation to use a potentiometer with a plastic shaft minimizes the risk of electric shock, while the note regarding the non-isolated metal case of the triac serves as a crucial reminder for proper handling and installation practices. All components should be rated for the expected electrical loads and voltages to maintain circuit integrity and safety.
In summary, the triac regulation circuit provides a practical solution for controlling the power of various electrical appliances, combining effective performance with necessary safety considerations. Proper component selection, circuit design, and adherence to safety protocols are essential for successful implementation in real-world applications.Triac regulation suited to regulate the power of mains appliances. It can regulate the brightness of incadescent light bulbs, halogen, dimmable energy savers, the power of heaters and other thermal appliances, engine (motor) regulation, etc. Fits as well to regulate certain types of Tesla transformer (eg SSTC). Power can be easily ad justed from 0 to 100% by simply turning the potentiometer. Triac regulation uses the triac as a switching element. Triac is triggered at some phase by pulse to the control electrode G (Gate) and remains conductive until the line passes zero voltage. There are also some regulators made of discrete components, but as the most reliable I found the involvement of an integrated circuit U2008B.
The schematic diagram below shows triac regulation circuit for 220V / 230V / 240V mains voltages. Power is adjusted by P1. If the regulations does not regulate in full range, adjust R1 or R2. The triac operates in quadrants II and III. Caution - note that the electrolytes in the diagram have positive pole at neutral. The resistors with no wattage noted are miniature. Triac Tc1 has to be sufficiently dimensioned according to the load. For higher powers, place it on the heatsink. You can use for example BT134, BT136 to 4A, BTB12 to 12A, BTA16 to 16A or BTB24 to 24A. Triac must also be rated to sufficient voltage, I recommend at least 600V. Warning: The whole circuit is at mains voltage! To ensure safety, it is necessary to use suitable potentiometer (with plastic shaft). Metal case of triac is not isolated from the mains! Connected appliance should always be treated as live, even if the regulation is set to zero power. The appliance is still under voltage! 🔗 External reference