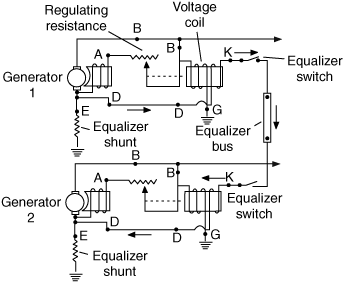
True Subwoofer Circuit

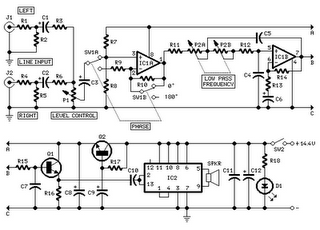
This is a true subwoofer circuit designed specifically for 15- to 18-inch woofers and is not compatible with 6- or 8-inch subwoofers. It features a bass-reflex design.
The true subwoofer circuit operates by utilizing a bass-reflex enclosure, which enhances low-frequency response through the strategic placement of a port or vent. This design allows for the generation of deeper bass tones by utilizing the rear sound wave produced by the woofer. The circuit typically includes an audio amplifier that provides the necessary power to drive the larger woofers effectively, ensuring optimal performance.
Key components of this circuit include a power amplifier, a crossover network, and the woofer itself. The power amplifier is responsible for boosting the audio signal to a level that can drive the woofer, while the crossover network filters out higher frequencies, allowing only the low frequencies to pass through to the subwoofer.
In terms of specifications, the circuit should be designed to handle the power requirements of the 15- to 18-inch woofers, which often demand higher wattage to perform effectively. Additionally, the enclosure's dimensions must be calculated to match the woofer's specifications, ensuring that the resonant frequency aligns with the desired output.
The use of high-quality capacitors and inductors in the crossover network is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and preventing distortion at high volumes. The overall design should prioritize efficient heat dissipation to prevent overheating during prolonged use, especially in high-power applications.
This circuit is ideal for home theater systems, professional audio setups, and any application where deep bass reproduction is critical. Proper implementation of this design will result in a powerful and accurate low-frequency response, enhancing the overall audio experience.This is true subwoofer circuit. This circuit is used for 15- to 18-inch woofers and will not work with 8- or 6- inch subwoofers. It has bass-reflex, a.. 🔗 External reference
The true subwoofer circuit operates by utilizing a bass-reflex enclosure, which enhances low-frequency response through the strategic placement of a port or vent. This design allows for the generation of deeper bass tones by utilizing the rear sound wave produced by the woofer. The circuit typically includes an audio amplifier that provides the necessary power to drive the larger woofers effectively, ensuring optimal performance.
Key components of this circuit include a power amplifier, a crossover network, and the woofer itself. The power amplifier is responsible for boosting the audio signal to a level that can drive the woofer, while the crossover network filters out higher frequencies, allowing only the low frequencies to pass through to the subwoofer.
In terms of specifications, the circuit should be designed to handle the power requirements of the 15- to 18-inch woofers, which often demand higher wattage to perform effectively. Additionally, the enclosure's dimensions must be calculated to match the woofer's specifications, ensuring that the resonant frequency aligns with the desired output.
The use of high-quality capacitors and inductors in the crossover network is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and preventing distortion at high volumes. The overall design should prioritize efficient heat dissipation to prevent overheating during prolonged use, especially in high-power applications.
This circuit is ideal for home theater systems, professional audio setups, and any application where deep bass reproduction is critical. Proper implementation of this design will result in a powerful and accurate low-frequency response, enhancing the overall audio experience.This is true subwoofer circuit. This circuit is used for 15- to 18-inch woofers and will not work with 8- or 6- inch subwoofers. It has bass-reflex, a.. 🔗 External reference