Turning gear from idling stop circuit diagram
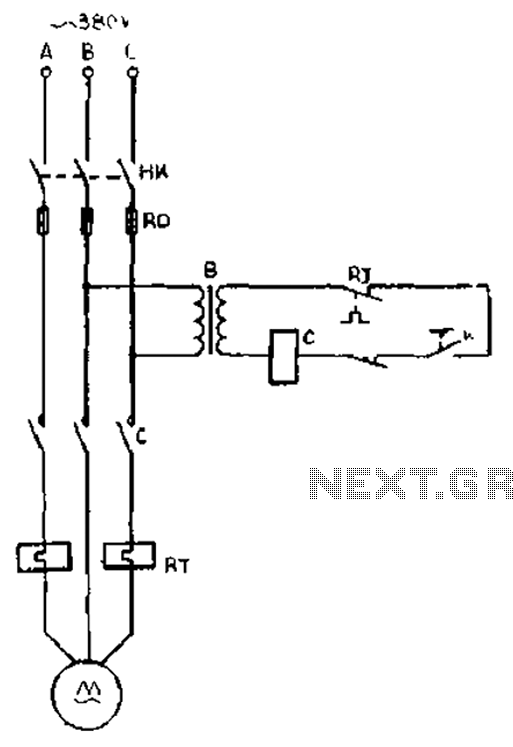
The gear lathe is unloaded from the stop line as depicted in the figure. When the turning clutch is in the stop position, the limit switch XWK is disengaged, which immediately powers the AC contactor coil C to stop the motor. This load can be achieved from the stop.
The described circuit involves a gear lathe system where a limit switch (XWK) plays a critical role in controlling the operation of the motor through an AC contactor (coil C). When the turning clutch is engaged in the stop position, the limit switch is activated, interrupting the current flow to the contactor coil. This results in the immediate deactivation of the motor, ensuring that the lathe is safely unloaded from the stop line.
In terms of the schematic, the limit switch XWK is connected in series with the AC contactor coil C. The AC supply feeds into the contactor, and the limit switch acts as a safety mechanism to prevent accidental motor operation when the lathe is not in use. The circuit may also include additional components such as fuses for overcurrent protection and indicators for operational status.
The functionality of this circuit is essential for maintaining safety and operational efficiency in a lathe system. By ensuring that the motor can only be powered when the clutch is in the appropriate position, the design minimizes the risk of injury and equipment damage. Proper labeling of components and adherence to electrical standards is crucial for the successful implementation of this schematic in a real-world application. As shown in FIG gear lathe unloaded from the stop line. When turning clutch in the stop position, the limit switch XWK is breaking, AC contactor coil C power immediately, stop the motor. Such load can be achieved from the stop.
The described circuit involves a gear lathe system where a limit switch (XWK) plays a critical role in controlling the operation of the motor through an AC contactor (coil C). When the turning clutch is engaged in the stop position, the limit switch is activated, interrupting the current flow to the contactor coil. This results in the immediate deactivation of the motor, ensuring that the lathe is safely unloaded from the stop line.
In terms of the schematic, the limit switch XWK is connected in series with the AC contactor coil C. The AC supply feeds into the contactor, and the limit switch acts as a safety mechanism to prevent accidental motor operation when the lathe is not in use. The circuit may also include additional components such as fuses for overcurrent protection and indicators for operational status.
The functionality of this circuit is essential for maintaining safety and operational efficiency in a lathe system. By ensuring that the motor can only be powered when the clutch is in the appropriate position, the design minimizes the risk of injury and equipment damage. Proper labeling of components and adherence to electrical standards is crucial for the successful implementation of this schematic in a real-world application. As shown in FIG gear lathe unloaded from the stop line. When turning clutch in the stop position, the limit switch XWK is breaking, AC contactor coil C power immediately, stop the motor. Such load can be achieved from the stop.