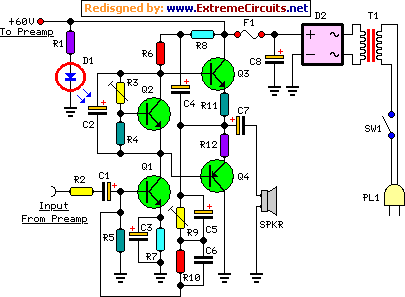
TV signal amplifier 470Mhz-860Mhz
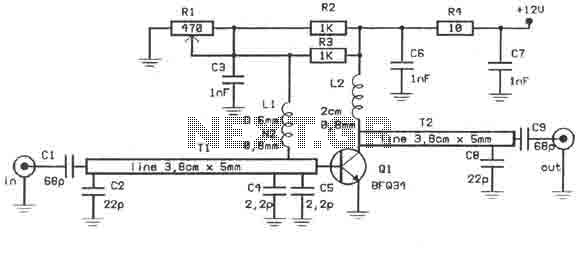
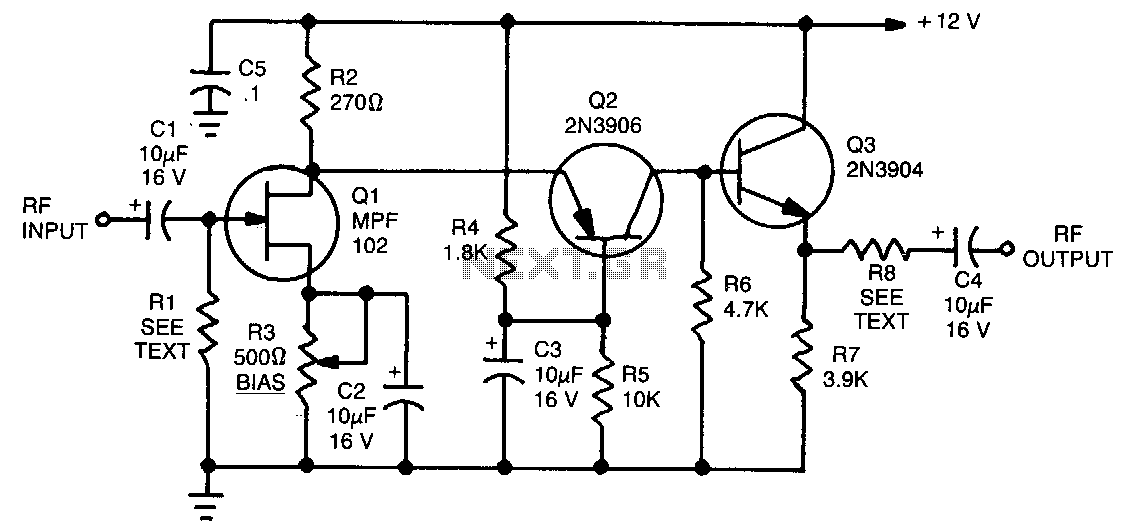
This amplifier is designed to amplify RF signals from an antenna by 10 dB and operates as a Class A amplifier using the BFQ34 transistor from Philips. The BFQ34 is packaged in an SOT122A case. The BFQ34T variant is available in the market but is not recommended due to differing characteristics. The input signal should be approximately 10 mW to achieve a 10 dB output; with an input of 0.5 mW, the output will be 5 dB. It is important to avoid overdriving the transistor, as this can lead to signal distortion characterized by artifacts, such as lines and lack of color. A stabilized power supply of 12 volts and 1 amp should be used, and the circuit should be housed in a compact metal enclosure.
This RF amplifier circuit employs the BFQ34 transistor, which is suitable for low-noise amplification in RF applications. The Class A configuration ensures that the transistor operates in the linear region, providing consistent amplification without significant distortion when the input signal is within the specified range. The choice of a 10 mW input signal is optimal for achieving the desired gain while maintaining signal integrity.
The BFQ34 transistor, with its SOT122A package, allows for efficient thermal management and compact design, essential for RF applications where space is limited. The recommendation against using the BFQ34T variant is critical, as different transistor characteristics can lead to suboptimal performance or even circuit failure.
The power supply requirement of 12 volts and 1 amp is crucial for ensuring that the transistor operates correctly without entering saturation or cutoff regions, which would compromise the amplifier's performance. A regulated power supply is advised to maintain a stable voltage under varying load conditions.
To prevent signal distortion, it is imperative to monitor the input levels and ensure they do not exceed the specified limits. Overdriving the transistor can introduce unwanted harmonics and reduce the overall fidelity of the amplified signal.
Enclosing the circuit in a metal box serves multiple purposes, including shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and providing physical protection for the components. The enclosure should be designed to allow for adequate ventilation to dissipate heat generated by the transistor during operation. Proper grounding techniques should be employed within the metal box to minimize noise and ensure reliable operation of the amplifier.This amplifier can amplify to 10dB the RF signal from antenna working as class A and is based on transistor BFQ34 of Philips. The transistor comes in case SOT122A. You may find the BFQ34T in market but better do not use it as it has different characteristics. Input signal should be about 10mW if we want 10dB output. So with 0.5mW we get 5dB. Do not overdrive the transistor because the signal will be distorted full of lines, without color etc. So use 12Volts with 1A stabilised power supply. The circuit should be enclosed in a small metal box.
This RF amplifier circuit employs the BFQ34 transistor, which is suitable for low-noise amplification in RF applications. The Class A configuration ensures that the transistor operates in the linear region, providing consistent amplification without significant distortion when the input signal is within the specified range. The choice of a 10 mW input signal is optimal for achieving the desired gain while maintaining signal integrity.
The BFQ34 transistor, with its SOT122A package, allows for efficient thermal management and compact design, essential for RF applications where space is limited. The recommendation against using the BFQ34T variant is critical, as different transistor characteristics can lead to suboptimal performance or even circuit failure.
The power supply requirement of 12 volts and 1 amp is crucial for ensuring that the transistor operates correctly without entering saturation or cutoff regions, which would compromise the amplifier's performance. A regulated power supply is advised to maintain a stable voltage under varying load conditions.
To prevent signal distortion, it is imperative to monitor the input levels and ensure they do not exceed the specified limits. Overdriving the transistor can introduce unwanted harmonics and reduce the overall fidelity of the amplified signal.
Enclosing the circuit in a metal box serves multiple purposes, including shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and providing physical protection for the components. The enclosure should be designed to allow for adequate ventilation to dissipate heat generated by the transistor during operation. Proper grounding techniques should be employed within the metal box to minimize noise and ensure reliable operation of the amplifier.This amplifier can amplify to 10dB the RF signal from antenna working as class A and is based on transistor BFQ34 of Philips. The transistor comes in case SOT122A. You may find the BFQ34T in market but better do not use it as it has different characteristics. Input signal should be about 10mW if we want 10dB output. So with 0.5mW we get 5dB. Do not overdrive the transistor because the signal will be distorted full of lines, without color etc. So use 12Volts with 1A stabilised power supply. The circuit should be enclosed in a small metal box.