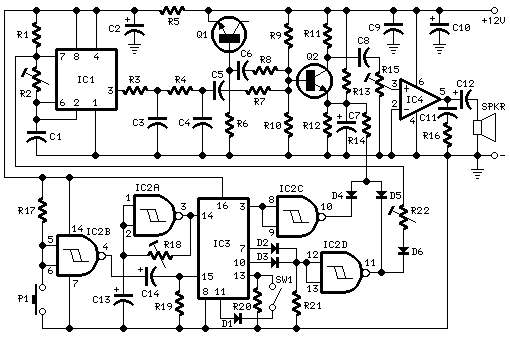
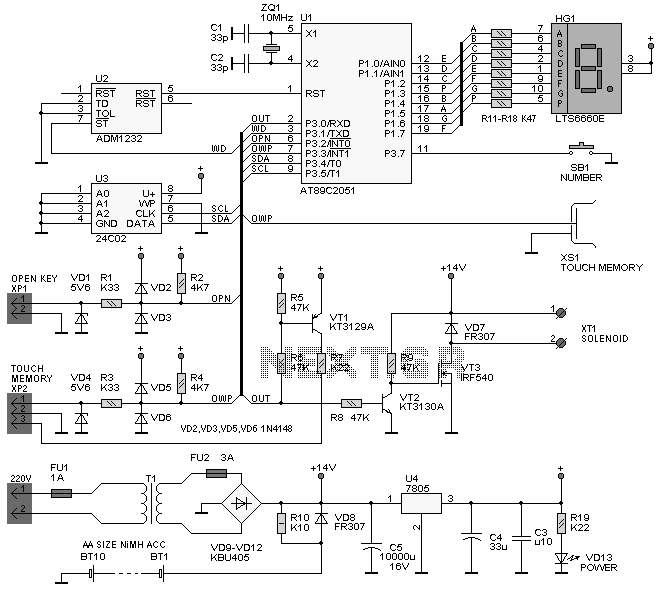
Two sirens sound with ic 555
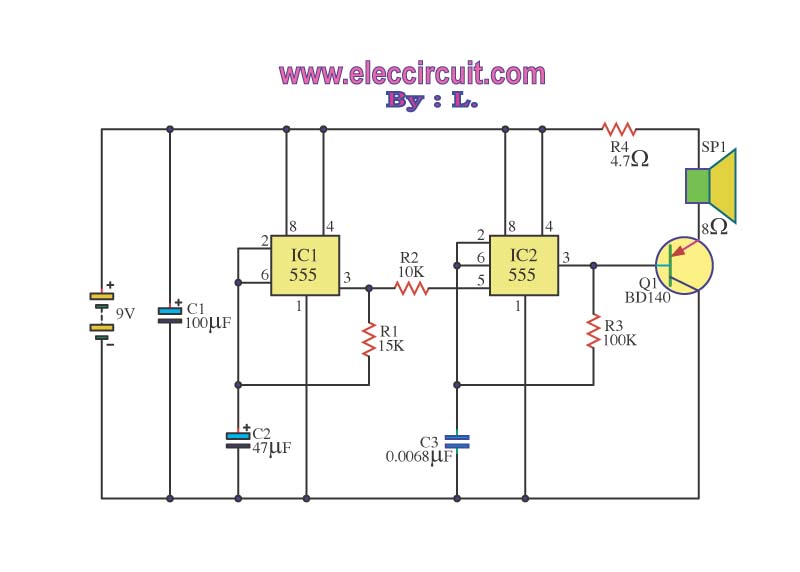
The operation of the circuit is divided into three parts: low frequency production, high frequency manufacturing, and low frequency extension.
The described circuit functions by segmenting its operation into three distinct sections, each serving a specific purpose in the overall system. The first section focuses on low frequency production, which is responsible for generating signals within a lower frequency range. This part of the circuit may utilize components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors to create oscillations or modulate signals effectively.
The second section of the circuit is dedicated to high frequency manufacturing. This part is designed to produce signals at higher frequencies, which may involve the use of specialized components such as RF amplifiers, oscillators, and filters. These components are essential for ensuring that the high frequency signals are generated accurately and efficiently, enabling the circuit to function properly in applications that require rapid signal processing.
The third section deals with the extension of low frequency production. This phase may involve amplifying or modifying the low frequency signals generated in the first section to enhance their amplitude or adjust their characteristics for better performance. This could include the use of operational amplifiers or other signal conditioning components.
Overall, the circuit's design allows for a versatile approach to signal generation and manipulation across different frequency ranges, making it suitable for various electronic applications. Each part of the circuit must be carefully designed and integrated to ensure seamless operation and optimal performance.Operation of the circuit. Circuit is divided into three parts: low frequency production. The manufacturing high frequency and extension of production low. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions by segmenting its operation into three distinct sections, each serving a specific purpose in the overall system. The first section focuses on low frequency production, which is responsible for generating signals within a lower frequency range. This part of the circuit may utilize components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors to create oscillations or modulate signals effectively.
The second section of the circuit is dedicated to high frequency manufacturing. This part is designed to produce signals at higher frequencies, which may involve the use of specialized components such as RF amplifiers, oscillators, and filters. These components are essential for ensuring that the high frequency signals are generated accurately and efficiently, enabling the circuit to function properly in applications that require rapid signal processing.
The third section deals with the extension of low frequency production. This phase may involve amplifying or modifying the low frequency signals generated in the first section to enhance their amplitude or adjust their characteristics for better performance. This could include the use of operational amplifiers or other signal conditioning components.
Overall, the circuit's design allows for a versatile approach to signal generation and manipulation across different frequency ranges, making it suitable for various electronic applications. Each part of the circuit must be carefully designed and integrated to ensure seamless operation and optimal performance.Operation of the circuit. Circuit is divided into three parts: low frequency production. The manufacturing high frequency and extension of production low. 🔗 External reference