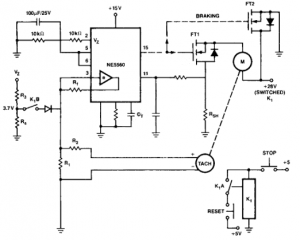
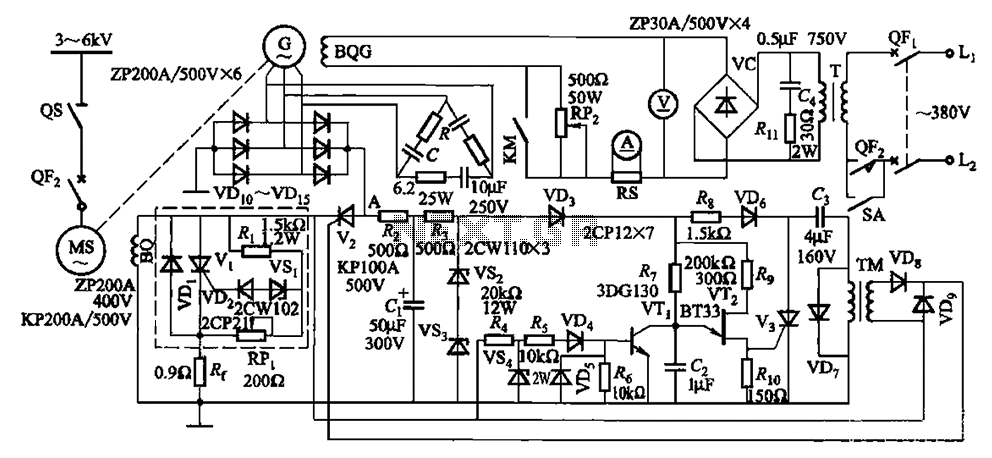
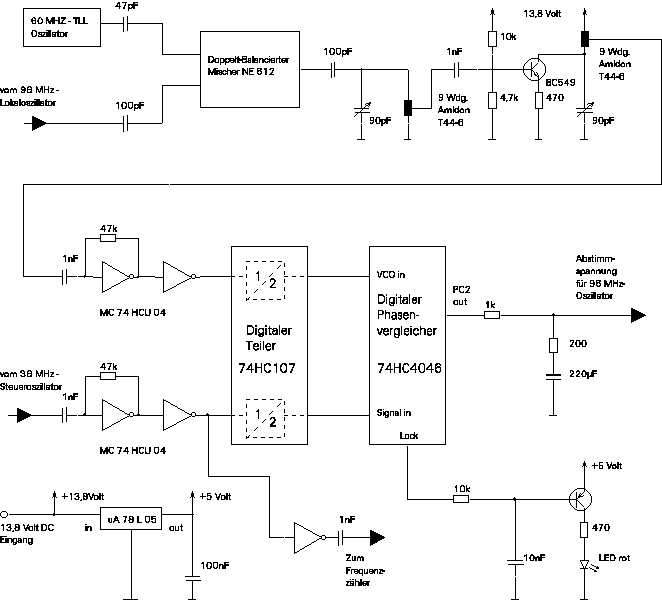
Car alarm circuit using 555 timer
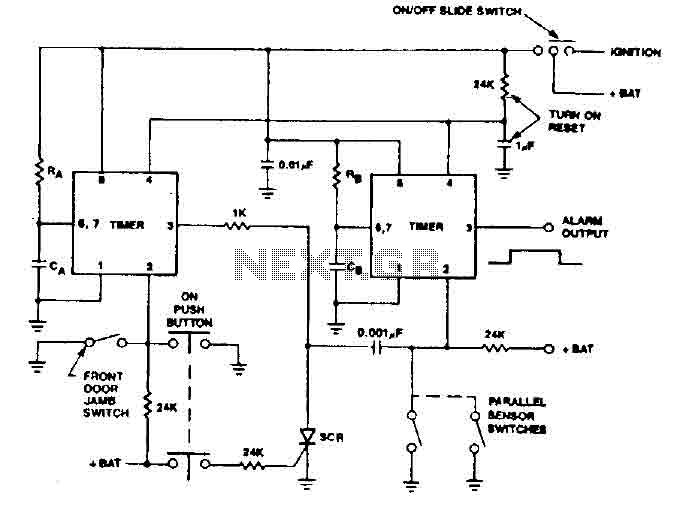
The 555 timer generates a reliable delay, enabling the driver to deactivate the alarm and eliminating the need for an external control switch that could be compromised. Additionally, the RCS prevents the activation of timer B unless it is triggered by strategically placed detector switches.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in various timing, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In this context, the 555 timer is employed to create a delay mechanism that allows for the controlled deactivation of an alarm system. This feature is particularly important in security applications, where the integrity of the system must be maintained without exposing vulnerabilities.
The configuration of the 555 timer can be set up in either monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired functionality. In monostable mode, a single trigger pulse will produce a single output pulse of a defined duration, determined by external resistors and capacitors connected to the timer. This output pulse can be used to deactivate the alarm after a specified delay, providing a window for the driver to safely disengage the system.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a Remote Control System (RCS) enhances the security of the timer operation. The RCS is designed to prevent the triggering of timer B unless certain conditions are met. Specifically, it requires activation through detector switches that are strategically placed, ensuring that unauthorized attempts to trigger the timer are thwarted. This design minimizes the risk of false alarms and enhances the overall reliability of the alarm system.
In summary, the integration of the 555 timer with an RCS in this application not only facilitates a controlled delay for alarm deactivation but also reinforces the security of the system by employing strategic triggering mechanisms. This approach effectively mitigates vulnerabilities associated with external control switches, ensuring that the alarm system remains robust against tampering.555 timer produces a guaranteed delay, allowing the driver to deactivate the alarm and the elimination of a control switch vulnerable outside. The RCS prevents triggering a timer timer B, unless B is triggered by timer switches strategically located detector.
The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit commonly used in various timing, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. In this context, the 555 timer is employed to create a delay mechanism that allows for the controlled deactivation of an alarm system. This feature is particularly important in security applications, where the integrity of the system must be maintained without exposing vulnerabilities.
The configuration of the 555 timer can be set up in either monostable or astable mode, depending on the desired functionality. In monostable mode, a single trigger pulse will produce a single output pulse of a defined duration, determined by external resistors and capacitors connected to the timer. This output pulse can be used to deactivate the alarm after a specified delay, providing a window for the driver to safely disengage the system.
Furthermore, the inclusion of a Remote Control System (RCS) enhances the security of the timer operation. The RCS is designed to prevent the triggering of timer B unless certain conditions are met. Specifically, it requires activation through detector switches that are strategically placed, ensuring that unauthorized attempts to trigger the timer are thwarted. This design minimizes the risk of false alarms and enhances the overall reliability of the alarm system.
In summary, the integration of the 555 timer with an RCS in this application not only facilitates a controlled delay for alarm deactivation but also reinforces the security of the system by employing strategic triggering mechanisms. This approach effectively mitigates vulnerabilities associated with external control switches, ensuring that the alarm system remains robust against tampering.555 timer produces a guaranteed delay, allowing the driver to deactivate the alarm and the elimination of a control switch vulnerable outside. The RCS prevents triggering a timer timer B, unless B is triggered by timer switches strategically located detector.