Two Transistor (Boys Radio) Schematic and Theory of Operation
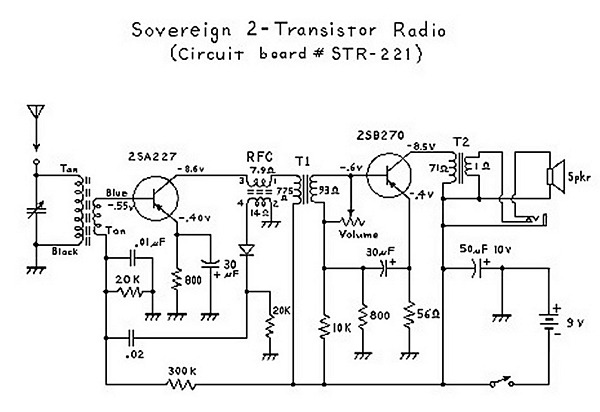
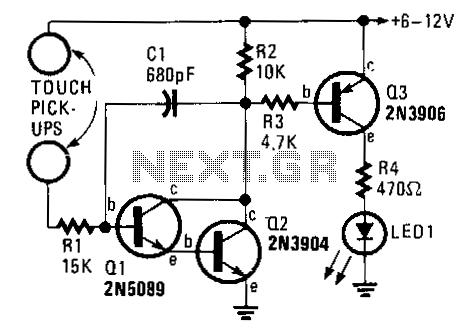
An analysis of certain radios reveals the impressive engineering by Japanese designers, particularly in creating a radio capable of driving a speaker with only two transistors. The first transistor (Q1) serves a dual function; it operates as an RF amplifier while also feeding some of the signal back to the antenna coil to enhance selectivity through regeneration.
The schematic involves a basic two-transistor radio circuit, which is a testament to minimalist design in electronics. The first transistor, Q1, is configured as a common-emitter amplifier, amplifying the radio frequency (RF) signals received by the antenna. This transistor's operation is critical, as it not only amplifies the incoming signals but also provides feedback to the antenna coil, which is typically a part of the LC circuit. This feedback is essential for regeneration, allowing the circuit to achieve better selectivity and sensitivity to desired frequencies.
The second transistor, Q2, is often configured as a class A amplifier, which drives the speaker directly. The output from Q1 is coupled to the base of Q2, where it is further amplified to a level sufficient to drive the speaker. The design may include passive components such as resistors and capacitors that help in biasing the transistors and filtering unwanted frequencies. The power supply for the circuit is typically low voltage, making it suitable for portable applications.
This simple yet effective design showcases the ingenuity of radio engineering, where minimal components can yield functional and efficient devices. The use of only two transistors illustrates the potential for compact and cost-effective solutions in radio technology.It has been interesting analyzing these radios. You have to give the Japanese credit for even making a radio that can drive a speaker with only 2 transistors! Basically, the first transistor (Q1) performs double-duty. It first acts as an RF amplifier, with some of the signal being fed back to the antenna coil to provide some regeneration for better selecti..
🔗 External reference
The schematic involves a basic two-transistor radio circuit, which is a testament to minimalist design in electronics. The first transistor, Q1, is configured as a common-emitter amplifier, amplifying the radio frequency (RF) signals received by the antenna. This transistor's operation is critical, as it not only amplifies the incoming signals but also provides feedback to the antenna coil, which is typically a part of the LC circuit. This feedback is essential for regeneration, allowing the circuit to achieve better selectivity and sensitivity to desired frequencies.
The second transistor, Q2, is often configured as a class A amplifier, which drives the speaker directly. The output from Q1 is coupled to the base of Q2, where it is further amplified to a level sufficient to drive the speaker. The design may include passive components such as resistors and capacitors that help in biasing the transistors and filtering unwanted frequencies. The power supply for the circuit is typically low voltage, making it suitable for portable applications.
This simple yet effective design showcases the ingenuity of radio engineering, where minimal components can yield functional and efficient devices. The use of only two transistors illustrates the potential for compact and cost-effective solutions in radio technology.It has been interesting analyzing these radios. You have to give the Japanese credit for even making a radio that can drive a speaker with only 2 transistors! Basically, the first transistor (Q1) performs double-duty. It first acts as an RF amplifier, with some of the signal being fed back to the antenna coil to provide some regeneration for better selecti..
🔗 External reference