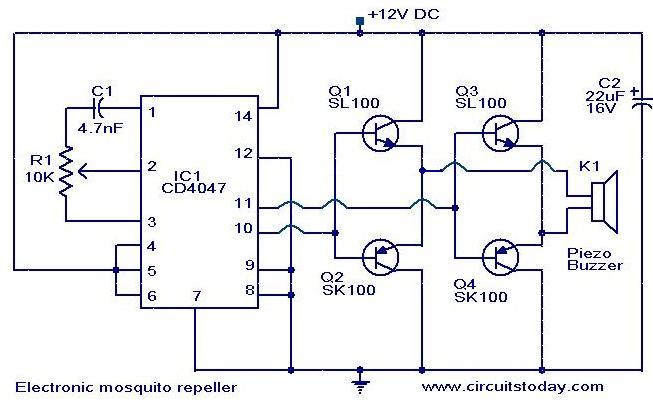
Ultrasonic pest repeller
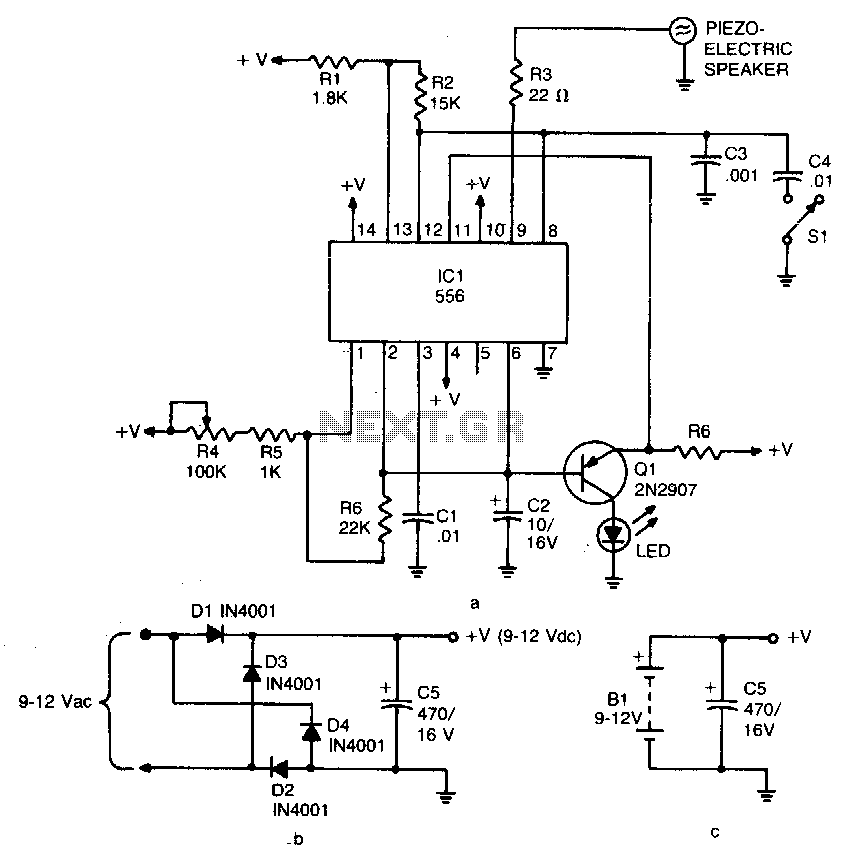
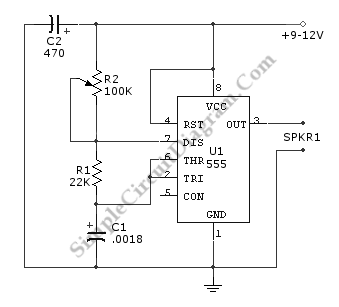
The device emits ultrasonic sound waves that sweep between 65,000 and 25,000 hertz. It is designed using a 556 dual timer, where one half functions as an astable multivibrator with an adjustable frequency ranging from 1 to 3 Hz. The second half also operates as an astable multivibrator but has a fixed free-running frequency of approximately 45,000 Hz. The 25-65 kHz sweep is achieved by coupling the voltage across C2 (the timing capacitor for the first half of the 556) through Q1 to the control voltage terminal (pin 11) of the second half of the 556. The device that radiates the ultrasonic sound is a piezo tweeter.
The schematic of the described device involves a 556 dual timer integrated circuit, which contains two independent timers. The first timer is configured as an astable multivibrator, generating a square wave output at a frequency adjustable between 1 Hz and 3 Hz. This output is used to control the timing capacitor C2, which influences the voltage across it and subsequently modulates the control voltage of the second timer.
The second timer is also set up as an astable multivibrator and operates at a fixed frequency of approximately 45 kHz. This frequency is critical for generating ultrasonic sound waves, which are beyond the audible range for humans but can be detected by certain animals and specialized equipment. The coupling of the voltage from the first timer to the control voltage terminal (pin 11) of the second timer allows for the modulation of the ultrasonic frequency, creating a sweeping effect between 25 kHz and 65 kHz.
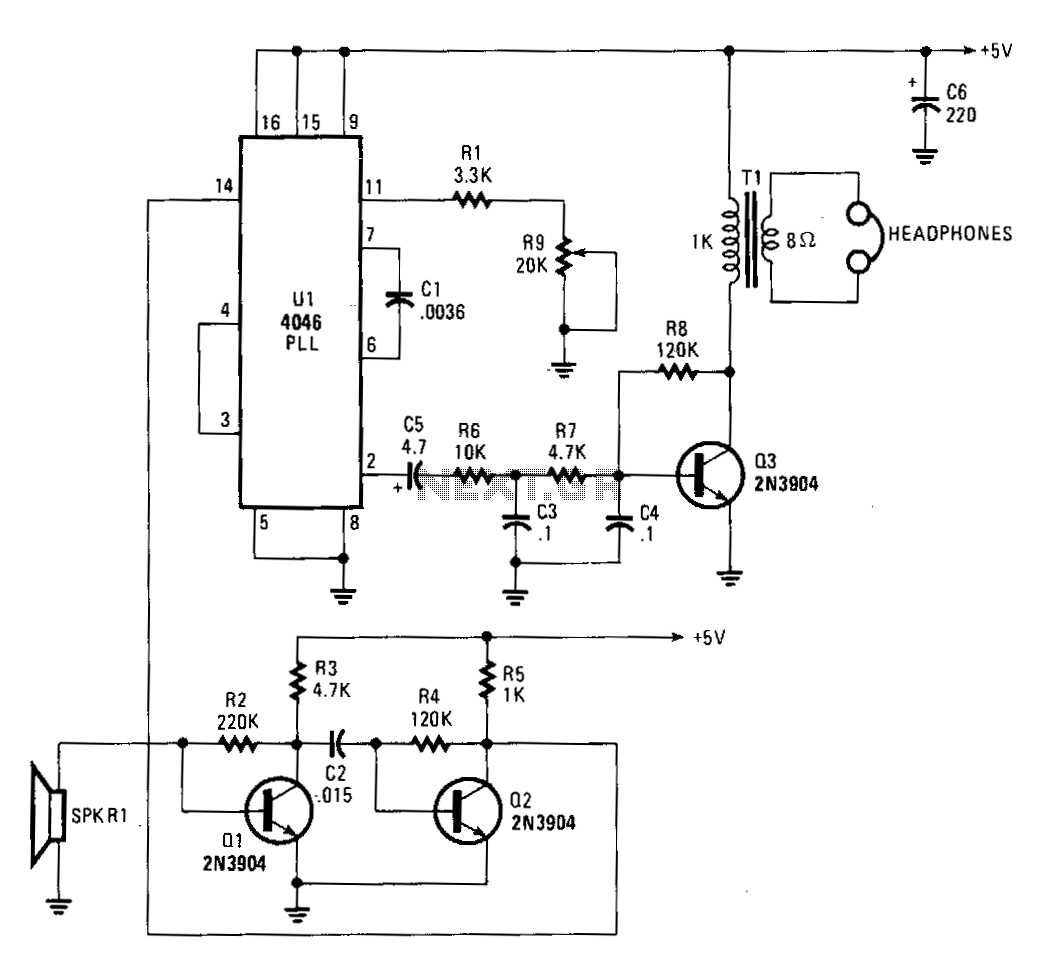
The output from the second timer drives a piezo tweeter, which is the component responsible for emitting the ultrasonic sound waves. The piezo tweeter converts the electrical signals generated by the timer into mechanical vibrations, producing sound waves at the specified ultrasonic frequencies. This design is useful in various applications, including pest control, ultrasonic cleaning, and certain types of communication systems. Overall, the circuit effectively combines frequency modulation and ultrasonic emission through a straightforward yet efficient configuration of the 556 dual timer IC.The device emits ultrasonic sound waves that sweep between 65,000 and 25,000 hertz. Designed around a 556 dual timer, one half operated as an astable multivibrator with an adjustable frequency of 1 to 3 Hz. The second half is also operated as an astable multivibrator but with a fixed free running frequency around 45,000 Hz
The 25-65 kHz sweep is accomplished by coupling the voltage across C2 (the timing capacitor for the first half of the 556) via Ql to the control voltage terminal (pin 11) of the second half of the 556. The device that radiates the ultrasonic sound is a piezo tweeter.
The schematic of the described device involves a 556 dual timer integrated circuit, which contains two independent timers. The first timer is configured as an astable multivibrator, generating a square wave output at a frequency adjustable between 1 Hz and 3 Hz. This output is used to control the timing capacitor C2, which influences the voltage across it and subsequently modulates the control voltage of the second timer.
The second timer is also set up as an astable multivibrator and operates at a fixed frequency of approximately 45 kHz. This frequency is critical for generating ultrasonic sound waves, which are beyond the audible range for humans but can be detected by certain animals and specialized equipment. The coupling of the voltage from the first timer to the control voltage terminal (pin 11) of the second timer allows for the modulation of the ultrasonic frequency, creating a sweeping effect between 25 kHz and 65 kHz.
The output from the second timer drives a piezo tweeter, which is the component responsible for emitting the ultrasonic sound waves. The piezo tweeter converts the electrical signals generated by the timer into mechanical vibrations, producing sound waves at the specified ultrasonic frequencies. This design is useful in various applications, including pest control, ultrasonic cleaning, and certain types of communication systems. Overall, the circuit effectively combines frequency modulation and ultrasonic emission through a straightforward yet efficient configuration of the 556 dual timer IC.The device emits ultrasonic sound waves that sweep between 65,000 and 25,000 hertz. Designed around a 556 dual timer, one half operated as an astable multivibrator with an adjustable frequency of 1 to 3 Hz. The second half is also operated as an astable multivibrator but with a fixed free running frequency around 45,000 Hz
The 25-65 kHz sweep is accomplished by coupling the voltage across C2 (the timing capacitor for the first half of the 556) via Ql to the control voltage terminal (pin 11) of the second half of the 556. The device that radiates the ultrasonic sound is a piezo tweeter.