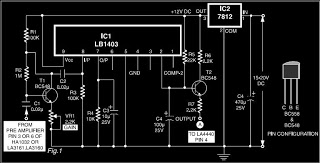
Ultrasonic sensors apply to parking sensor system

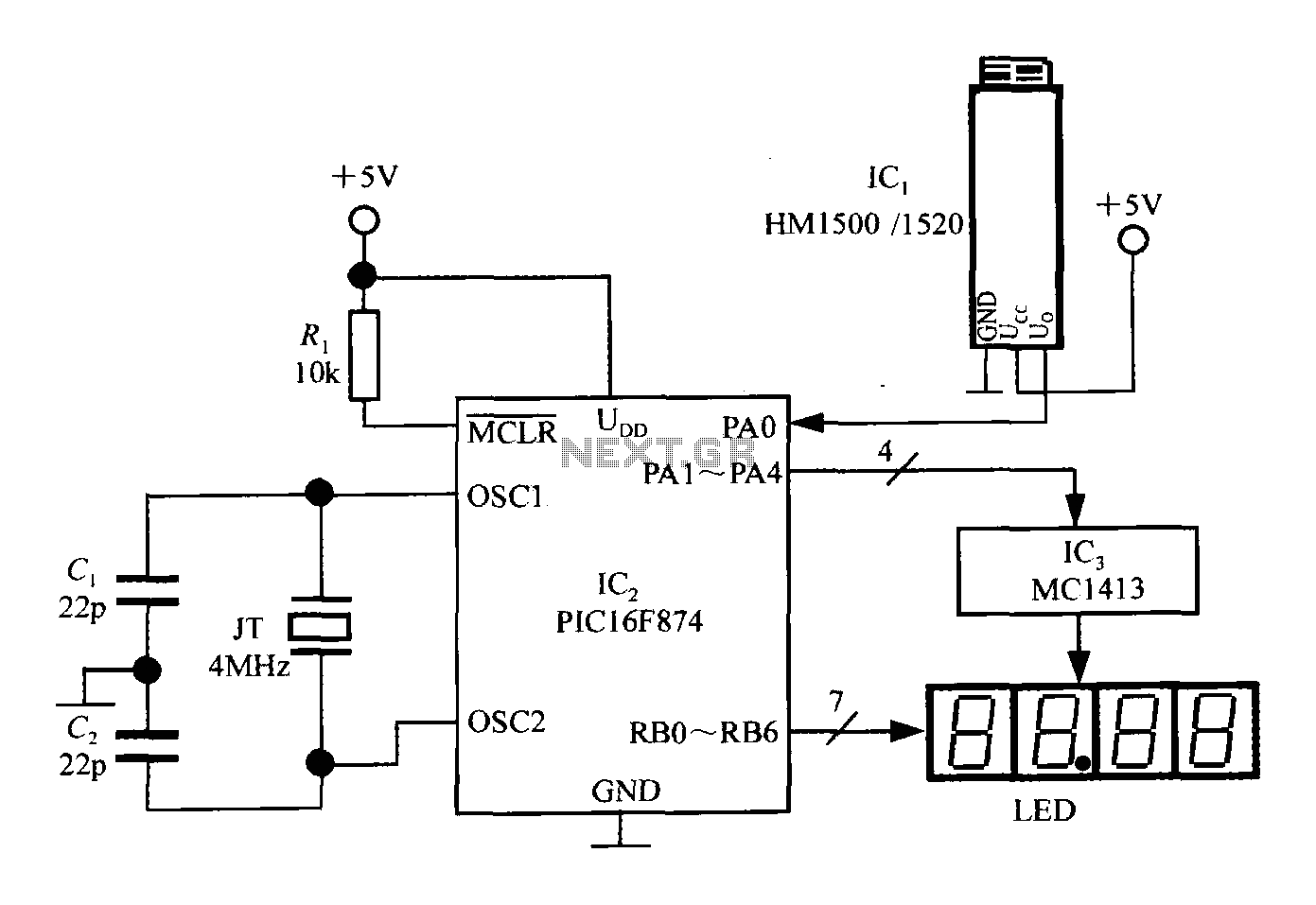
The ultrasonic sensor controls and displays information through a buzzer or visual interface, alerting the driver to nearby obstacles using auditory signals or an intuitive display. This system alleviates issues related to stopping, reversing, and maneuvering around the vehicle, while also assisting the driver in maintaining clear sightlines and addressing visual blind spots. The ultrasonic parking sensor operates by emitting ultrasonic pulses from a transducer, which are then reflected by surrounding objects. The sensor receives these reflected waves, converts them into electrical signals, and calculates the distance to the object based on the time taken for the sound waves to travel to and from the object. When an object is within a designated safe distance during reversing, the system provides alerts to the driver.
The ultrasonic parking sensor system is comprised of several key components that work together to enhance vehicle safety during low-speed maneuvers. The primary component is the ultrasonic transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves that are inaudible to humans. These waves travel through the air and bounce off nearby obstacles, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, or stationary objects.
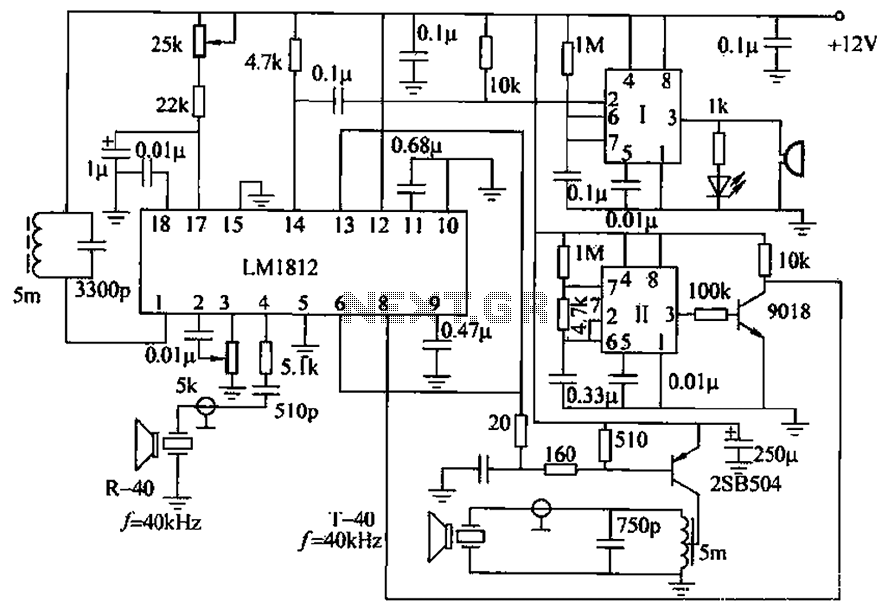
The sensor module is designed to continuously emit these ultrasonic pulses at regular intervals. As the sound waves encounter an object, they are reflected back to the sensor. The time delay between the emission of the pulse and the reception of the echo is critical for distance measurement. The system calculates this distance using the speed of sound in air, which is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature.
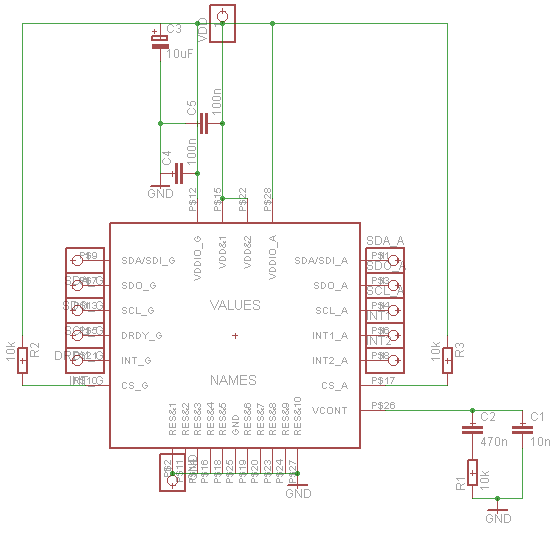
An integrated microcontroller processes the received signals. It converts the time delay into a distance measurement and compares this distance to predefined thresholds to determine if an object is within a potentially hazardous range. If an object is detected within this range, the microcontroller activates an alert mechanism, which can be either an audible buzzer or a visual display on the vehicle's dashboard.
The audible alert typically consists of a series of beeps that increase in frequency as the vehicle approaches an obstacle, providing the driver with real-time feedback about proximity. The visual display can take the form of LED indicators that illuminate progressively or a graphical representation on a screen, showing the distance to the nearest obstacle.
In addition to its primary function of obstacle detection, the ultrasonic sensor system can be integrated with other vehicle systems, such as rear-view cameras or parking assist technologies, to provide a comprehensive safety solution. This integration enhances the driver's situational awareness, reduces the likelihood of accidents during parking or reversing, and ultimately contributes to safer driving practices.
Proper installation and calibration of the ultrasonic sensors are critical for optimal performance. The sensors should be mounted at the appropriate height and angle to ensure accurate detection of obstacles. Environmental factors, such as weather conditions and the presence of dirt or debris on the sensor surface, can also affect performance, necessitating regular maintenance checks to ensure reliability.By the ultrasonic sensor, control and display (or buzzer) and local composition, it can tell the driver his around obstacles by voice or a more intuitive display case. Relieve the driver stop, reverse and start to visit around the vehicle caused by problems, and to assist the driver to clean the line of sight angle and sight ambiguous death of the
shortcomings of progressive drive insurance. Ultrasonic parking sensor works by ultrasonic pulse from the sensor (transducer) to issue, reflected by the surface acoustic wave sensor to receive the same after the conversion into electrical signals, then, through the time of transmitting and receiving sound waves to calculate the distance from the sensor to the measured object. When close to a safe distance when reversing, it can tell the driver his around obstacles by voice or a more intuitive display case.
🔗 External reference
The ultrasonic parking sensor system is comprised of several key components that work together to enhance vehicle safety during low-speed maneuvers. The primary component is the ultrasonic transducer, which emits high-frequency sound waves that are inaudible to humans. These waves travel through the air and bounce off nearby obstacles, such as other vehicles, pedestrians, or stationary objects.
The sensor module is designed to continuously emit these ultrasonic pulses at regular intervals. As the sound waves encounter an object, they are reflected back to the sensor. The time delay between the emission of the pulse and the reception of the echo is critical for distance measurement. The system calculates this distance using the speed of sound in air, which is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature.
An integrated microcontroller processes the received signals. It converts the time delay into a distance measurement and compares this distance to predefined thresholds to determine if an object is within a potentially hazardous range. If an object is detected within this range, the microcontroller activates an alert mechanism, which can be either an audible buzzer or a visual display on the vehicle's dashboard.
The audible alert typically consists of a series of beeps that increase in frequency as the vehicle approaches an obstacle, providing the driver with real-time feedback about proximity. The visual display can take the form of LED indicators that illuminate progressively or a graphical representation on a screen, showing the distance to the nearest obstacle.
In addition to its primary function of obstacle detection, the ultrasonic sensor system can be integrated with other vehicle systems, such as rear-view cameras or parking assist technologies, to provide a comprehensive safety solution. This integration enhances the driver's situational awareness, reduces the likelihood of accidents during parking or reversing, and ultimately contributes to safer driving practices.
Proper installation and calibration of the ultrasonic sensors are critical for optimal performance. The sensors should be mounted at the appropriate height and angle to ensure accurate detection of obstacles. Environmental factors, such as weather conditions and the presence of dirt or debris on the sensor surface, can also affect performance, necessitating regular maintenance checks to ensure reliability.By the ultrasonic sensor, control and display (or buzzer) and local composition, it can tell the driver his around obstacles by voice or a more intuitive display case. Relieve the driver stop, reverse and start to visit around the vehicle caused by problems, and to assist the driver to clean the line of sight angle and sight ambiguous death of the
shortcomings of progressive drive insurance. Ultrasonic parking sensor works by ultrasonic pulse from the sensor (transducer) to issue, reflected by the surface acoustic wave sensor to receive the same after the conversion into electrical signals, then, through the time of transmitting and receiving sound waves to calculate the distance from the sensor to the measured object. When close to a safe distance when reversing, it can tell the driver his around obstacles by voice or a more intuitive display case.
🔗 External reference