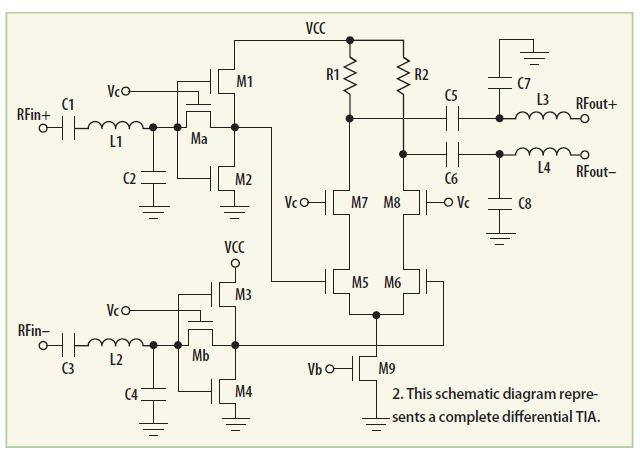
UNITY GAIN FOUR INPUT AUDIO MIXER
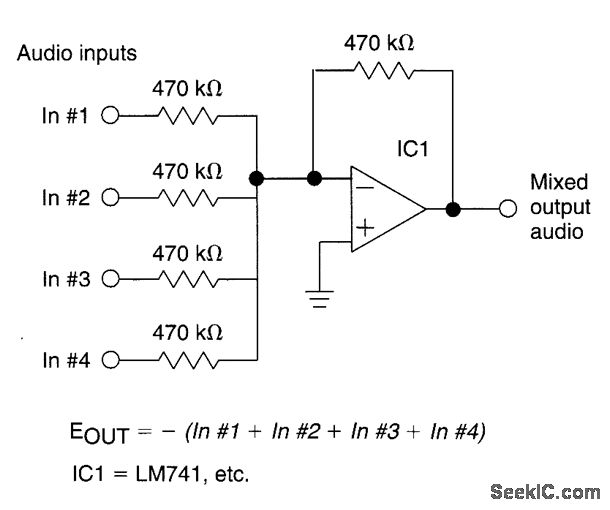
The circuit features four inputs. The voltage gain between each input and the output is maintained at unity by the relative values of the 470kΩ input resistor and the 470kΩ feedback resistor.
The described circuit operates as a voltage buffer or unity-gain amplifier, utilizing operational amplifiers (op-amps) to ensure that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage. Each of the four inputs is connected to the non-inverting terminal of an op-amp, while the output of the op-amp is fed back to the inverting terminal through a feedback resistor of 470kΩ. The input resistor, also rated at 470kΩ, serves to limit the input current and stabilize the circuit.
In a typical application, the circuit can be used in signal conditioning, where multiple signals need to be processed without introducing any gain or attenuation. The unity gain ensures that the output signal is an accurate representation of the input signal, making it ideal for interfacing with other stages of a system, such as analog-to-digital converters or further amplification stages.
The choice of resistor values (470kΩ) plays a crucial role in determining the input impedance of the circuit. With both the input and feedback resistors being equal, the input impedance is effectively high, allowing the circuit to interface with various signal sources without loading them down. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications where the source impedance may be high.
Furthermore, the circuit's design can be expanded to include additional features, such as filtering or buffering, by incorporating capacitors or additional op-amp stages, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Overall, this configuration provides a robust solution for maintaining signal integrity across multiple inputs, ensuring that the output remains faithful to the original input signals.The circuit has four inputs. The voltage gain between each input and the output is held at unity by the relative values of the 470k © input resistor and the 470k © feedback resistor. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a voltage buffer or unity-gain amplifier, utilizing operational amplifiers (op-amps) to ensure that the output voltage closely follows the input voltage. Each of the four inputs is connected to the non-inverting terminal of an op-amp, while the output of the op-amp is fed back to the inverting terminal through a feedback resistor of 470kΩ. The input resistor, also rated at 470kΩ, serves to limit the input current and stabilize the circuit.
In a typical application, the circuit can be used in signal conditioning, where multiple signals need to be processed without introducing any gain or attenuation. The unity gain ensures that the output signal is an accurate representation of the input signal, making it ideal for interfacing with other stages of a system, such as analog-to-digital converters or further amplification stages.
The choice of resistor values (470kΩ) plays a crucial role in determining the input impedance of the circuit. With both the input and feedback resistors being equal, the input impedance is effectively high, allowing the circuit to interface with various signal sources without loading them down. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications where the source impedance may be high.
Furthermore, the circuit's design can be expanded to include additional features, such as filtering or buffering, by incorporating capacitors or additional op-amp stages, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Overall, this configuration provides a robust solution for maintaining signal integrity across multiple inputs, ensuring that the output remains faithful to the original input signals.The circuit has four inputs. The voltage gain between each input and the output is held at unity by the relative values of the 470k © input resistor and the 470k © feedback resistor. 🔗 External reference