low power tia tunes gain 24 ghz
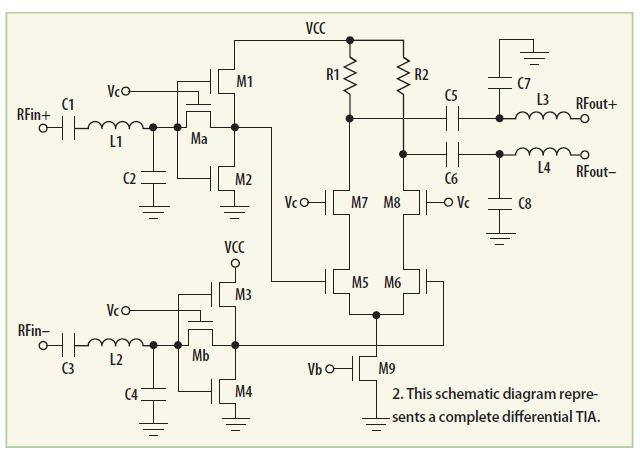
This transimpedance amplifier utilizes a current-reuse stage and a cascaded differential stage to provide a continuous gain tuning range of 15 dB, along with a low noise figure of 1.061 dB at 2.4 GHz.
The transimpedance amplifier (TIA) is designed to convert input current signals into output voltage signals, making it particularly useful in applications such as photodetection and optical communication systems. The architecture incorporates a current-reuse stage, which enhances efficiency by allowing the same current to be used in multiple stages of amplification. This approach not only conserves power but also improves the overall gain performance of the amplifier.
The cascaded differential stage further contributes to the amplifier's performance by providing high linearity and better noise performance. This stage is crucial in maintaining signal integrity, especially in high-frequency applications such as 2.4 GHz, where signal degradation can occur due to various factors like thermal noise and flicker noise.
The continuous gain tuning range of 15 dB allows for flexibility in adjusting the amplifier's performance according to the specific requirements of the application. By fine-tuning the gain, the amplifier can accommodate different input signal levels while maintaining optimal noise performance.
The low noise figure of 1.061 dB is particularly noteworthy, as it indicates the amplifier's ability to minimize the addition of noise to the signal during amplification. This characteristic is essential in sensitive applications where signal fidelity is paramount.
Overall, this transimpedance amplifier design is well-suited for high-frequency applications, providing a combination of efficient power usage, adjustable gain, and low noise performance, which are critical for effective signal processing in modern electronic systems.This transimpedance amplifier employs a current-reuse stage and cascade differential stage to achieve a continuous gain tuning range of 15 dB and low noise figure of 1.061 dB at 2.4 GHz.. 🔗 External reference
The transimpedance amplifier (TIA) is designed to convert input current signals into output voltage signals, making it particularly useful in applications such as photodetection and optical communication systems. The architecture incorporates a current-reuse stage, which enhances efficiency by allowing the same current to be used in multiple stages of amplification. This approach not only conserves power but also improves the overall gain performance of the amplifier.
The cascaded differential stage further contributes to the amplifier's performance by providing high linearity and better noise performance. This stage is crucial in maintaining signal integrity, especially in high-frequency applications such as 2.4 GHz, where signal degradation can occur due to various factors like thermal noise and flicker noise.
The continuous gain tuning range of 15 dB allows for flexibility in adjusting the amplifier's performance according to the specific requirements of the application. By fine-tuning the gain, the amplifier can accommodate different input signal levels while maintaining optimal noise performance.
The low noise figure of 1.061 dB is particularly noteworthy, as it indicates the amplifier's ability to minimize the addition of noise to the signal during amplification. This characteristic is essential in sensitive applications where signal fidelity is paramount.
Overall, this transimpedance amplifier design is well-suited for high-frequency applications, providing a combination of efficient power usage, adjustable gain, and low noise performance, which are critical for effective signal processing in modern electronic systems.This transimpedance amplifier employs a current-reuse stage and cascade differential stage to achieve a continuous gain tuning range of 15 dB and low noise figure of 1.061 dB at 2.4 GHz.. 🔗 External reference