Urban Sensing Networks using Arduino
Government data sets available online are often sourced from major metropolitan areas or infrastructural centers. With an easy-to-follow introduction to new software and technologies, the urban sensor kit allows anyone to obtain location-specific information and share it with a growing community of designers, researchers, and others. This urban sensor kit is designed to foster a user-controlled community that can collectively form a large global network aimed at sustainable urban and architectural design. This guide aims to assist in creating an urban sensor kit that can collect, record, and share accurate, up-to-date locational information, resulting in precise, site-specific data sets. The project enables users to connect their own humidity, temperature, and photocell sensors to host a webpage that is shared within the network. This webpage displays stored data collected from each user, showcasing sensor history and activity in graphical formats through a Pachube feed, allowing contributions to the urban network.
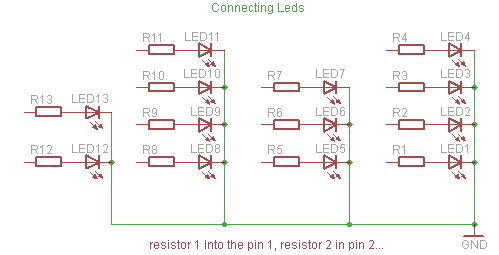
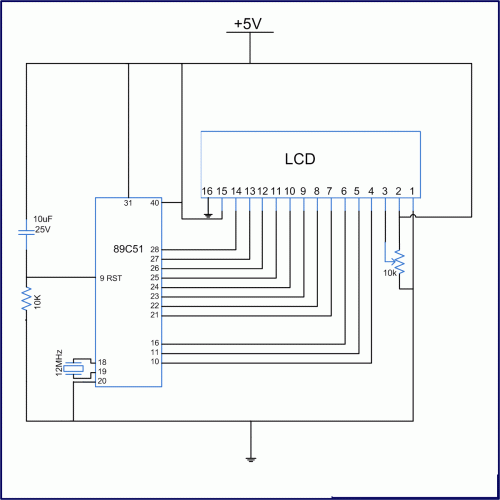
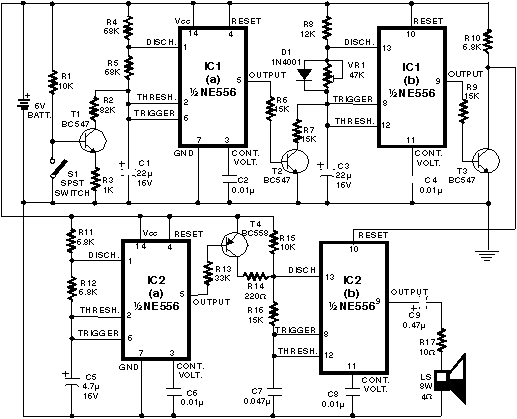
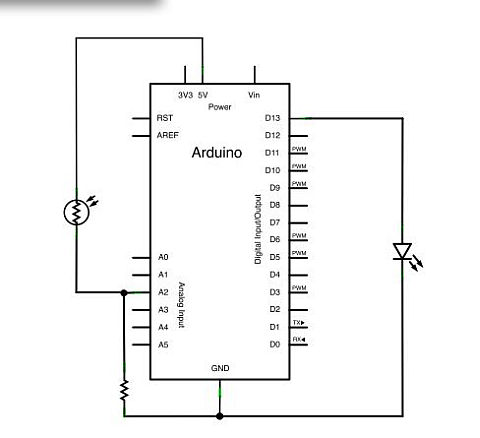
The urban sensor kit is an innovative solution that integrates various sensors to gather environmental data, which can be crucial for urban planning and sustainability efforts. The kit typically includes a microcontroller as the central processing unit, which interfaces with multiple sensors, such as humidity sensors, temperature sensors, and light sensors (photocells). These sensors are responsible for measuring specific environmental parameters, which the microcontroller collects and processes.
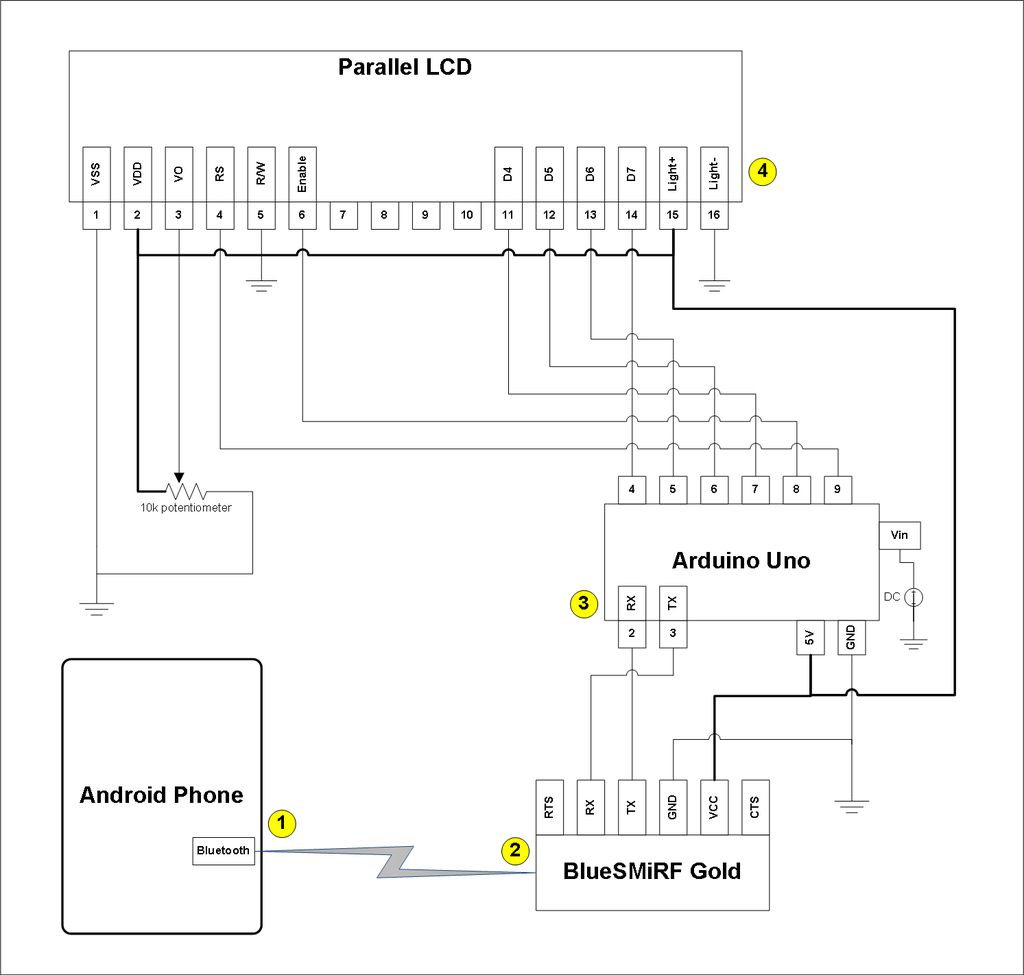
The microcontroller can be programmed using user-friendly software, allowing individuals with minimal technical expertise to configure their kits easily. Data collected by the sensors is typically transmitted wirelessly to a cloud-based platform or a local server, where it can be accessed by other users in the network. This data sharing is essential for creating a comprehensive database that can be utilized by designers and researchers to analyze trends and make informed decisions regarding urban development.
The webpage hosted by each user serves as a dashboard that displays real-time data from their sensors. This interface can include visual representations of the data, such as graphs and charts, making it easier for users to interpret the information. The integration with Pachube or similar platforms allows for seamless data visualization and sharing, enhancing collaboration among community members.
In summary, the urban sensor kit is a versatile tool that empowers individuals to contribute to a larger initiative focused on sustainable urban design. By collecting and sharing location-specific data, users can engage in a collaborative effort to improve urban environments and promote sustainability. The project exemplifies how technology can facilitate community involvement in addressing modern urban challenges.Often government data sets available to us online are taken from major nearby metropolitan areas or infrastructural centers. With an easy to follow introduction to new softwares and technologies the urban sensor kit allows anyone to obtain location specific information and share that information with a growing community of designers, researcher
s, and many others. This urban sensor kit is designed to create a user controlled community that, together will be able to form a large global network towards the future sustainable urban and architectural design. This Instructable is aimed to help you create your own urban sensor kit that will be able to collect, record, and share accurate and up-to-date locational information, creating the most precise and site specific data sets available.
This project will allow you to hook up your own humidity, temperature and photocell sensor at home to host a webpage shared between the rest of the network. The webpage contains stored data collected from each user and displays information on sensor`s history and activity in graph forms in a Pachube feed.
Now you too can contribute towards our urban network! 🔗 External reference
The urban sensor kit is an innovative solution that integrates various sensors to gather environmental data, which can be crucial for urban planning and sustainability efforts. The kit typically includes a microcontroller as the central processing unit, which interfaces with multiple sensors, such as humidity sensors, temperature sensors, and light sensors (photocells). These sensors are responsible for measuring specific environmental parameters, which the microcontroller collects and processes.
The microcontroller can be programmed using user-friendly software, allowing individuals with minimal technical expertise to configure their kits easily. Data collected by the sensors is typically transmitted wirelessly to a cloud-based platform or a local server, where it can be accessed by other users in the network. This data sharing is essential for creating a comprehensive database that can be utilized by designers and researchers to analyze trends and make informed decisions regarding urban development.
The webpage hosted by each user serves as a dashboard that displays real-time data from their sensors. This interface can include visual representations of the data, such as graphs and charts, making it easier for users to interpret the information. The integration with Pachube or similar platforms allows for seamless data visualization and sharing, enhancing collaboration among community members.
In summary, the urban sensor kit is a versatile tool that empowers individuals to contribute to a larger initiative focused on sustainable urban design. By collecting and sharing location-specific data, users can engage in a collaborative effort to improve urban environments and promote sustainability. The project exemplifies how technology can facilitate community involvement in addressing modern urban challenges.Often government data sets available to us online are taken from major nearby metropolitan areas or infrastructural centers. With an easy to follow introduction to new softwares and technologies the urban sensor kit allows anyone to obtain location specific information and share that information with a growing community of designers, researcher
s, and many others. This urban sensor kit is designed to create a user controlled community that, together will be able to form a large global network towards the future sustainable urban and architectural design. This Instructable is aimed to help you create your own urban sensor kit that will be able to collect, record, and share accurate and up-to-date locational information, creating the most precise and site specific data sets available.
This project will allow you to hook up your own humidity, temperature and photocell sensor at home to host a webpage shared between the rest of the network. The webpage contains stored data collected from each user and displays information on sensor`s history and activity in graph forms in a Pachube feed.
Now you too can contribute towards our urban network! 🔗 External reference