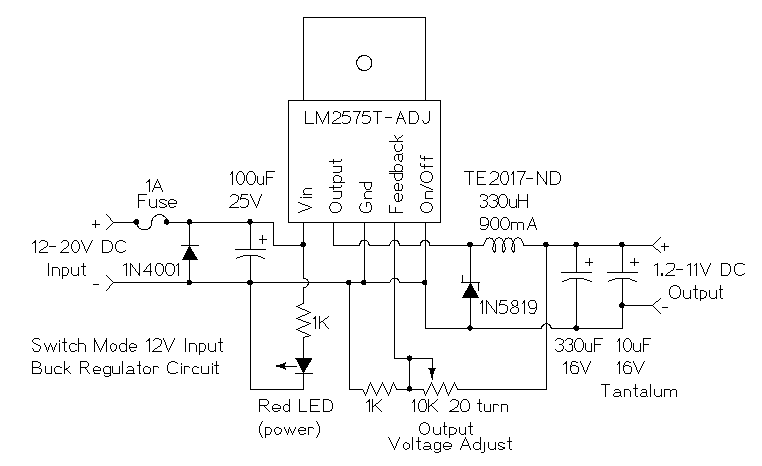
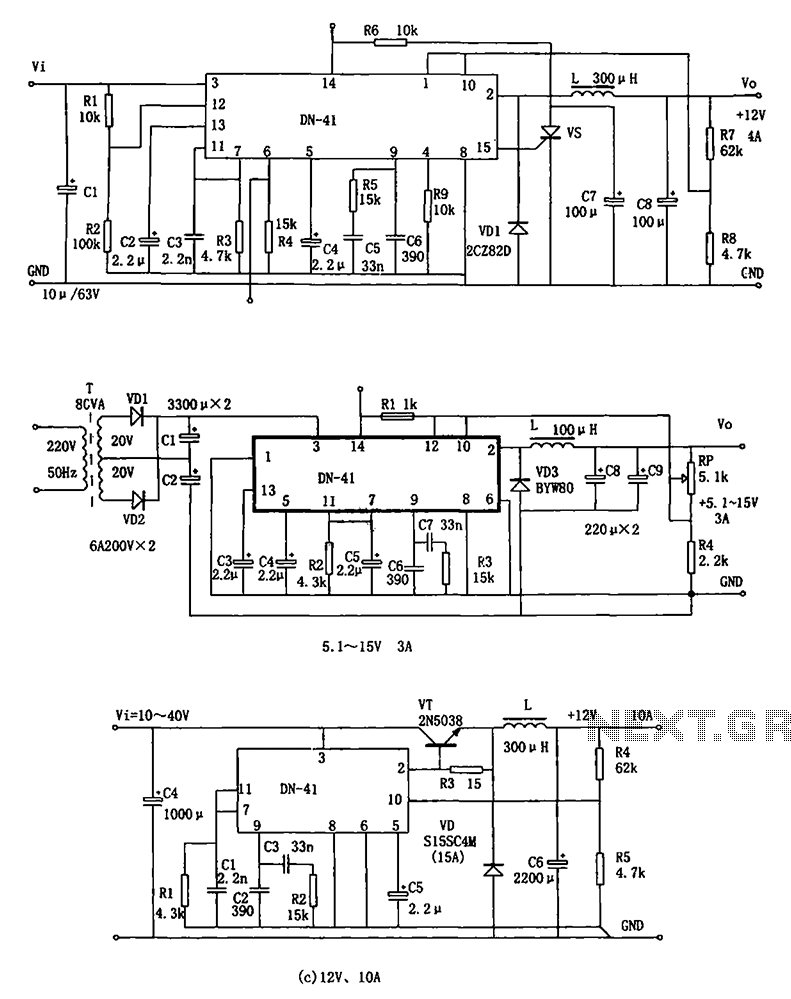
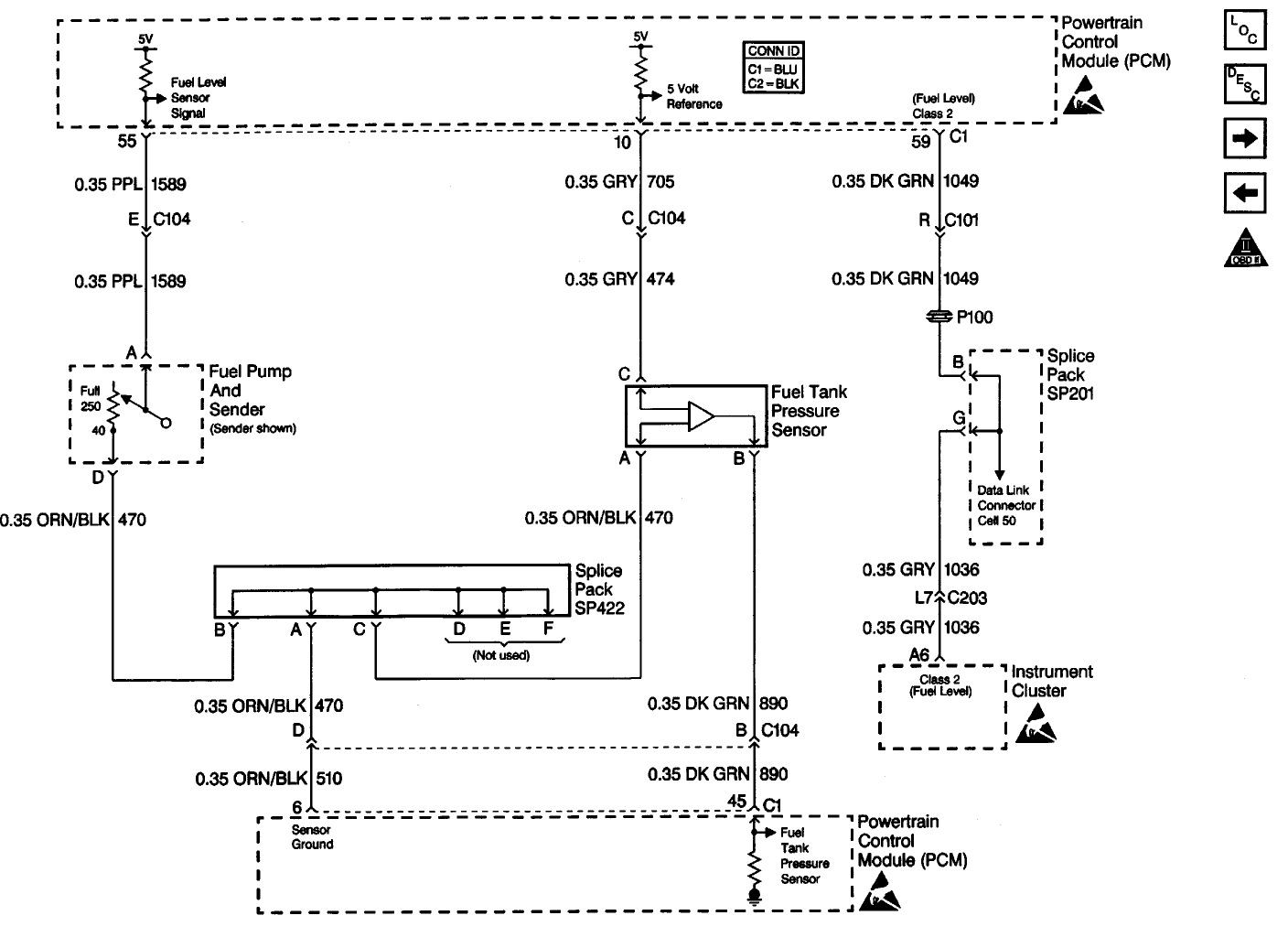
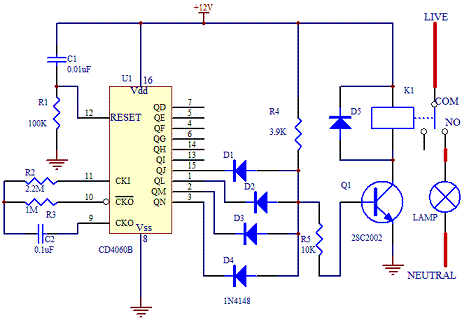
Use for the Tesla Switch
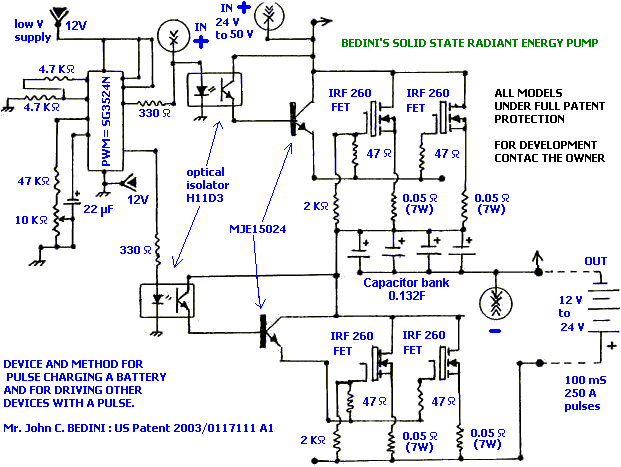
Thank you very much. I will try that. @StevanC, what do you think? Are we making some progress, or should we stick to your design, ScratchRobot?
The provided text appears to be a conversation regarding the evaluation of progress on a project, specifically referencing a design called ScratchRobot. To create a comprehensive electronic schematic description, it is essential to clarify the context and technical details of the ScratchRobot design.
The ScratchRobot is an educational robotics platform designed to facilitate learning in programming and electronics. It typically integrates a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, with various sensors and actuators to create an interactive and programmable robot. The schematic for such a design would include the following key components:
1. **Microcontroller Unit (MCU)**: The heart of the ScratchRobot, responsible for processing inputs from sensors and controlling outputs to actuators. The schematic should depict the connections between the MCU and other components, highlighting the power supply pins, ground connections, and I/O pins used for communication.
2. **Power Supply Circuit**: This section of the schematic should illustrate how the robot is powered, whether through batteries, a USB connection, or an external power supply. It is crucial to include voltage regulators if different components require different operating voltages.
3. **Input Sensors**: Various sensors may be included in the design, such as ultrasonic distance sensors, infrared sensors, or light sensors. The schematic should show how these sensors connect to the MCU, including any necessary pull-up or pull-down resistors.
4. **Output Actuators**: The ScratchRobot may utilize motors, servos, or LEDs as output devices. The schematic must detail the connections for motor drivers or relay circuits that control these actuators, ensuring that the power requirements and control signals are appropriately managed.
5. **Communication Interfaces**: If the ScratchRobot is designed to communicate with other devices or networks, the schematic should include details on communication protocols such as I2C, SPI, or UART. This may involve additional components like transceivers or Bluetooth modules.
6. **User Interface**: Depending on the complexity of the ScratchRobot, a user interface might be included, such as buttons or a touchscreen. The schematic should provide details on how these components are wired to the MCU.
7. **Debugging and Programming Ports**: It is advisable to incorporate programming headers or debugging ports in the schematic to facilitate easy access for code uploading and troubleshooting.
Overall, a well-structured schematic for the ScratchRobot will provide a clear visual representation of all components, their interconnections, and the operational flow of the system. Proper labeling and annotations will enhance understanding and facilitate further development or modifications to the design.Thank you very much I will try that. @StevanC What do you think, are we making some progress or should we stick to your design scratchrobot.. 🔗 External reference
The provided text appears to be a conversation regarding the evaluation of progress on a project, specifically referencing a design called ScratchRobot. To create a comprehensive electronic schematic description, it is essential to clarify the context and technical details of the ScratchRobot design.
The ScratchRobot is an educational robotics platform designed to facilitate learning in programming and electronics. It typically integrates a microcontroller, such as an Arduino or Raspberry Pi, with various sensors and actuators to create an interactive and programmable robot. The schematic for such a design would include the following key components:
1. **Microcontroller Unit (MCU)**: The heart of the ScratchRobot, responsible for processing inputs from sensors and controlling outputs to actuators. The schematic should depict the connections between the MCU and other components, highlighting the power supply pins, ground connections, and I/O pins used for communication.
2. **Power Supply Circuit**: This section of the schematic should illustrate how the robot is powered, whether through batteries, a USB connection, or an external power supply. It is crucial to include voltage regulators if different components require different operating voltages.
3. **Input Sensors**: Various sensors may be included in the design, such as ultrasonic distance sensors, infrared sensors, or light sensors. The schematic should show how these sensors connect to the MCU, including any necessary pull-up or pull-down resistors.
4. **Output Actuators**: The ScratchRobot may utilize motors, servos, or LEDs as output devices. The schematic must detail the connections for motor drivers or relay circuits that control these actuators, ensuring that the power requirements and control signals are appropriately managed.
5. **Communication Interfaces**: If the ScratchRobot is designed to communicate with other devices or networks, the schematic should include details on communication protocols such as I2C, SPI, or UART. This may involve additional components like transceivers or Bluetooth modules.
6. **User Interface**: Depending on the complexity of the ScratchRobot, a user interface might be included, such as buttons or a touchscreen. The schematic should provide details on how these components are wired to the MCU.
7. **Debugging and Programming Ports**: It is advisable to incorporate programming headers or debugging ports in the schematic to facilitate easy access for code uploading and troubleshooting.
Overall, a well-structured schematic for the ScratchRobot will provide a clear visual representation of all components, their interconnections, and the operational flow of the system. Proper labeling and annotations will enhance understanding and facilitate further development or modifications to the design.Thank you very much I will try that. @StevanC What do you think, are we making some progress or should we stick to your design scratchrobot.. 🔗 External reference