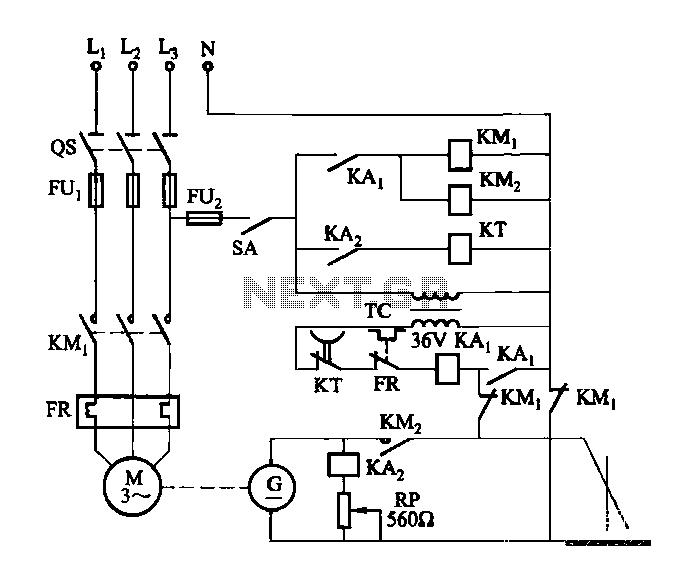
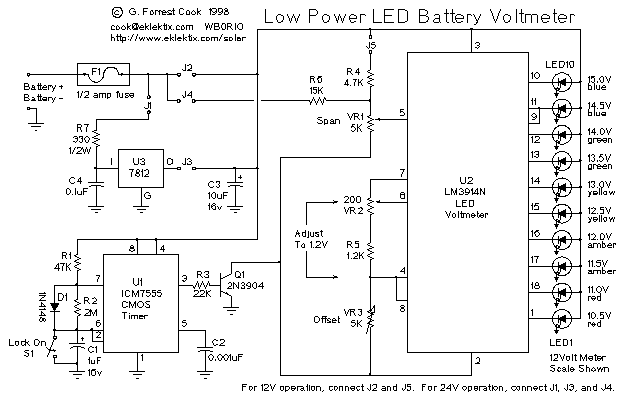
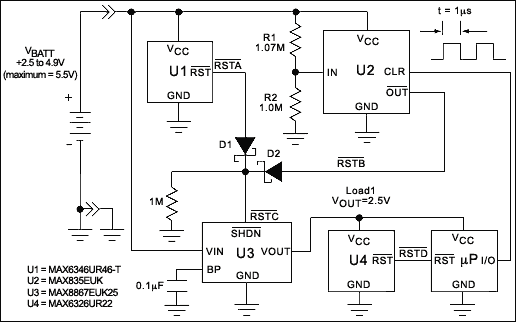
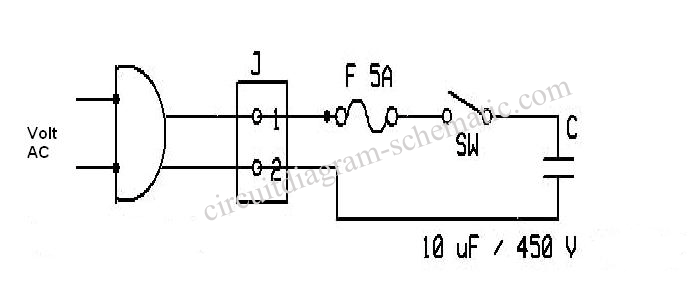
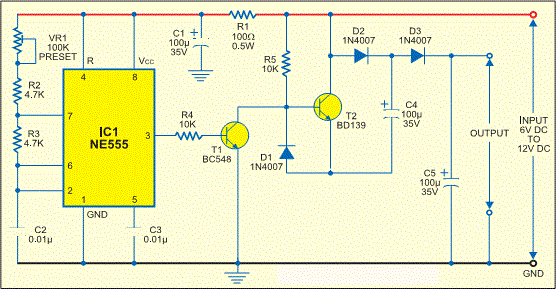
Variable DC Power Supply

A Variable DC Power Supply is one of the most useful tools on the electronics hobbyist's workbench. This circuit is not an absolute novelty, but it is simple, reliable, rugged, and short-proof, featuring variable voltage up to 24V and variable current limiting up to 2A. Well suited to supply the circuits shown in this website. You can adapt it to your own requirements as explained in the notes below.
A Variable DC Power Supply circuit typically consists of several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, a voltage regulator, and a current limiting circuit. The transformer steps down the AC mains voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the application. The rectifier, often a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC. Following this, a filter capacitor smooths the output voltage to reduce ripple, providing a more stable DC voltage.
The voltage regulator component is crucial for achieving the desired output voltage. Linear voltage regulators, such as the LM317, are commonly used due to their simplicity and effectiveness. They allow for adjustable output voltage by incorporating a variable resistor (potentiometer) in the feedback loop. This setup enables the user to set the output voltage anywhere from 1.25V to 24V, depending on the design.
Incorporating a current limiting feature is essential for protecting both the power supply and the connected load. This can be achieved using a simple resistor in series with the load or through more sophisticated methods such as using a current sensing resistor and an operational amplifier to control the output based on the load current. The current limit can typically be adjusted using another potentiometer, allowing for flexibility in various applications.
To enhance the robustness of the circuit, it is advisable to include fuses or circuit breakers to protect against short circuits and overload conditions. Additionally, proper heat sinking for the voltage regulator and other power components is necessary to prevent thermal failure during prolonged use.
In conclusion, a Variable DC Power Supply is a versatile and essential tool for electronics enthusiasts, capable of delivering adjustable voltage and current to a wide range of circuits. The design can be tailored to specific needs, making it a valuable addition to any electronics workbench.A Variable DC Power Supply is one of the most useful tools on the electronics hobbyist`s workbench. This circuit is not an absolute novelty, but it is simple, reliable, "rugged" and short-proof, featuring variable voltage up to 24V and variable current limiting up to 2A. Well suited to supply the circuits shown in this website. You can adapt it to your own requirements as explained in the notes below. 🔗 External reference
A Variable DC Power Supply circuit typically consists of several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, a voltage regulator, and a current limiting circuit. The transformer steps down the AC mains voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the application. The rectifier, often a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC. Following this, a filter capacitor smooths the output voltage to reduce ripple, providing a more stable DC voltage.
The voltage regulator component is crucial for achieving the desired output voltage. Linear voltage regulators, such as the LM317, are commonly used due to their simplicity and effectiveness. They allow for adjustable output voltage by incorporating a variable resistor (potentiometer) in the feedback loop. This setup enables the user to set the output voltage anywhere from 1.25V to 24V, depending on the design.
Incorporating a current limiting feature is essential for protecting both the power supply and the connected load. This can be achieved using a simple resistor in series with the load or through more sophisticated methods such as using a current sensing resistor and an operational amplifier to control the output based on the load current. The current limit can typically be adjusted using another potentiometer, allowing for flexibility in various applications.
To enhance the robustness of the circuit, it is advisable to include fuses or circuit breakers to protect against short circuits and overload conditions. Additionally, proper heat sinking for the voltage regulator and other power components is necessary to prevent thermal failure during prolonged use.
In conclusion, a Variable DC Power Supply is a versatile and essential tool for electronics enthusiasts, capable of delivering adjustable voltage and current to a wide range of circuits. The design can be tailored to specific needs, making it a valuable addition to any electronics workbench.A Variable DC Power Supply is one of the most useful tools on the electronics hobbyist`s workbench. This circuit is not an absolute novelty, but it is simple, reliable, "rugged" and short-proof, featuring variable voltage up to 24V and variable current limiting up to 2A. Well suited to supply the circuits shown in this website. You can adapt it to your own requirements as explained in the notes below. 🔗 External reference