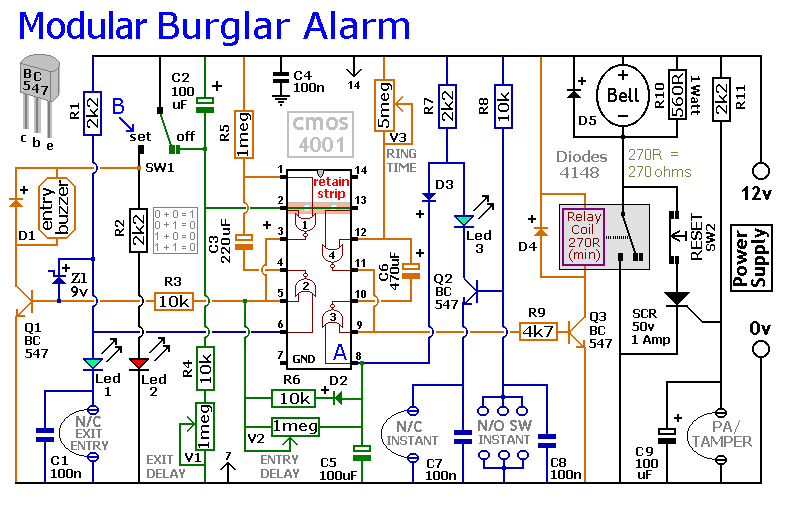
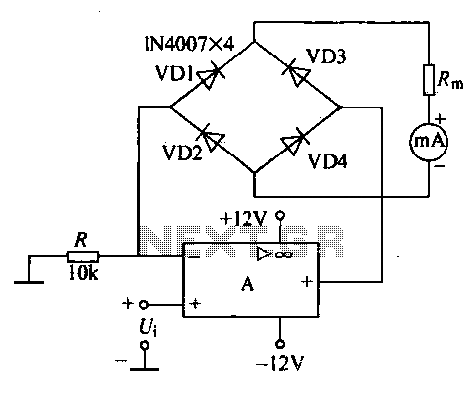
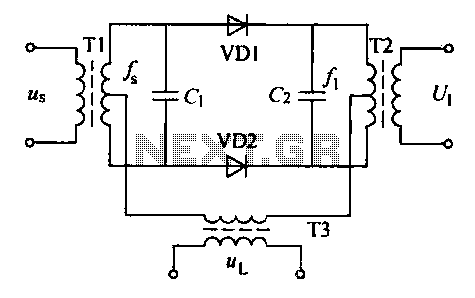
Variable Q Filter For 400Hz Circuit
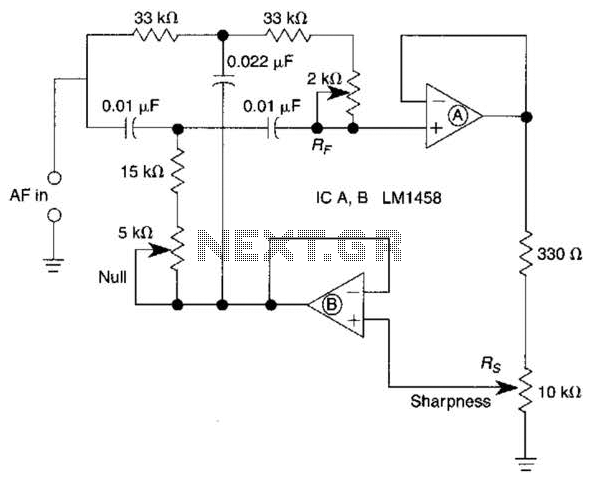
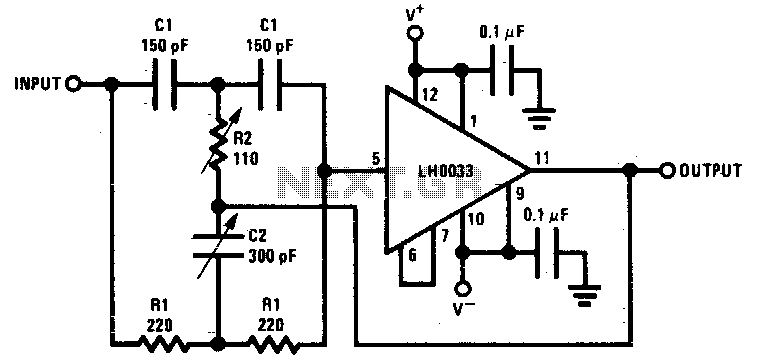
A bootstrapped twin notch filter in this circuit can yield an effective Q of up to 10. Rs adjusts the feedback, hence the Q. Values of C1 and C2 can be changed to alter the frequency. RF is a fine-tune null control.
The bootstrapped twin notch filter is a sophisticated circuit configuration designed to achieve high selectivity and precision in filtering specific frequency components from a signal. The effective quality factor (Q) of up to 10 indicates the circuit's ability to provide sharp frequency discrimination, which is essential in applications such as audio processing, communications, and instrumentation.
In this circuit, the resistor Rs plays a crucial role in adjusting the feedback loop, thereby influencing the overall Q factor of the filter. By modifying Rs, the feedback level can be tuned, allowing for precise control over the filter's response characteristics. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in scenarios where the frequency response needs to be optimized for different signal conditions.
Capacitors C1 and C2 are integral to determining the filter's center frequency. By selecting appropriate values for these capacitors, the user can effectively shift the notch frequency to target specific unwanted frequencies within the signal spectrum. This feature enhances the filter's versatility, making it suitable for various applications requiring frequency manipulation.
The RF component serves as a fine-tune null control, providing additional adjustment capabilities to achieve the desired notch depth and position. This control allows for meticulous calibration, ensuring that the filter operates optimally in its intended application.
When designing this circuit, careful consideration should be given to the selection of components to maintain stability and performance across varying operating conditions. Proper layout and grounding techniques are also essential to minimize noise and interference, further enhancing the filter's effectiveness. Overall, the bootstrapped twin notch filter represents a powerful tool for precise frequency management in electronic systems. A bootstrapped twin notch filter in this circuit can yield an effective Q of up to 10. Rs adjusts the feedback, hence the Q. Values of C1 and C2 can be changed to alter the frequency. RF is a fine-tune null control.
The bootstrapped twin notch filter is a sophisticated circuit configuration designed to achieve high selectivity and precision in filtering specific frequency components from a signal. The effective quality factor (Q) of up to 10 indicates the circuit's ability to provide sharp frequency discrimination, which is essential in applications such as audio processing, communications, and instrumentation.
In this circuit, the resistor Rs plays a crucial role in adjusting the feedback loop, thereby influencing the overall Q factor of the filter. By modifying Rs, the feedback level can be tuned, allowing for precise control over the filter's response characteristics. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in scenarios where the frequency response needs to be optimized for different signal conditions.
Capacitors C1 and C2 are integral to determining the filter's center frequency. By selecting appropriate values for these capacitors, the user can effectively shift the notch frequency to target specific unwanted frequencies within the signal spectrum. This feature enhances the filter's versatility, making it suitable for various applications requiring frequency manipulation.
The RF component serves as a fine-tune null control, providing additional adjustment capabilities to achieve the desired notch depth and position. This control allows for meticulous calibration, ensuring that the filter operates optimally in its intended application.
When designing this circuit, careful consideration should be given to the selection of components to maintain stability and performance across varying operating conditions. Proper layout and grounding techniques are also essential to minimize noise and interference, further enhancing the filter's effectiveness. Overall, the bootstrapped twin notch filter represents a powerful tool for precise frequency management in electronic systems. A bootstrapped twin notch filter in this circuit can yield an effective Q of up to 10. Rs adjusts the feedback, hence the Q. Values of C1 and C2 can be changed to alter the frequency. RF is a fine-tune null control.