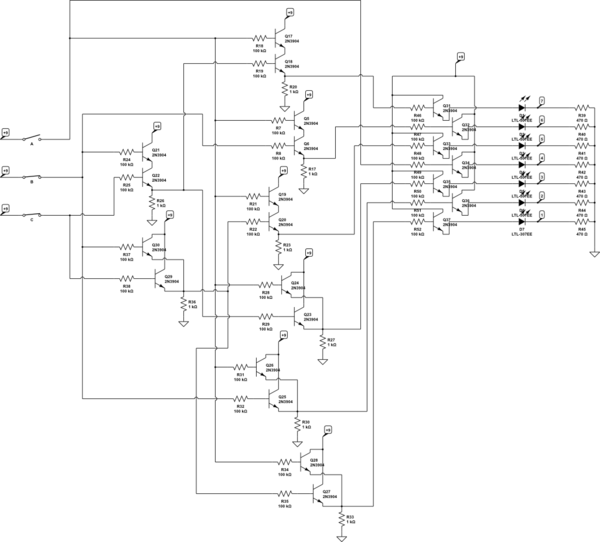
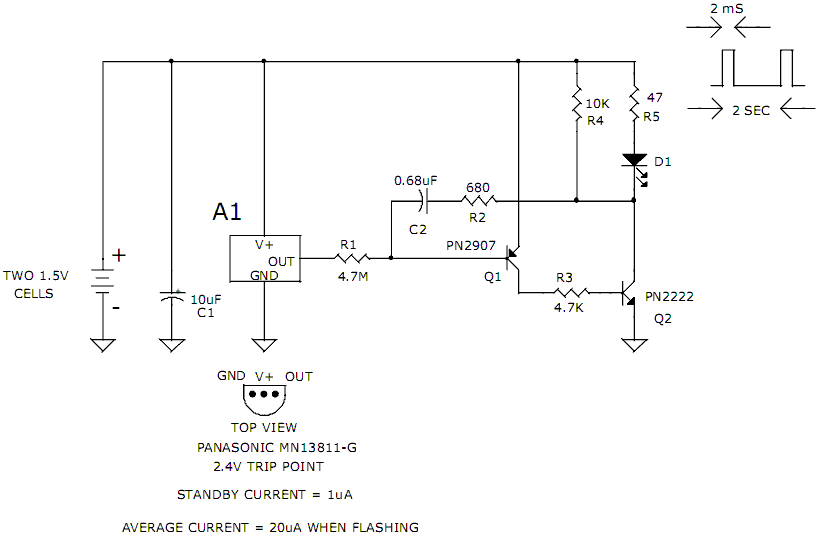
Variable Voltage Regulator
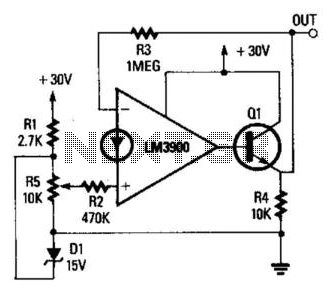
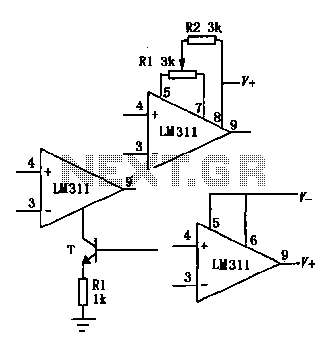
The operational amplifier (op amp) is configured as a non-inverting DC amplifier with a gain determined by the ratio of resistors R3 and R2. The input voltage to the op amp can vary between 0 and 15 V through resistor R5. Consequently, the output voltage can vary approximately from 0.5 to 30 V. The output current has been enhanced by incorporating transistor Q1 into the output stage.
The described circuit utilizes an operational amplifier in a non-inverting configuration, which is a popular choice for applications requiring signal amplification without phase inversion. The gain of the amplifier is set by the feedback resistors R3 and R2, following the formula \( \text{Gain} = 1 + \frac{R3}{R2} \). This allows for precise control over the amplification factor, making it versatile for different applications.
The input voltage is adjustable between 0 and 15 V through resistor R5, which serves as a variable resistor (potentiometer) in the circuit. This feature enables the user to tailor the input signal level according to the requirements of the specific application. The output voltage range of approximately 0.5 to 30 V suggests that the op amp is capable of amplifying the input signal significantly, depending on the gain setting.
To enhance the output current capability, which is often limited in standard op amp configurations, a transistor (Q1) has been added to the output stage. This transistor acts as a current booster, allowing the circuit to drive larger loads without compromising performance. The transistor is likely configured in a common-emitter or emitter-follower arrangement, depending on the desired output characteristics and load requirements.
Overall, this circuit configuration is suitable for various applications, including sensor signal conditioning, audio amplification, and other scenarios where a stable and adjustable DC voltage output is necessary. The careful selection of components and configuration ensures reliable performance across the specified input voltage range. The op amp is wired as a 2 noninverting dc amplifier with a gain that is determined by the R3/R2 ratio. The inp ut voltage to the op amp is variable between 0 and 15 V via R5. The output voltage is therefore variable over the approximate range from 0.5 to 30 V. The available output current has been boosted by adding transistor Ql to the output.
The described circuit utilizes an operational amplifier in a non-inverting configuration, which is a popular choice for applications requiring signal amplification without phase inversion. The gain of the amplifier is set by the feedback resistors R3 and R2, following the formula \( \text{Gain} = 1 + \frac{R3}{R2} \). This allows for precise control over the amplification factor, making it versatile for different applications.
The input voltage is adjustable between 0 and 15 V through resistor R5, which serves as a variable resistor (potentiometer) in the circuit. This feature enables the user to tailor the input signal level according to the requirements of the specific application. The output voltage range of approximately 0.5 to 30 V suggests that the op amp is capable of amplifying the input signal significantly, depending on the gain setting.
To enhance the output current capability, which is often limited in standard op amp configurations, a transistor (Q1) has been added to the output stage. This transistor acts as a current booster, allowing the circuit to drive larger loads without compromising performance. The transistor is likely configured in a common-emitter or emitter-follower arrangement, depending on the desired output characteristics and load requirements.
Overall, this circuit configuration is suitable for various applications, including sensor signal conditioning, audio amplification, and other scenarios where a stable and adjustable DC voltage output is necessary. The careful selection of components and configuration ensures reliable performance across the specified input voltage range. The op amp is wired as a 2 noninverting dc amplifier with a gain that is determined by the R3/R2 ratio. The inp ut voltage to the op amp is variable between 0 and 15 V via R5. The output voltage is therefore variable over the approximate range from 0.5 to 30 V. The available output current has been boosted by adding transistor Ql to the output.